- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Quincke's edema: causes, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Kinds
- Causes of Quincke's edema
- What swells with Quincke's edema
- Quincke's edema symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment of angioedema
- First aid
- Home treatment
- When hospitalization is necessary
- Video
Quincke's edema (angioneurotic edema) is a type of allergic reaction, which is characterized by the occurrence of edema of the skin, mucous membranes, subcutaneous fatty tissue.
This pathology accounts for about 2% of all allergy cases. Angioneurotic edema occurs in all age groups of patients, but children and young women are more susceptible to its development. In children of the first months of life, the disease is especially difficult, often ends in death. The hereditary form of pathology is most often found in male patients.

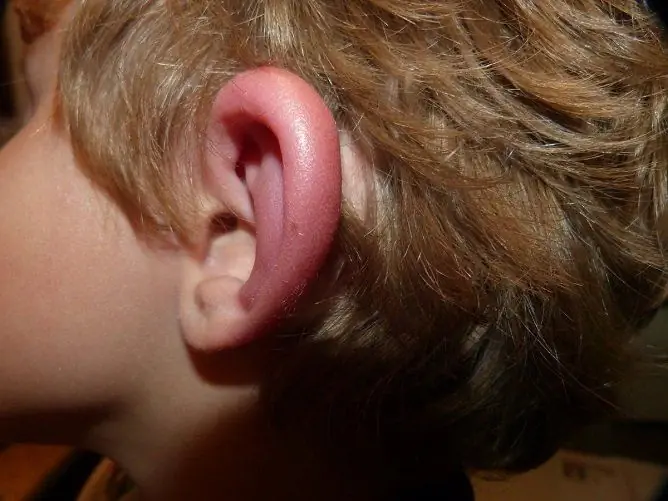
Quincke's edema often develops in the lip area
The prognosis depends on the severity of the disease and the timeliness of initiation of therapy. With a hereditary form, relapses are often observed throughout the patient's life.
Kinds
Angioneurotic edema can be:
- isolated;
- combined with urticaria.
By the nature of the course - acute and chronic recurrent.
In addition, it is congenital and acquired.
Causes of Quincke's edema
The main cause of pathology is one or another form of allergy.
The reason for the development of the congenital form may be a deficiency of the C1-inhibitor, which may consist both in its insufficient production, and in insufficient activity and increased use.
The acquired form of pathology can be observed if the patient has neoplasms of the lymphatic system, a number of infectious and autoimmune diseases.
In about 1/4 of the total number of patients, the disease is due to a genetic predisposition, in 30% of cases it is acquired, in the rest of the patients it is not possible to find the exact cause.
If it is not possible to determine the etiology of the pathological condition, the patient is diagnosed with idiopathic angioedema.
The table shows a number of allergens, under the influence of which the development of a pathological process can occur.
| Allergen group | Explanation |
| Food | Most often fruits, nuts, eggs, milk, honey, fish, chocolate, food additives |
| Medicines | Often antibiotics, B vitamins, anesthetics, antihypertensive drugs (angiotensin II receptor antagonists, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), oral contraceptives |
| Plant pollen | Birch, hazel, alder, fescue, wormwood, quinoa, any flowering plants |
| Chemicals | Especially household chemicals, cosmetics, turpentine, phenol |
| Dust | Mainly home and library |
| Microorganisms | Viruses, bacteria, microscopic fungi |
| Pets, insects | Animal wool, bird feathers, food for aquarium fish, insect poison |
Also, the pathological process can develop with false allergies (pseudo-allergies), in which a person has an increased sensitivity to certain drugs, food products against the background of the absence of an immunological stage.
Risk factors include helminthic infestations, endocrine diseases, and some diseases of internal organs. In young children, a predisposition to allergic reactions can be triggered by the use of cow's milk.
Stressful situations, alcohol consumption, damage to mucous membranes, hypothermia of the body can also contribute.
What swells with Quincke's edema
Due to the violation of the permeability of the vessels of the capillary bed and their expansion, the subcutaneous or submucous tissue swells.
Most often, well-limited swelling occurs on the face (lips, tongue, cheeks, eyelids), mucosal involvement is less common, however, edema may appear on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, or respiratory tract.
Other localizations:
- neck;
- upper chest;
- scrotum in men;
- limbs (especially fingers).
With swelling in the larynx and / or tongue, there is a risk of impaired airway patency, asphyxia, and even death. Pathology can be complicated by the development of anaphylactic shock in the patient.
In children, this pathological condition is often combined with bronchial asthma. In this age group of patients, intestinal forms of pathology, as well as damage to the meninges, are observed more often than in adults.
Quincke's edema symptoms
Swelling usually occurs suddenly 2-5 minutes, during and in the absence of treatment disappears within 2-3 days. Less often, the pathology develops gradually, while the symptoms increase in a few hours. When pressed, the swollen area is dense. The skin color at the site of the development of the pathological process does not change, there is no itching.
The hereditary form, which is associated with pathology of the complement system, usually manifests itself before the age of 20. This form is characterized by a slow increase in symptoms throughout the day and a gradual reverse development within 3-5 days.

