- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Internal hemorrhoids: when is it time to stop being shy and go to the proctologist
Internal hemorrhoids are a proctological pathology characterized by enlargement of the veins of the rectal plexus, discharge of blood from the anus, inflammation and prolapse of nodes. The nodes are located directly under the mucous membrane inside the lumen of the rectum.

Symptoms of internal hemorrhoids
The main symptoms of internal hemorrhoids include the following:
- discharge of blood from the anus (traces of blood can remain on underwear, toilet paper, in the feces);
- falling out of "bumps";
- pain syndrome;
- itching in the anal area;
- secretion of mucus.
If the above symptoms are found, the patient needs to consult a specialist as soon as possible. The earlier you visit the doctor's office, the more favorable the result will be.
Most often, internal hemorrhoids are associated with the following factors:
- overeating;
- excessive physical exertion;
- hereditary predisposition;
- stool disorders (diarrhea or constipation);
- excess weight;
- arterial hypertension;
- varicose veins in the pelvic area, lower extremities;
- pregnancy and childbirth.
About the pathogenesis of hemorrhoids
In the case of prolonged exposure to destructive factors, the flow of arterial blood into the cavernous veins of the rectum increases. The outflow, in turn, either remains at the initial level or decreases. This condition leads to the development of hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies. They increase in size, and their walls are compacted. Due to superficial damage to the cavernous veins of hemorrhoids, bleeding occurs.
Specialists divide internal hemorrhoids into the following stages:
- First. The patient is experiencing discomfort at this stage. He has rectal bleeding.
- Second. This stage involves the loss of nodes, the appearance of itching, mucus. Hemorrhoids fall out, but you can correct them yourself.
- Third. At this stage, the patient is faced with the same sensations as at the previous one. But in order to solve the problem, you need to study the manual guide for repositioning the knots.
- Fourth. At the last stage, internal hemorrhoids are accompanied by bleeding, regular prolapse of nodes, incontinence of the anal sphincter, and severe pain. At this stage, it is impossible to put hemorrhoids back into the anal canal.
Complications
If you do not turn to a specialist in time, you can face such serious complications:
- the appearance of anal fissures;
- rectal bleeding (may be "acute" or stop suddenly);
- prolonged bleeding (ranging from the release of a few drops of blood and ending with profuse discharge);
- thrombosis of external, internal hemorrhoids;
- necrosis, entrapment of nodes in the anus;
- insufficiency of the anal sphincter;
- chronic or acute paraproctitis (the patient begins to complain of an increase in body temperature, pain and swelling in the anal area).
Diagnostics, treatment methods
Effective treatment of this ailment is impossible without a thorough examination. Diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids includes the following:
- Collection of anamnesis (individual, family). The doctor is interested in the symptoms and duration of the disease, the nature of the feces, the patient's complaints. A very important role is also played by a tendency to allergies, pathologies, and oncology.
- Visual inspection of the affected area. The specialist detects oozing, rashes, swelling, cracks, etc. To determine them, the patient must lie on the couch on his left side, bend his knees.
- Examination of the anal canal using fingers. The doctor examines the soreness of the walls, the presence of defects or scars of the mucous membrane, tumors or polyps, the tone of the anal sphincter.
- Anoscopy. For this, an anal speculum is used. It can be used to examine an area located at a distance of 10 cm from the anus.
- Sigmoidoscopy. The specialist uses a tube with a light bulb, lens, bulb and eyepiece. This device examines the rectum of the rectosigmoid section up to 25 cm.
- Irrigoscopy. This is an X-ray examination of the rectum. For this procedure, barium sulfate is used. The contrast is injected retrograde (into the rectum in the form of an "enema").
To cure internal hemorrhoids, the doctor may prescribe the following procedures to the patient:
- conservative therapy;
- minimally invasive treatment;
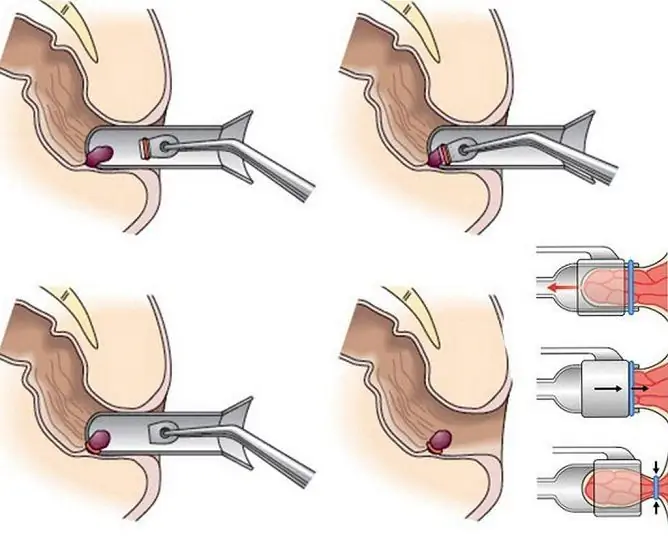
- sclerosis of hemorrhoids;
- ligation of knots with latex rings;
- IR photocoagulation;
- laser vaporization;
- surgical intervention.

Prevention of internal hemorrhoids
To prevent the appearance and development of internal hemorrhoids, it is required to carry out preventive measures in time. These include following a strict diet. Overeating, alcohol abuse, the intake of spicy, spicy, fatty foods are prohibited.
It is required to avoid the appearance of constipation. For this, it is necessary to normalize the diet and increase water intake. Efficient food products are seaweed, wheat bran, flax family.
Internal hemorrhoids can also occur in people who spend most of their time in a sitting position. To avoid this pathology, it is recommended to periodically organize walks.
Based on materials from the encyclopedia probolezny.ru
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.