- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hypertension grade 3 - what is it?
The content of the article:
- What is it - grade 3 hypertension and its risks
- Causes and risk factors for the development of hypertension
- Symptoms of hypertension of the third degree
- Treatment
- Video
Hypertension grade 3 is characterized by a significant increase in blood pressure, which leads to an increase in the load on the heart, which is why patients develop heart failure. The risk of complications increases, even in the absence of other adverse factors. This pathology requires medical intervention and long-term, often lifelong therapy.

Grade 3 - the most severe in the course of hypertension
What is it - grade 3 hypertension and its risks
Arterial hypertension (hypertension) is an increase in blood pressure (BP) that goes beyond the normal range, i.e., above 130/90 mm Hg. Art. ICD-10 code - I10-I15. Hypertension makes up the vast majority of all cases of hypertension and is recorded in 35-40% of adults. With age, the incidence increases. Recently, more and more pathology is diagnosed in patients under 40 years of age.
Essential hypertension is divided into three degrees:
- BP is 140-159 90-99 mm Hg. Art.;
- HELL - 160-179 per 100-109 mm Hg. Art.;
- BP - 180 to 110 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
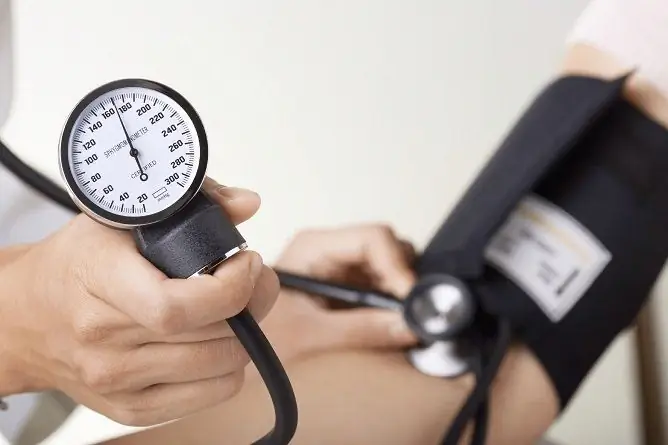
To make a diagnosis, the data obtained during the collection of complaints, the study of the medical history, an objective examination of the patient, and most importantly, the measurement of blood pressure are used. The pressure is measured three times, on both hands, and daily monitoring of blood pressure is also prescribed. Additionally, electrocardiography, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, biochemical and clinical blood tests, and general urine analysis are prescribed.
Depending on the degree of likelihood of damage to target organs (i.e., those organs that suffer more than others from circulatory disorders, for example, the heart and brain), there are 4 risk groups:
- 1 risk - the likelihood of complications is less than 15%, there are no aggravating factors;
- 2 risk - the probability of adverse consequences is estimated in the range 15-20%, there are no more than three aggravating factors;
- 3 risk - the likelihood of complications - 20-30%, there are more than three aggravating factors;
- 4 risk - the risk of developing complications exceeds 30%, there are more than three aggravating factors, damage to target organs is observed.
The main aggravating factors include smoking, passive lifestyle, obesity, stress, unhealthy diet, endocrine disruption.
In case of hypertension of the 3rd degree, the risk of 3 can be obtained by a group of disabilities, since this condition is accompanied by disorders of the heart, brain, kidneys, and visual analyzer. Even more often, disability is given with the diagnosis of hypertension of the 3rd degree of risk 4, since such patients may have impaired speech, thinking, motor functions, and paralysis.
The prognosis depends on the timeliness and adequacy of the treatment, the patient's compliance with the doctor's prescriptions. At grade 3 disease with risk 4, the prognosis is poor due to the extremely high risk of life-threatening complications.
Causes and risk factors for the development of hypertension
Of all cases of hypertension, 95% is due to hypertension (primary, or essential hypertension). In the remaining 5%, secondary or symptomatic arterial hypertension (neurological, stress, renal, hemodynamic, drug, hypertension of pregnant women) is recorded.
Hypertension develops under the influence of unfavorable endogenous and exogenous factors, but as a rule, it is not possible to identify the exact cause that triggers the pathological mechanism.
