- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cardiac edema
The content of the article:
- Development mechanism
- Cardiac edema: symptoms that distinguish them from others
- Diagnostic methods
-
Treatment
- Main treatment
- Symptomatic treatment
- Folk remedies
- Diet and general principles
- Video
Cardiac edema is one of the signs of chronic heart failure. Pathology can develop as a complication of arterial hypertension, heart defects, coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy and other diseases.
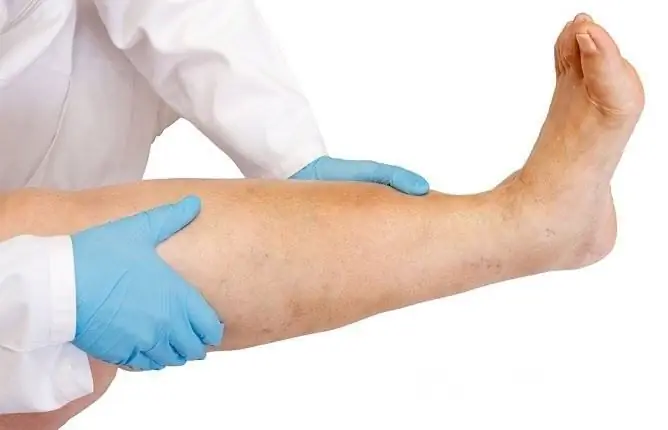
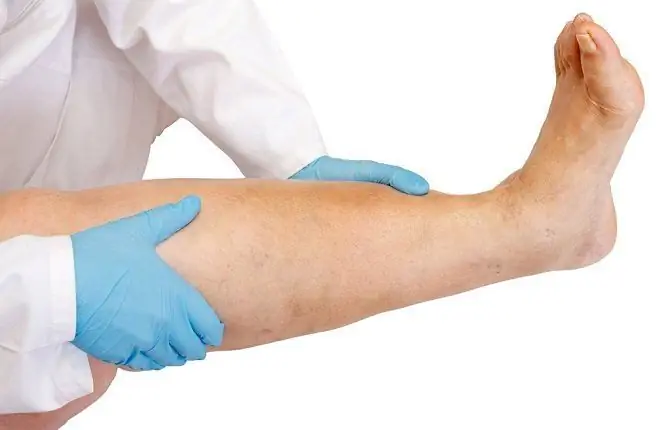
The appearance of edema on the legs with heart pathologies indicates the development of heart failure
Development mechanism
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump the required amount of blood. The blood in the body begins to stagnate and the veins, peripheral tissues and lungs fill with fluid. The accumulation of liquid leads to an increase in the hydrostatic pressure in the vessels.
Due to the increase in hydrostatic pressure, symptoms of heart failure appear:
- peripheral edema;
- dyspnea;
- enlargement of the liver and spleen.
With left ventricular failure, stagnation occurs in the pulmonary circulation, which is manifested by shortness of breath, coughing and hemoptysis.
With right ventricular failure - stagnation in the systemic circulation, this is manifested by edema of peripheral tissues, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. With heart failure, peripheral edema occurs first, which have the following localization:
- feet;
- shins;
- in the lumbar region;
- on hands.
Most often, the legs are swollen; the face and upper limbs with heart failure swell much less frequently. Often, edema is localized only in the lower extremities, which is associated with a pressure gradient.
Cardiac edema: symptoms that distinguish them from others
Puffiness is a symptom that can occur not only with heart failure, but also with other diseases. Therefore, it is important to carry out differential diagnosis between edema of different origin.
| Feature name | With heart failure | With other pathologies |
| Localization | Lower limbs (feet and legs) | With renal failure, edema is localized on the face, with thrombosis, only one limb often swells |
| Time of occurrence and stopping | Strengthen in the evening, pass after a night's rest | In case of renal failure, on the contrary, they increase in the morning |
| Soreness | Not typical | With thrombosis, the soreness of the affected area is determined |
| Rate of occurrence | Gradually, symptoms worsen over several months | With thrombosis, symptoms develop within 3 days, with other pathologies, more often gradually |
| Pitting on pressure | After pressing, the fossa remains for some time | The fossa persists in chronic venous insufficiency and deep vein thrombosis |
| Skin changes over the affected area | Not typical | With a lymphatic origin, there is a thickening of the skin, with chronic venous insufficiency, the skin is brown |
Peripheral edema is the main, but not the only symptom of heart failure. The characteristic signs of cardiac dysfunction include:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. Shortness of breath is a sign of increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation. At first it occurs during physical exertion, and then disturbs even at rest.
- Heart cough. Also indicates congestion in the lungs. The cough occurs mainly at night, increases with physical exertion, goes away or decreases at rest.
- Fatigue and weakness. They arise due to the fact that the myocardium (heart muscle) does not pump enough blood and oxygen to the organs. Normal physical work is difficult, it takes more time for a break.
