- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Testosterone: what it is, functions, norm, correction
The content of the article:
- The functions of testosterone in the body
- Testosterone norm and its laboratory research
- Increased testosterone
- Decreased testosterone content
-
Correction of the hormone testosterone in men
Diet to increase testosterone
- Correction of testosterone in women
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone produced by the Leydig cells of the testes in men, the adrenal cortex in both sexes, and the ovaries in women. The hormone is a product of the intermediate metabolism of cholesterol. In boys, the hormone is responsible for androgenization, in men and women it is necessary for the formation of bone and muscle tissue, the normal functioning of the nervous system, in women it is also involved in the synthesis of estradiol.

Testosterone is responsible for male sex characteristics and is also involved in the formation of bones and muscles
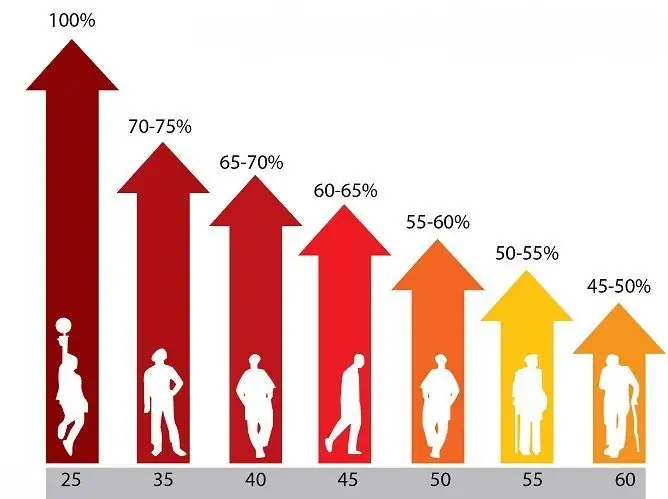
Testosterone is produced under the influence of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones of the anterior pituitary gland. The level of this hormone in the blood depends on the diet and life in general, the physical activity of a person and some other factors. With puberty in males, the secretion of the hormone increases significantly. After 50-60 years, the level of testosterone in the blood begins to decline. In adult men, the maximum concentration of the hormone is observed in the morning, by the evening it decreases. Testosterone is present in the blood in two forms - free and bound to proteins (albumin and globulins, which bind sex hormones). Approximately 1-2% of the hormone is in free form; its decay occurs in the liver.
Testosterone is biologically inactive and weakly binds to androgen receptors. Directly in the cells, the hormone undergoes reduction through the enzyme 5α-reductase, after which it can act on the receptors of target organ cells. This produces dihydrotestosterone (the biologically active form of this hormone). In some cases (with a genetically determined decrease in activity or complete absence of 5α-reductase in tissues), partial or complete insensitivity of tissues to the hormone is observed. With this pathology, a chromosomal male fetus can be born with male, intermediate, or female external genital organs.
The most specific effect of the hormone is manifested in the target tissues, in which its selective accumulation is observed. These tissues include: the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, epididymis, seminiferous tubules, uterus, ovarian follicles, hypothalamus.
The functions of testosterone in the body
Testosterone promotes calcium retention in bone tissue, in men, under its influence, a specific structure of bones is formed, especially the pelvis, which increases its support function. In the case of a hormone deficiency in young men, the skeleton develops according to the female type.
Testosterone takes part in the development of male genital organs and secondary male sexual characteristics, regulates sexual behavior and sperm development, ejaculate formation, causes hair growth on the face, chest, pubis (less often on the back), reduces hair growth on the head (especially on the crown), affects the lining of the larynx, which leads to coarsening of the voice.
The male hormone plays a role in the regulation of phosphorus and nitrogen metabolism in the body, and in women it is responsible for the regression of the follicle in the ovary.
The anabolic properties of the hormone are manifested mainly by the stimulation of protein synthesis in tissues (mainly in muscle tissue), which contributes to an increase in muscle mass. For this purpose, testosterone preparations are used by athletes. However, their prolonged use leads to a decrease in the production of this hormone by the body and requires the use of drugs to restore the secretion of its own hormone.
Testosterone is a marker of the body's androgenic status.
Testosterone norm and its laboratory research
Total Testosterone Rate:
- in men - 8.5-32 nmol / l;
- in women of childbearing age - 0.38-1.97 nmol / l.
Free fraction rate:
- in men over 14 years old - 13.9-104 pmol / l;
- in women - from 1.4 to 24.6 pmol / l.
Depending on the method for determining the norm and the units of measurement in different laboratories may be different.
A testosterone test is usually prescribed for the following indications:
- differentiation of true and false premature puberty in boys under 10 years of age;
- suspicion of hypogonadism in men (with decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, osteoporosis, gynecomastia, infertility);
- differentiation of primary and secondary hypogonadism;
- diagnosis of reproductive disorders in men;
- determining the cause of virilization and hirsutism;
- suspicion of testicular neoplasms producing testosterone;
- Jacobs syndrome (XYY chromosome set);
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- suspicion of neoplasms of the adrenal cortex;
- suspicion of gestational trophoblastic tumors;
- a decrease in the concentration of globulin that binds sex hormones;
- assessment of testosterone replacement therapy, antiandrogen therapy (with premature puberty, idiopathic hirsutism, prostate cancer, etc.).
To assess androgen metabolism in the body, it may be necessary to determine the concentration of the free fraction of the hormone (with an increased or decreased concentration of globulin that binds sex steroids). An analysis for free testosterone is also prescribed at a normal level of total testosterone in women with signs of hyperandrogenism, assessment of ongoing hormonal therapy, etc.
Blood for analysis is taken in the morning before 11:00 on an empty stomach, after the last meal, at least eight hours should pass. Blood is drawn from a vein.
Women need to agree with the doctor on which day of the cycle to take blood (determined depending on the purpose of the study). On the eve, you should not eat fatty foods and undergo significant physical exertion. In the case of taking medications before the study, it is necessary to clarify with the doctor the need to cancel them.

