- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids: what is sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids, advantages and disadvantages of the method, possible complications
The content of the article:
- Sclerotherapy, or sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids
- Indications and contraindications
- Advantages and disadvantages of the method
- Possible complications
- Brief information about hemorrhoids
- Video
Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive method of treatment in which a node is removed by stopping its blood supply. Sclerosing drugs for the treatment of hemorrhoids have been used for a long time and have proven their effectiveness, therefore sclerotherapy is widely used.
The best results of sclerotherapy treatment are achieved when the internal hemorrhoids of stages 1 and 2 are removed, when they are still small. At 3, and even more so at 4 stages of the disease, the effectiveness of the method decreases.
It should be understood that sclerotherapy can eliminate hemorrhoids, but has no effect on the causes of the development of the disease. If the factors contributing to its development are not eliminated, a relapse is not excluded. Therefore, complex treatment of hemorrhoids, in addition to sclerotherapy, includes lifestyle correction. Adequate physical activity, avoidance of physical and mental overload, a balanced diet that prevents constipation, refusal to abuse alcohol and smoking is necessary.

Sclerotherapy is effective for stage 1 and 2 hemorrhoids
Sclerotherapy, or sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids
Sclerotherapy consists of injecting a special drug into the hemorrhoid that causes the vessel walls to stick together (sclerosis), called a sclerosant. After this, the blood supply to the node is disrupted, it gradually dies, then the necrotic tissue is independently and painlessly removed outside during bowel movements.
Sclerosant is injected with a special syringe with a thin needle, which ensures painlessness. The manipulation is performed on an outpatient basis. Two hours before the procedure, the patient is given a cleansing enema.
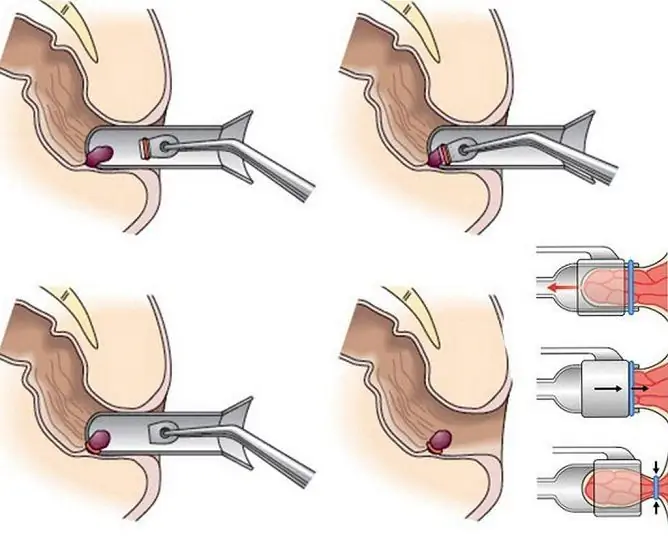
The patient is placed in the knee-elbow position or on the gynecological chair in the supine position, with the lower extremities brought to the stomach. In the presence of concomitant pathologies, the patient can be laid on his side. The doctor treats his hands with an antiseptic solution, and then lubricates the skin around the patient's anus with the same drug and, through an anoscope, the rectal mucosa. The anoscope in the rectum is fixed with the left hand at the level of the anorectal line, due to which the internal hemorrhoids located in the lower ampullar section of the rectum above the anorectal line are clearly visible.
The needle of a special syringe is inserted through the lumen of the anoscope into the hemorrhoid at an angle of 45 ° from top to bottom by about 1.5 cm until the feeling of failure. 0.5-2 ml of sclerosant is injected depending on the size of the hemorrhoid. In one procedure, the drug is injected into no more than two nodes. If necessary, repeat the procedure 1.5-2 weeks after the previous one.
During a properly conducted sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids, according to patients' reviews, there is no pain. With insufficiently deep (superficial) administration of the drug, there is a sharp local blanching of the mucous membrane and the formation of swelling. In such a situation, the needle is removed or pushed further into the hemorrhoid, and the procedure continues. If the needle was inserted too deeply, it is possible to inject a sclerosing drug into the muscular membrane of the rectum, while the patient experiences severe pain. In such a situation, the procedure is stopped, and the patient's condition is monitored daily for 5-7 days.
