- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Laryngitis in infants: treatment, emergency measures
The content of the article:
- Symptoms of laryngitis in infants
- How to treat laryngitis in infants
- First aid for stenosis of the larynx
- Prevention
- Video
Laryngitis in infants is a dangerous disease. It can even occur in newborns, very often in an acute form. When the first signs are detected, it is necessary to immediately call a doctor to prescribe treatment, since at this age the disease is quite dangerous.

When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
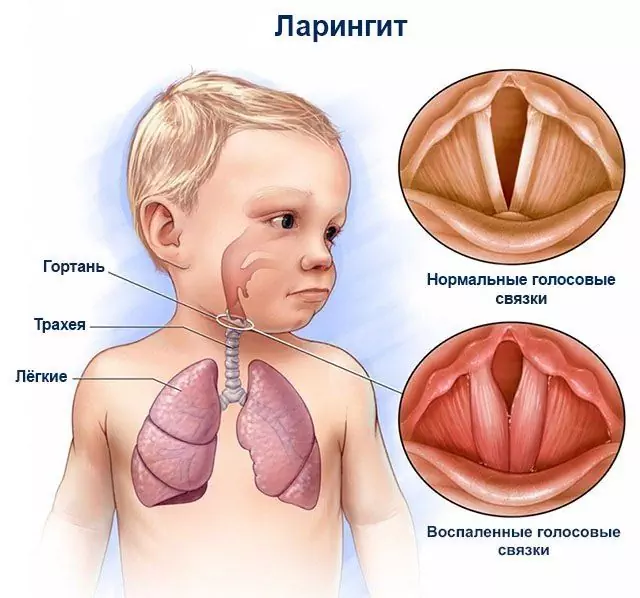
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the lining of the larynx. According to the famous pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky, the cause of the disease in 99% of cases is a viral or bacterial infection. In rare cases, the disease occurs as a result of an allergic reaction.
The development of laryngitis in a newborn is facilitated by the anatomical structure, namely:
- very narrow lumen of the larynx (4-5 mm) and narrow shortened vocal cords;
- high location of the larynx, which facilitates the penetration of infection;
- a large number of nerve receptors in muscle tissue, which leads to increased excitability.

The anatomical features of the larynx in newborns contribute to the development of the disease
This becomes the reason that children are prone to the rapid onset of edema of the laryngeal mucosa. Also, the occurrence of laryngitis is facilitated by unformed immunity and a tendency to develop allergies. Children often react to new foods, drugs or laundry detergents.
Symptoms of laryngitis in infants
Laryngitis begins acutely, sometimes within hours. This often occurs against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection, and, as a rule, the disease proceeds with an increase in body temperature. The baby becomes lethargic, restless, does not sleep well and refuses to eat.
The baby's voice changes, sometimes completely disappears. Due to the fact that the larynx is significantly narrowed, respiratory failure and hypoxia occur. This is evidenced by noisy rapid breathing, which is accompanied by a whistle. Against this background, the nasolabial triangle may turn blue (see photo).

The development of respiratory failure and hypoxia is evidenced by the cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle
Almost always, laryngitis proceeds with a cough that resembles a dog barking. Most often, seizures are observed at night. Parents need to be very careful, because at any time the baby may develop stenosis of the larynx. Factors contributing to its occurrence:
- allergy to drugs or food;
- overheating or hypothermia;
- severe coughing fits;
- prolonged screaming or crying;
- sudden changes in air temperature;
- being in a dusty room;
- inhalation of cigarette smoke;
- pungent odors;
- eating a cold drink or food.
The following symptoms indicate that an infant develops stenosis of the larynx:
- breathing becomes very rapid and noisy;
- heartbeat quickens.
Beads of sweat appear in the baby, and his skin becomes bluish. The child throws his head back, the vessels on his neck begin to pulsate.
If medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the child develops frothy discharge from the nose and mouth, cramps occur, and the skin becomes cold to the touch. A severe attack can result in respiratory arrest and death.
How to treat laryngitis in infants
Since there is a high probability of developing serious complications, the treatment of laryngitis in infants is carried out in a hospital setting. Usually, hormonal drugs are prescribed to eliminate swelling and reduce inflammation. They are injected or inhaled using a nebulizer.

With the help of a nebulizer, hormones and alkaline solutions can be administered
Also, to reduce edema, antihistamines are prescribed (Fenistil, Suprastin, Tavegil). Medications based on ibuprofen or paracetamol can lower body temperature.
Antiviral agents or antibiotics are prescribed if necessary. In complex treatment, antitussive or expectorant drugs are used. The child is discharged after normalization of breathing, restoration of voice and appetite.
First aid for stenosis of the larynx
If a baby develops an attack of suffocation, it is necessary:
- call emergency help;
- open a window in the room to provide fresh air. It is also recommended to turn on the humidifier, open hot water in the bathroom and, when steam appears, bring the child there. In the presence of a nebulizer, inhalation with alkaline water or hormonal drugs is carried out.
You can eliminate the spasm with a spoon, which is pressed on the root of the tongue.
In the event that the baby has already had such attacks, the first-aid kit should have antihistamines and hormonal drugs in the form of injections. If it is impossible to deliver the child to the hospital in a timely manner, they are administered intramuscularly at home.
In case of cardiac arrest, resuscitation measures are performed, consisting of chest compressions and artificial respiration. For this, the child is laid on a flat surface and a roller is placed under his neck, allowing his head to be thrown back. With two fingers of the right hand, they find a point in the middle of the chest and press it inward. If the procedure is performed correctly, the chest is lifted.
After thirty clicks, mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration is performed. In this case, the child's nose is covered with a hand and air is blown into it, after which the baby exhales on its own. After each exhalation, five pressures on the chest are made. The procedure is carried out until the heartbeat recovers or an emergency medical aid arrives.
During the procedure, it is necessary to control the force of pressing, since there is a possibility of a fracture of the chest.
Prevention
To avoid the development of the disease in an infant, it is necessary to provide him with comfortable living conditions. The room where the child is located must be regularly ventilated and kept clean. The air temperature in it should not exceed 22 ° C, while special attention should be paid to air humidity. For these purposes, a special humidifier can be used.
The baby should get enough fluid. Between feedings, he should be given water to drink, whether he is breastfed or bottle-fed.

Acute introduction of complementary foods is the prevention of the development of allergic laryngitis
To avoid the development of allergic laryngitis, it is recommended to introduce complementary foods with caution, preferably one product at a time, constantly monitoring the baby's reaction.
With your child, you need to regularly walk in the fresh air, even in cold and rainy weather.
Laryngitis in infants is a dangerous disease, therefore, when the first symptoms are detected, you must immediately call a doctor. It is in the parents' best interest to learn how to perform chest compressions and artificial respiration.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.