In 50% of cases, Quincke's edema is accompanied by urticaria
Urticaria occurs in about 50% of cases. Some patients may experience a decrease in blood pressure, high heart rate, increased sweating, confusion, anxiety, and anxiety. In children, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle may be observed.
Manifestations in different parts of the body:
| Location | Symptoms |
| Larynx area | Speech is disturbed, hoarseness of the voice appears, wheezing, barking cough, hyperemia of the skin of the face may develop, after a while pallor of the skin may be noted |
| Meninges | Headache, photophobia, stiff neck muscles, speech and / or vision disorders, nausea and vomiting, convulsions, paralysis |
| Mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract | Intestinal obstruction may develop, which is characterized by defecation disorders, severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting |
| The mucous membrane of the bladder and urethra | Pain during urination, urinary retention |
| Synovial membrane of joints | Decreased mobility in the joint, pain when moving |
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is carried out on the basis of the clinical picture, collection of complaints and anamnesis (including family), an objective examination. Additionally, laboratory tests (allergy tests), laryngoscopy, colonoscopy, and in difficult cases, diagnostic laparoscopy may be required.
With the development of angioedema on the face and other open parts of the body, the diagnosis of pathology, as a rule, is not difficult. However, they can occur when the mucous membranes of internal organs are involved in the pathological process.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with edema that developed against the background of the superior vena cava syndrome, disorders of the kidneys, liver, heart, and hypothyroidism.
Treatment of angioedema
First aid
Pathology can pose a threat to the patient's life, therefore, with its rapid development, especially in the head and neck (throat) area, it is necessary to provide the patient with first aid:
- Interrupt contact with the allergen (if known).
- Call an ambulance.
- Help the patient to get into a sitting position, small children can be picked up.
- Provide fresh air (open a window, loosen or remove tight clothing).
- Apply a pressure bandage or cold compress above the injection or bite site (with the development of pathology against the background of parenteral administration of drugs or an insect bite).
- Give the patient several tablets of activated carbon (the drug can be dissolved in warm water).

As a first aid, the patient is given activated carbon
Home treatment
Puffiness in some cases can go away on its own and do not require special treatment, but a doctor's consultation is still necessary.
In most cases, antihistamines are used. You may need to take glucocorticosteroids, enterosorbents.
Patients with a tendency to allergies are advised to follow a hypoallergenic diet. It is necessary, if possible, to avoid contact with the causative allergen, as well as give up bad habits.
With a hereditary form of the disease, antifibrinolytic drugs, androgens, and a C1 inhibitor are used. Diuretics may be prescribed. In some cases, hemosorption is required (extrarenal blood purification). It is recommended to avoid injury, stressful situations, to carry out prevention and timely treatment of infectious diseases of viral etiology.
When hospitalization is necessary
If the patient has a moderate to severe reaction, hospitalization is usually required.
Also, hospitalization may be required in the following cases:
- the presence of pronounced signs of laryngeal edema;
- the disease has developed against the background of the use of medicines;
- the presence of a number of pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, respiratory tract;
- childhood.
To restore the patency of the airways, it may be necessary to carry out infusion therapy, the introduction of an adrenaline solution subcutaneously, tracheal intubation, and conicotomy.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.