Blood for testosterone testing is taken from a vein on an empty stomach
Barbiturates, combined hormonal contraceptives, estrogens, antispasmodics can affect the results upward, antiandrogenic, antipsychotic drugs, glucocorticoids, glucose, ethanol, and some antibacterial drugs downward.
Increased testosterone
An increased concentration of the hormone testosterone in the blood is observed in the following diseases or conditions:
- idiopathic precocious puberty in males;
- adrenal hyperplasia in boys;
- some tumors of the adrenal cortex;
- extragonadal neoplasms that produce gonadotropin;
- gestational trophoblastic tumors;
- polycystic ovary syndrome (in about 20% of the total number of cases);
- testicular feminization syndrome;
- virilizing ovarian tumors;
- hirsutism.
Increased production of the hormone by the adrenal glands causes a violation of its synthesis in the ovaries and leads to virilization in women. High testosterone in the blood causes skin problems (seborrhea, acne), as the secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands increases.
With premature puberty, the testosterone level in boys is increased in comparison with the age norm, but corresponds to the norm for adult males.
In women, there is a physiological increase in the male hormone after exercise and during pregnancy.
Decreased testosterone content
A decrease in the concentration of the hormone is characteristic of the following pathologies:
- autotoxication syndrome with severe renal failure;
- liver failure;
- Down syndrome;
- myotonic dystrophy;
- cryptorchidism;
- primary and secondary hypogonadism;
- obesity in men;
- menopause in women, premature ovarian failure;
- delayed puberty in males.
Correction of the hormone testosterone in men
In order to increase the level of the hormone in a natural way, patients, first of all, need to normalize sleep, since it is in the phase of deep sleep that sex hormones, including testosterone, are produced. Continuous night sleep should be at least seven hours.
Overweight men need to normalize it, since testosterone is converted into estrogens in adipose tissue.

To increase testosterone, men should normalize their lifestyle, improve sleep, diet and exercise.
Adequate physical activity is required to increase testosterone levels. The duration of the workout should not exceed one hour (about 15 minutes of warm-up and about 45 minutes of the workout itself), since with longer physical exertion, increased production of cortisol, which is a testosterone antagonist, occurs. It is advisable to limit the number of workouts to three per week, the break between workouts should be at least one day. First of all, it is necessary to use large muscles (back, chest, lower limbs), it is recommended to include basic strength exercises in the training program.
Other types of physical activity that increase the male hormone include sprint running, walking, and exercises aimed at strengthening the pelvic muscles.
The rejection of bad habits is of no small importance, it is especially important to limit the use of alcoholic beverages, since alcohol contributes to the conversion of testosterone into estrogens. Adequate sexual activity, avoidance of stressful situations, and increased immunity are also recommended.
Medication correction by using synthetic testosterone analogs is used when carrying out hormone replacement therapy in elderly men in whom the hormone is significantly reduced.
Diet to increase testosterone
For the normal production of hormones, including testosterone, it is necessary to provide the body with the necessary nutrients. The diet of patients with low hormone levels should be balanced in terms of protein, fat and carbohydrate content and enriched with vitamins, micro- and macroelements. It is important to follow your diet and avoid overeating, especially at night.
The diet includes foods rich in zinc: seafood (crabs, squid, oysters), fish (herring, carp, anchovies), nuts (pistachios, walnuts, peanuts, almonds), seeds (sunflower, pumpkin).
It is also necessary to consume enough foods containing calcium, magnesium, selenium, vitamins C, D, E and group B, omega-3- and omega-6-unsaturated fatty acids. For this purpose, citrus fruits, red grapes, cabbage, fish oil, honey, eggs, coffee, flaxseed oil, milk are included in the diet.

To correct testosterone, a diet high in vitamins, micro- and macroelements is required
It is necessary to drink about 1.5 liters of water per day; during active sports, the amount of water should be increased. You should not replace water with sugary soft drinks and packaged juices. It is also recommended to give up fatty foods, cut down on fast carbohydrates (white bread, pastries, sugar and sugar-containing foods).
Correction of testosterone in women
To lower testosterone levels in women, as a rule, they resort to drug therapy. Oral contraceptives, calcium gluconate, vitamin complexes (especially vitamin D) are prescribed. With an increase in the concentration of the hormone due to the presence of a neoplasm, surgical treatment or radiotherapy is performed.
It is possible to somewhat reduce the level of the hormone with the help of a dairy-plant diet and refusal of excessive physical exertion, in particular, strength training. You should also give up the use of alcoholic beverages and smoking, normalize your lifestyle (full night sleep, reasonable alternation of work and rest).
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.