- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Internal hemorrhoids
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Internal hemorrhoid symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Internal hemorrhoid treatment
- Potential consequences and complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Internal hemorrhoids - a disease caused by varicose veins and hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies of the final part of the rectal ampulla. Pathology is widespread, according to medical statistics, it affects 4-5% of the adult population of the planet. In the general structure of proctological diseases, the share of internal hemorrhoids accounts for 35-40%. More than 80% of women giving birth have an expansion of the venous plexuses of the rectal wall of varying severity. Repeated labor increases the risk of developing the disease.

Internal hemorrhoids - expansion of veins in the lumen of the rectum
Causes and risk factors
The main reasons leading to the formation of internal hemorrhoids are:
- violation of the outflow of blood through the venules from the cavernous bodies located in the wall of the rectum;
- the laying of enlarged cavernous bodies in the process of embryogenesis;
- congenital functional failure of the connective tissue;
- violation of the nervous regulation of the tone of the muscular membrane of the venous wall.
The main risk factors for the development of internal hemorrhoids include:
- increased venous pressure due to pregnancy, hard physical labor, prolonged work in a sitting or standing position, chronic constipation, a sedentary lifestyle;
- non-observance of the optimal water balance (with insufficient water intake, the feces become denser, as a result of which the process of defecation is accompanied by a significant increase in pressure in the venous plexuses of the rectal ampulla);
- alcohol and spicy food abuse (provokes irritation of the rectal mucosa, thereby creating the prerequisites for the formation of hemorrhoids);
- malignant tumors of the rectum;
- obesity;
- cirrhosis of the liver with symptoms of portal hypertension;
- chronic intestinal infections leading to damage to the rectal mucosa;
- atrophy of muscle fibers (observed in the elderly);
- strong nervous stress (have a negative effect on the functioning of the nervous system and its innervation of the venous walls);
- anal sex.
Two factors are always involved in the pathological mechanism of the formation of internal hemorrhoids: weakness of the venous walls and an increase in internal rectal pressure. They lead to the expansion of the venous sinuses and their gradual protrusion.

A sedentary lifestyle, improper nutrition lead to weakness of the venous walls, the development of internal hemorrhoids
The internal hemorrhoid is a mature cavernous tissue located under the rectal mucosa, represented by several lacunas (cavities) and separate vessels of the venous type with folded walls, due to which it can quite easily change the volume.
Internal hemorrhoid symptoms
Internal hemorrhoids differ from external ones in the absence of any external signs of the disease in the early stages. This is due to the fact that hemorrhoids are located inside the lumen of the rectum in the submucosal space at some distance from the sphincter.
The clinical signs of internal hemorrhoids are determined by the size of the dilated cavernous sinuses. Depending on this, 4 stages of the disease are distinguished.
- The expansion of the venous plexus is insignificant and practically does not cause discomfort to the patient. With constipation, hard feces can injure the hemorrhoid, leading to inflammation. In this case, exudate is released, provoking itching and burning around the anus. After defecation, most patients notice slight discomfort in the anus and rectum. Sometimes, after a bowel movement, traces of blood are visible on the toilet paper. However, most often, bleeding from hemorrhoids at this stage is so insignificant that it can only be detected by laboratory tests (analysis of feces for occult blood, fecal microscopy).
- The size of the hemorrhoids increases so much that they are perceived by the patient as a foreign body in the rectum. Under the influence of physical exertion, defecation, coughing, these nodes go out through the anus, and then they are independently drawn inward. Almost every act of bowel movement is accompanied by painful sensations, bloody discharge. Prolonged bleeding causes iron deficiency anemia, sometimes to a significant degree. After a while, the disease can spontaneously go into remission, that is, the signs of internal hemorrhoids become mild, however, under the influence of provoking factors, an exacerbation soon occurs again.
- Hemorrhoids become so large that they easily fall out of the lumen of the rectal ampulla. They can no longer be adjusted independently, they can only be adjusted manually. Complications often occur, such as rectal bleeding, anus fissure.
- Hemorrhoids constantly sag outward, it is not possible to correct them due to their large size even manually. Patients complain of constant pain in the rectum, anus, perineum, aggravated by any, including minor, physical activity. Exacerbations are frequent and accompanied by pronounced clinical signs.

Stages of internal hemorrhoids
Diagnostics
Early diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids is difficult, since there are no external signs of the disease, and the patient's complaints are scarce. If the doctor assumes the pathology of the veins of the rectum, then he performs a digital examination of its ampoule. The study determines the size, density and location of varicose veins, their soreness, density. Internal hemorrhoids have the shape of a mulberry to the touch, bleed easily. Against the background of long-standing internal hemorrhoids, the nodes and the mucous membrane of the rectum easily fall out, which is clearly visible during digital examination.

Internal hemorrhoids are well palpated during digital examination of the rectum
A more detailed study of the features of hemorrhoids is carried out using anoscopy. An anoscope tube with a special illumination system is inserted into the rectum to a depth of 10 cm. If the nodes are located higher, then sigmoidoscopy is shown instead of anoscopy. Endoscopic research methods make it possible to obtain detailed information about the state of the rectal mucosa, the size and number of protrusions of the cavernous bodies, and also help to identify or exclude other proctological diseases. In the course of an endoscopic examination, if necessary, a biopsy of the rectal wall is performed, followed by a histological analysis of the tissue obtained. This makes it possible to timely diagnose malignant neoplasms of the rectum, which in the early stages are clinically manifested by signs of internal hemorrhoids.
In the absence of the possibility of endoscopic examination of the rectum, they resort to irrigoscopy. To do this, a suspension of barium sulfate is injected into the rectum, and then an X-ray examination is performed. Irrigoscopy makes it possible to diagnose the presence of anal fistulas and protuberances of the intestinal wall, which can also be formed by hemorrhoids.
To assess the obturator functions of the sphincter, sphincterometry is performed.
2-3 days before any instrumental method of examining the intestines, the patient is prescribed a diet with a minimum content of coarse plant fibers. The night before and on the morning of the study, a cleansing enema is required.
Instrumental methods for examining the intestines are contraindicated in exacerbation of internal hemorrhoids, since they contribute to increased bleeding and the spread of the inflammatory process.

