- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
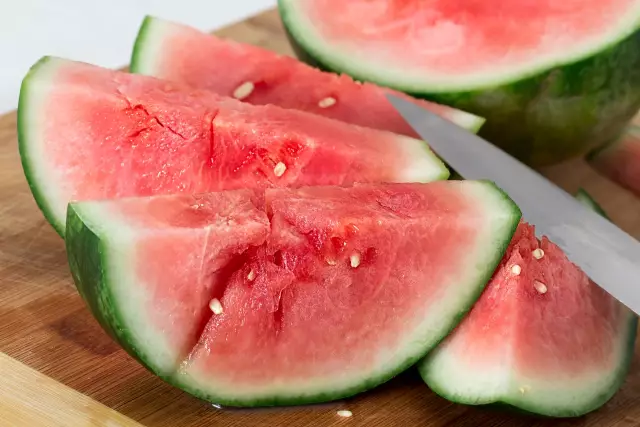
Calorie content of watermelon

Watermelon is a herbaceous annual plant belonging to the pumpkin family, with oval, spherical, flattened pumpkin fruits. The fruits of watermelon acquire a different color of the peel, the ripe pulp acquires a red, pink or raspberry hue, in rare cases - white or yellow. Morphologically, a watermelon is similar to a berry. In addition to its bright taste properties, watermelon has a number of pharmacological features. Due to the low calorie content of watermelon, the fruits can be consumed with health and body benefits.
The calorie content of watermelon is up to 35 calories per 100 g of ripe fruit pulp, which allows you to consume watermelon in unlimited quantities.
Calorie content of watermelon: nutritional and energy value of the fruit
The calorie content of watermelon turns its fruits into a useful dietary product that can not only help to significantly reduce weight, but also normalize many body functions. So, watermelon pulp has choleretic, diuretic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, tonic properties. The use of watermelon normalizes metabolic processes in the body, enhances intestinal peristalsis. Watermelon has a mild laxative effect, removing toxins and toxins from the body, and also promotes gentle removal of stool deposits from the intestines. With its low calorie content, watermelon is a source of soft dietary fiber - fiber, which, without providing the body with energy, plays an important role in its life. Fiber helps to slow down the absorption of carbohydrates, fats, proteins,contributing to a longer saturation of the body after a meal.
With a low calorie content of watermelon, the fruits are a source of useful micro- and macroelements, vitamins for the body. 100 g of watermelon pulp contains about 10% of easily digestible sugars (fructose, glucose, sucrose). The pulp of a ripe watermelon also contains pectin substances (physiologically active substances that have a number of beneficial properties for the body), proteins, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, iron in its organic form. Watermelon is a source of vitamins: niacin, riboflavin, folic, ascorbic acid, thiamine. Watermelon seeds also have useful properties, which are often thrown away when the pulp is consumed. However, they contain up to 25% fatty oils, as well as linolenic, linoleic, palmitic acids.
With a low calorie content of watermelon, its pulp is enriched with lycopene, a carotenoid pigment that determines the color of the fruit pulp. This carotenoid has a powerful antioxidant effect, leads to a decrease in oxidative stress, which, in turn, slows down the processes of atherosclerotic changes in the body, protects DNA, helping to prevent oncogenesis (the formation of malignant and benign neoplasms). Lycopene reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, eye diseases, and inflammatory processes in the body. The recommended daily intake of lycopene for a person is up to 5 mg. 1 kg of watermelon pulp contains up to 25 mg of lycopene.
How many calories are in a watermelon: an effective watermelon diet
The low calorie content of watermelon, along with its beneficial properties, turns this fruit into a unique dietary product. An effective watermelon diet allows not only to reduce weight, but also to cleanse the body of toxins and toxins, as well as restore the balance of macro- and microelements, and get a powerful vitamin charge.
The low calorie content of watermelon allows you to reduce weight by eating tasty and not limiting the amount of delicious fruit.
There are several types of low-calorie effective watermelon diets. Nutritionists recommend arranging fasting days on a watermelon in the summer. During the fasting day, only watermelon pulp is consumed, all drinks are excluded from the diet, except for purified water. The fruit of a watermelon is 90% water, therefore, as a rule, watermelon discharge is an excellent thirst quencher. The unloading efficiency on a watermelon is low. Weight goes away gradually when a person returns to a normal diet.
Due to its low calorie content, watermelon can complement any diet as a healthy treat, thereby reducing physical and psychological stress for the body with a limited intake of nutrients from food.

A longer watermelon diet is a special diet lasting up to 7 days. Throughout the diet, the diet allows unlimited consumption of watermelon. Each meal can be supplemented with black or whole grain bread. For lunch with such a diet, boiled meat of low-fat varieties (preferably poultry), stewed vegetables, and whole grain bread is recommended. Porridge is allowed as a side dish. The watermelon diet excludes fermented milk products to avoid the development of diarrhea and recommends low-fat yoghurts when leaving the diet to restore intestinal microflora after cleansing the soft fiber of the watermelon pulp.
The pulp of watermelon, which practically does not contain calories, is also used in the preparation of various salads, desserts, and drinks.
Regardless of how many calories are in a watermelon, the pulp of this fruit can be consumed without restrictions. However, it should be borne in mind that watermelon diets are not recommended for patients with diabetes mellitus, kidney stones, with complicated diseases of the pancreas, prostate, pyelonephritis. With its low calorie content, watermelon also poses a certain threat to the body. For quick ripening, watermelons are treated with nitrates, which accumulate in watermelon peels and pulp. Once in the body, nitrates are converted into nitrites (elements that destroy hemoglobin in the blood) and nitrosamines (highly toxic compounds that damage the liver, causing bleeding, convulsions, coma). Nitrosamines have a powerful carcinogenic effect; when a large dose is ingested, the compound exhibits mutagenic properties.
Despite the low calorie content of watermelon, its taste and high content of nutrients, the fruits must be chosen with extreme care. The best period for consuming watermelons and following the watermelon diet is late August and early September. It is by this period that the fruits have time to ripen without fertilizers and chemicals.
Benefits of watermelon: calories and vitamins
Watermelon is a useful product that allows you to simulate the fast saturation of the body. The pulp of watermelon, which has very limited calories, is saturated with vitamins PP, beta-carotene, B1, B2, B6, B9, C, E, many of which are not synthesized in the body. The unique properties of watermelon, in which there are practically no calories (up to 35 calories per 100 g of pulp), are also explained by the fact that the body needs to spend more energy on digesting watermelon and excreting digestive products than it enters the body with a portion of the fruit pulp. The calorie content of watermelon can be neglected when calculating the daily caloric content of the diet when following various diets.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.