- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Betaine
Instructions for use:
- 1. Pharmacological action
- 2. Release form
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Storage conditions
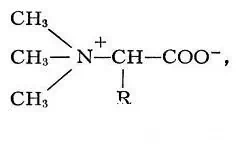
Betaine is a synthetic drug with pronounced hepatoprotective and choleretic properties.
pharmachologic effect
The active substance Betaine has a choleretic, hepatoprotective, digestive enzymatic and lipolytic effect.
The drug activates fat metabolism in the liver and stimulates the formation and secretion of bile, helping to improve digestion.
Also, Betaine has a pronounced choleretic and cholekinetic effect, reducing the fat content in hepatocytes, helping to neutralize toxic substances and improve liver function.
Release form
The Betaine preparation containing the active ingredient betaine citrate is produced in several dosage forms:
- 200 mg tablets;
- Granulate for preparation of oral solution, in a bottle of 25 g;
- Effervescent tablets, 10 pieces per tube.
Betaine analogs include Acidin-pepsin and Gastropect.
Indications for Betaine use
According to the instructions, Betaine is used for functional disorders associated with digestion, including:
Dyspeptic disorders - discomfort in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium, heartburn, nausea, belching, flatulence
- Drowsiness and discomfort after eating;
- Slowdown in digestion, as well as impaired digestion of food due to abundant consumption of food rich in fats and proteins, irregular nutrition or excess consumption of ethanol.

As an auxiliary therapy, Betaine is used for moderately severe hypertriglyceridemia, fatty hepatosis and atheromatosis. Treatment is considered to be most effective if a consistent diet is followed.
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated to use only in case of hypersensitivity to the Betaine components.
Mode of application
According to the instructions, Betaine is used three times a day. The tablets should be taken with a sufficient amount of liquid, the effervescent tablets and granules are dissolved in 1/2 glass of water. A single dose is 1 tablet or 3-6 g of granulate. The most effective is the use of the drug between meals. The duration of treatment is prescribed individually by the doctor.
Betaine can be taken for diabetes. When treating, it should be borne in mind that the drug can lower the acidity of gastric juice, as well as reduce the activity of antibiotics.
Side effects
According to the instructions, betaine causes mild allergic reactions associated with hypersensitivity to the active substance.
Storage conditions
Betaine can be purchased without a doctor's prescription and has a manufacturer's recommended shelf life of 3 years.
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!