- Enlargement of the abdomen. It occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostic methods
If peripheral edema develops, consult a doctor. The doctor will conduct an examination, including the cardiovascular system:
- blood pressure measurement;
- auscultation of the heart - there may be muffled tones, gallop rhythm;
- percussion of the heart - the expansion of the boundaries of cardiac dullness is determined;
- auscultation of the lungs - crepitus or wet rales are heard with an increase in pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
To determine the primary disease, an additional examination is prescribed, which is aimed at assessing the function of the heart, kidneys and liver.
| Study title | Description | |
| Specific for heart failure | Electrocardiography | Allows you to identify rhythm disturbances, as well as hypertrophy of the right or left heart. |
| Echocardiography | The main research method for chronic heart failure. Echocardiography can be used to assess the degree of impaired cardiac output, hypertrophy or dilatation of the heart chambers. | |
| Atrial natriuretic hormone | A marker specific for heart failure. | |
| General clinical | General blood analysis | Used to rule out anemia. |
| General urine analysis | It is used to exclude proteinuria, since increased excretion of protein in the urine can also lead to swelling. | |
| Chest X-ray | It is used to exclude pulmonary embolism, pneumonia. Also, with the help of radiography, congestion in the lungs can be detected. | |
| Blood chemistry | The renal complex (creatinine, urea) is prescribed to exclude the renal origin of edema. Hepatic (ALT, AST, bilirubin, prothrombin index) - exclude hepatic origin. | |
Treatment
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause, that is, the disease that led to heart failure. For this, medications are used, if necessary, surgical intervention. To get rid of the actual edema, diuretics and a special diet are used.
Main treatment
The main treatment for congestive heart failure is medication. The following groups of drugs are used:
| Drug group name | Description |
| ACE inhibitors | They prevent myocardial remodeling, so their use stops the progression of heart failure. Examples: Lisinopril, Captopril, Enalapril. |
| Beta blockers | Decrease the heart rate, and therefore the myocardial oxygen demand decreases. This group includes Atenolol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Nebivolol. |
| Diuretics | Potassium-sparing diuretics such as Spironolactone are used for long-term treatment of chronic heart failure. They can be combined with fast acting diuretics such as Furosemide, Hypothiazide. |
| Cardiac glycosides | Increase the contractility of the heart (increase cardiac output). Digoxin is the most commonly used. |
| Potassium preparations | They are prescribed in combination with other drugs, since diuretics stimulate the excretion of not only excess fluid, but also potassium. |
Symptomatic treatment
To quickly reduce the swelling, diuretics (diuretics) are used. These are drugs that stimulate the elimination of water and sodium from the body. Thus, tissue congestion and, consequently, edema are reduced.
To quickly reduce edema, loop diuretics are used, which can increase urine output several times. Loop diuretics include Furosemide, Torasemide.
Diuretics are also used for long-term treatment of heart failure. They remove excess fluid, which prevents the appearance of puffiness.
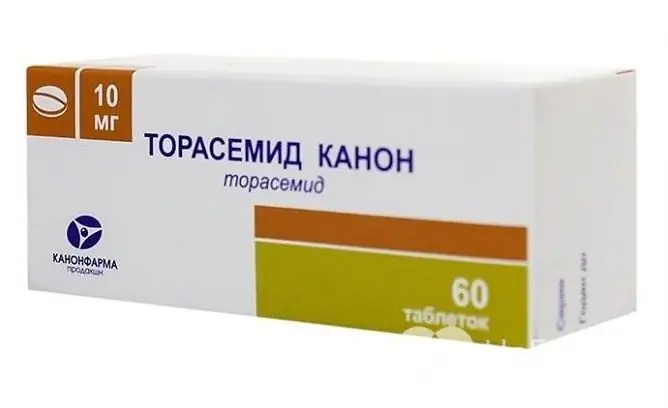
Torasemide is one of the loop diuretics used to treat cardiac edema
Folk remedies
In some cases, you can use medicinal plants that have a diuretic effect:
- bearberry leaves;
- field horsetail;
- birch buds.
Decoctions or infusions are prepared from them, which are taken orally. These medicinal plants stimulate the excretion of urine, which leads to less fluid accumulation in peripheral tissues.
Diet and general principles
With heart failure, you must follow a special diet, which is aimed at reducing the accumulation of fluid in the body.
How to eat with heart disease:
- Eliminate or reduce salt intake to 1.5 g per day.
- Salt already prepared food, not food during cooking.
- Increase your intake of fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Limit your intake of fatty dairy products.
- Make sure that the amount of fluid that is consumed per day is equal to the amount of fluid that is excreted.
In addition, with pathology of the heart, it is necessary to exclude alcohol consumption, quit smoking and do regular moderate physical activity. Heavy physical activity is contraindicated in heart failure, as it can lead to decompensation. Therefore, you should not abruptly start running or exercising in the gym. With heart disease, moderate physical activity is indicated - walking, swimming, yoga.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.