Sclerotherapy is used as a method of stopping prolonged hemorrhoidal bleeding. In this case, after setting a cleansing enema, an anoscope is inserted into the patient's anal canal and fixed in such a way that there is a hemorrhoidal node in its lumen, which is bleeding. After that, 1-2 ml of sclerosant is injected into the node, and its wall is slightly pressed with a swab (sterile probe-swab). The bleeding usually stops at the end of the procedure.
After the completion of the manipulation, the patient must remain in the clinic for an hour (in a standing or sitting position). If the condition is stable, he is allowed to go home.
Pain after removal of hemorrhoids by sclerotherapy occurs in about 80% of patients. In this case, the pain is expressed slightly and lasts no more than a few days, if necessary, it is easily removed with analgesic drugs.
After sclerotherapy, the patient can lead a normal life. There are no restrictions on physical activity, but it is not recommended to lift weights for at least 2-3 weeks (with a persisting tendency to hemorrhoids, it is better not to lift them at all). After 1.5-2 weeks, a follow-up examination is carried out, during which the effectiveness of treatment is assessed.

Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive procedure that takes about 10 minutes
Indications and contraindications
Sclerotherapy is carried out at 1, 2, less often 3 stages of hemorrhoids. At stages 3 and 4, sclerotherapy is used if it is necessary to stop bleeding in the course of preparing the patient for the removal of nodes by other methods.
Contraindications to sclerotherapy are inflammatory processes in the perineum and rectum, acute hemorrhoids, anal fissures, paraproctitis, allergy to sclerosing drugs. The procedure is not recommended for pregnant women and women during lactation.
The presence of a combined form of the disease in a patient with the absence of clear boundaries between the external and internal hemorrhoids is a relative contraindication - that is, with caution in some cases, sclerotherapy of the hemorrhoid can still be performed.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of sclerotherapy include simplicity, safety, painlessness, no need for hospitalization and postoperative rehabilitation. Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids can be used in elderly patients for whom other methods of treatment are contraindicated.
The disadvantages of the method include the impossibility of using it for large hemorrhoids.
Possible complications
If sclerosant enters the subcutaneous tissue, acute paraproctitis may develop, ulceration may develop on the rectal mucosa, and acute pain may develop in the muscular layer of the rectum. If the drug enters the anal vein, the patient may feel a strange taste in the mouth, and pain in the liver may also appear. If sclerosant enters this blood vessel, the procedure should be stopped immediately.
Other possible complications include thrombosis of internal and / or external hemorrhoids with the development of perianal edema and hyperemia of the skin of the perineum. Such complications usually occur when sclerosing three or more hemorrhoids in one procedure, as well as in the case of treatment of a combined form of hemorrhoids with the absence of clear boundaries between the internal and external hemorrhoids.
In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, sclerosant can enter the enlarged prostate, causing the development of prostatitis, abscess, and remotely - infertility.
Complications of sclerotherapy are extremely rare, usually they are associated with a violation of the technique of the procedure.
Brief information about hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are enlarged due to stretching, weakened and overflowing blood vessels of the hemorrhoidal plexus, internal and / or external. With an exacerbation of hemorrhoids, the nodes become inflamed, they are easily injured by dense feces and bleed.
Hemorrhoids are of the following types:
- internal - the nodes are localized in the anal canal;
- external - nodes outside surround the anus;
- combined, or mixed - both internal and external hemorrhoids are present.
In addition, hemorrhoids have 4 stages of development:
- Hemorrhoids are located in the anal canal and do not fall out of the anus.
- Hemorrhoids sometimes fall out of the anus (usually during bowel movements or excessive physical exertion), but return to the rectum on their own.
- The nodes fall out of the anus even with a slight load, they cannot be adjusted on their own, but they can be adjusted manually.
- The nodes are constantly in a dropped state and cannot be adjusted.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.