- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Chickenpox in infants: causes, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Development reasons
- Symptoms of chickenpox in infants
- Congenital chickenpox
- How many days does the incubation period last
-
Chickenpox treatment in newborns and infants
- Drug therapy
- General recommendations
- Video
Chickenpox is rarely diagnosed in infants. Whatever the route of infection, the pathology in newborns is severe and leads to complications from various organs and systems of the body.

Chickenpox in infants can be severe
According to statistics, chickenpox is as hard as monthly babies, babies at the age of 6 months to 1 year are tolerated. This is due to the fact that innate immunity at this age is already reduced, and its own has not yet been formed.
Development reasons
At such an early age, children can get sick with a viral pathology transmitted by airborne droplets if:
- a woman contracted an infection during pregnancy a few days before giving birth, and antibodies did not have time to form in her body (congenital chickenpox);
- a newborn whose mother has never had chickenpox has come into contact with an infected person.

One of the possible routes of infection transmission is vertical
In the first three months of life, transmittable antibodies from a mother who had an infection before pregnancy act as a guarantee against infection with chickenpox. In children of three months and older, the risk of infection through contact with an infected person increases, since the amount of these antibodies decreases sharply.
However, if during this period they receive breast milk, thanks to the antibodies contained in it, the period of protection against infection is extended to six months, or the developed chickenpox is mild.
Symptoms of chickenpox in infants
The most characteristic symptom of the disease is a red rash, which in a short time turns into bubbles filled with liquid. Chickenpox, depending on the intensity of manifestations, can occur in two forms:
| Severity | Symptoms |
| Light form | An increase in body temperature is not noted, rashes in small quantities appear only on the limbs, trunk, scalp, neck and face |
| Severe form | The body temperature rises to 37, less often to 40 ° C, on the skin and mucous membranes, including on the eyelids and in the mouth, papules filled with a transparent liquid are detected, which is clearly visible in the photo. The rash is very itchy, causing special discomfort to the baby |
In both cases, the child becomes whiny, looks lethargic and painful. The rash initially looks like red spots, chaotically spread throughout the body, and after a day they turn into bubbles filled with transparent liquid and begin to itch.
New elements continue to appear on average for another 3-8 days. A feature of the course of pathology in infants is that they are less sprinkled with papules than older children or adults.
The baby's condition improves as soon as new drips stop appearing. Regardless of whether the parents treat the bubbles with special drying agents or not, they dry out over time, become crusty and disappear after 7-14 days.
Congenital chickenpox
The diagnosis of congenital chickenpox is made in cases when a newborn falls ill before 11 days of life. The disease begins with a sharp increase in body temperature, vomiting and, in some cases, seizures.

A particular danger is the congenital form of the disease.
The child refuses breastfeeding for several days, is in a state of mild excitement, or, conversely, becomes weak and sleepy. After several days, the skin and mucous membrane of the mouth and nose begins to show characteristic itchy papules.
How many days does the incubation period last
The incubation period is the period of time that passes between the infection of the body until the first symptoms appear. Chickenpox in children goes through three stages:
- Adaptation of the virus in the body.
- Active multiplication of infected cells.
- The penetration of the virus into the blood and the appearance of the first characteristic symptoms of pathology.
Despite the fact that the general condition of the child is deteriorating, it is during this period that the first antibodies begin to be produced. In general, in infants, the incubation period is short and may not exceed 7 days.
For those who do not have immunity to chickenpox, the danger of infection is contact with an infected baby in a period that begins 2 days before the first rash and lasts up to 5 days after the appearance of the last papules.
Chickenpox treatment in newborns and infants
Therapy in young children is prescribed by a pediatrician after examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. Of particular importance in the effectiveness of the methods of treatment used is the observance of the doctor's recommendations by the parents and the timely appeal for medical help when the patient's condition worsens.
In severe cases, when there are suspicions that the bubbles protruding in the throat area may interfere with the normal breathing of the baby, emergency hospitalization is required.
Drug therapy
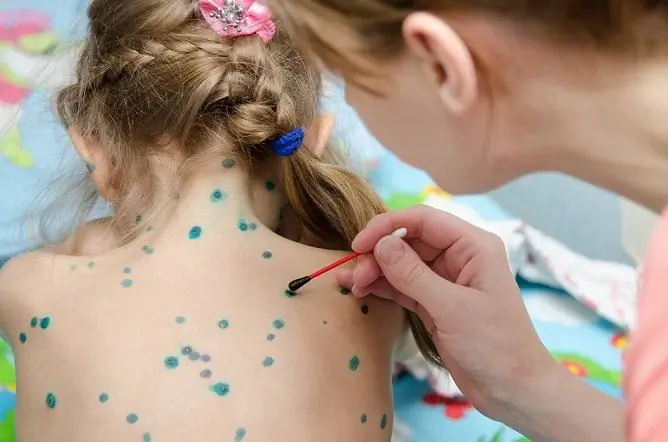
The papules protruding on the skin locally, with a slight seizure of healthy tissues, are lubricated with cotton wool soaked in Zelenka. Thanks to this, the rash dries up faster and delivers less discomfort.
The drug is a highly active and fast-acting antiseptic with antimicrobial activity, the use of which in chickenpox prevents papule suppuration.

With severe itching, Fenistil gel can be used
To reduce itching in places where the rash is most concentrated, the doctor may recommend lubricating Fenistil with gel or another antipruritic external agent, the use of which is permissible in newborns or infants. It should be borne in mind that in children under 2 years of age, the gel is contraindicated to be applied simultaneously to all affected areas.
If chickenpox in infants is accompanied by fever, paracetamol is used in the form of rectal suppositories or oral syrups in dosages appropriate for the patient's age.
General recommendations
With a mild course of the disease, an abundant drink is prescribed. In children who are breastfed, whose diet has already been supplemented with complementary foods, for the period of chickenpox, any food other than breast milk should be canceled, and water should be offered as often as possible.

In children who are breastfed during the chickenpox period, it is recommended to cancel any complementary foods
Due to severe itching, the baby may begin to scratch the skin. This often leads to the formation of wounds and deep scars that remain for life, and in some cases, the development of a secondary skin infection. To prevent this from happening, during the illness, the child's nails should be cut shortly and the papules should not be combed, distracting his attention in every possible way.
In addition to basic treatment, parents should pay particular attention to the hygiene of the child. It is important to avoid wrapping and overheating the baby's body, as excessive heat leads to increased sweat production and, as a result, increased itching. The baby's diapers and clothes should be changed as often as possible, and the bedding should be changed every day.
After the shower, it is better to blot the baby's skin with a natural cloth or a soft towel, but do not wipe it dry, as this can damage the papules and increase itching.
Since during the period of pathology, the already not fully formed immune defense of the body is weakened, in order to avoid infection with other infectious agents, it is better to exclude the baby's contacts with strangers.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.