Risk factors include stress, psychoemotional lability, overwork, unhealthy diet (excessive use of salt, fatty, fried foods, non-compliance with the diet), overweight, genetic predisposition, physical inactivity, bad habits. Arterial hypertension can be a consequence of metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic lesions of the blood vessels.
Symptoms of hypertension of the third degree
A persistent increase in blood pressure may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, or not attract the attention of the patient. The early symptoms are mostly persistent headache, which is usually attributed to causes other than pressure. Often, the disease attracts attention only with the onset of a hypertensive crisis.
At stage 3 of the disease, the patient has a headache, tinnitus, chest pain, fatigue, weakness, irritability, and periodic dizziness. These symptoms can be permanent, but more often appear with an increase in blood pressure. In addition, the disease is accompanied by drowsiness, irritability, and deterioration of cognitive abilities.
A hypertensive crisis manifests itself as a high intensity headache, which the patient describes as compressing, bursting. Analgesics do not stop it. Black dots flicker before the eyes, nausea and vomiting appear, pulse quickens, sweating increases, urination becomes more frequent, the tongue may become numb. Deterioration of health becomes critical, therefore, a patient in this state needs to call an ambulance as soon as possible - treatment of a hypertensive crisis is carried out in a hospital setting.
Third-degree hypertension often leads to life-threatening complications. These are metabolic disorders, pathologies of the cardiovascular and / or urinary system: myocardial infarction, stroke, heart and renal failure, sudden cardiac death, angina pectoris, aortic aneurysm, nephropathy, diabetes mellitus, retinopathy.
A dangerous sign for this degree of the disease is a sharp drop in blood pressure, which means a deterioration in the contractile function of the heart muscle.
In the case of the development of heart failure, difficulty breathing, severe dizziness, pain in the heart, and shortness of breath join the main symptoms of the disease. Some patients have hemoptysis. Such signs are the reason for immediate seeking emergency medical help.
Treatment
With symptomatic arterial hypertension, a complete cure of the patient is possible provided that the cause that caused the increase in blood pressure is eliminated. Essential hypertension at this stage is incurable, since its causes are unknown. Nevertheless, the competent selection of antihypertensive drugs and their administration in strict accordance with the doctor's prescription are able to maintain blood pressure within the normal range, which minimizes the risk of developing dangerous complications.
Drug therapy is usually combined. Diuretic drugs, direct renin inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, calcium antagonists, beta-blockers are used. A combination of a diuretic and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or diuretic, a calcium antagonist, and a beta-blocker is often prescribed.

In the treatment of grade 3 hypertension, several main groups of drugs are used.
In order to prevent the development of complications, the main therapy can be supplemented with glucose-lowering drugs, antiplatelet, lipid-lowering drugs and others, depending on the concomitant pathology.
The most important part of the treatment is changing the lifestyle and improving it. First of all, it is necessary to resolutely give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol (information that small doses of alcohol help with hypertension is not true).
Excessive physical activity is contraindicated for the patient, but physical inactivity is also destructive. Regular, but not excessive physical activity is necessary - walking, cycling, swimming, yoga (when choosing sports activities, you should consult with your doctor). Overweight patients need correction, while strict diets should be avoided, and weight loss should be achieved with a slight decrease in daily calories and regular, but not excessive physical exercise.
It is necessary to follow a diet, and not temporary, but permanent - it should become the norm. Salty, smoked, spicy and fatty foods, semi-finished products, fast food (contains large amounts of fats and salt), any tonic drinks are excluded from the diet. The basis of the diet should be dairy and fermented milk products, vegetables, cereals, fruits and berries, fish, lean meat, seafood. The consumption of table salt is reduced to 5 g per day. Some patients need to follow a drinking regimen - this issue must be discussed with the attending physician.
Patients with the third degree of hypertension need constant medical supervision and supportive therapy throughout their lives. Regular examination, regardless of how you feel, should be carried out 1-3 times a year (agreed with the attending physician). Hypertensive patients need to constantly monitor their blood pressure at home.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.