Endoscopic examination of the rectum allows you to determine the degree of hemorrhoids
Laboratory methods in the diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids are rather auxiliary in nature. These include:
- a general blood test (with bleeding, a reduced concentration of hemoglobin is determined, with inflammation of hemorrhoids - leukocytosis and accelerated ESR);
- coprogram and feces for occult blood - allow to identify even minimal bleeding, to clarify the features of intestinal functions;
- feces for cysts of lamblia and eggs of worms - allows you to exclude helminthic invasion and the associated cause of perianal itching.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- anal fissure;
- diverticulosis;
- rectal polyp;
- congenital malformations of the rectum and perianal region;
- hypertrophied anal papilla;
- anal condylomas;
- paraproctitis;
- villous swelling;
- prolapse of the rectum;
- rectal cancer.
Internal hemorrhoid treatment
With uncomplicated internal hemorrhoids, accompanied by rare bleeding, conservative therapy is indicated, aimed at regulating the stool, normalizing blood circulation in the rectum and eliminating inflammation. For these purposes, appoint:
- pararectal novocaine blockade according to A. V. Vishnevsky;
- ointments and suppositories with local anesthetics;
- laxatives;
- microclysters with Vishnevsky liniment, rosehip oil or sea buckthorn oil;
- ointments and suppositories with proteolytic enzymes and / or heparin;
- nicotinic acid;
- Detralex (with exacerbation of internal hemorrhoids);
- physiotherapy procedures - ultraviolet irradiation with a quartz lamp, UHF.
In case of significant bleeding, the patient may be prescribed hemostatic agents.

The early stages of internal hemorrhoids are successfully treated with rectal suppositories
Unfortunately, conservative treatment of internal hemorrhoids rarely provides a lasting positive result. Heavy physical exertion, errors in the diet, stress, as a rule, lead to another exacerbation.
With frequent exacerbations or a complicated course of internal hemorrhoids, surgical treatment is indicated, which should be preceded by a short course (5-6 days) of anti-inflammatory therapy. Surgical treatments for internal hemorrhoids include:
- Sclerosing injections. A special substance called a sclerosant is injected into the varicose plexus, which leads to adhesion of the vascular walls, and subsequently the lumen of the vessel is overgrown with fibers of connective tissue. The operation is indicated for patients with chronic hemorrhoids without pronounced inflammation and loss of nodes.
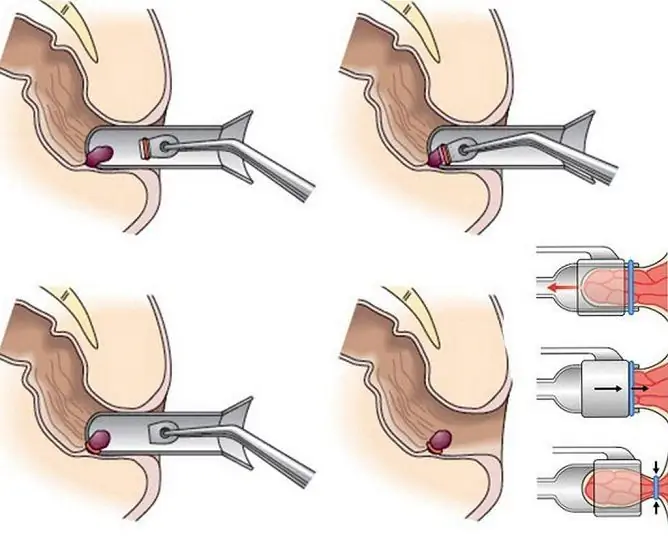
- Ligation with latex rings. The procedure is performed using a special apparatus. The indications for it are: a difficult general condition of the patient, prolapse of hemorrhoids, significant inflammatory changes.
- Classic resection of hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidectomy). It is performed in patients with chronic hemorrhoids complicated by heavy bleeding and / or prolapse of nodes. In most cases, Milligan-Morgan surgery is performed.

Latex ring ligation is a minimally invasive method for treating internal hemorrhoids
Potential consequences and complications
Complications of internal hemorrhoids are:
- anal itching;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- fecal incontinence;
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids, clinically manifested by sharp pain in the rectum and anus;
- infringement of the fallen out hemorrhoids with the development of their necrosis;
- paraproctitis;
- sepsis;
- phlegmon of the soft tissues of the pelvis.
Forecast
With a timely visit to a proctologist and adequate treatment, the prognosis is generally favorable. If complications develop, the prognosis worsens.
Prevention
Prevention of internal hemorrhoids consists in the following measures, which should be systemic in nature:
- timely treatment of diarrhea and constipation;
- thorough toilet of the anus after each bowel movement;
- the inclusion in the diet of a sufficient amount of fruits and vegetables;
- compliance with the optimal drinking regime;
- regular gymnastics, walks in the fresh air;
- limiting excessive physical exertion;
- refusal to wear tight belts, modeling underwear;
- refusal to abuse alcohol.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!