- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
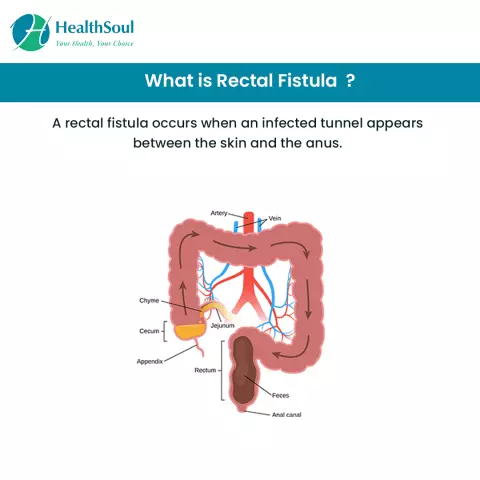
Rectal fistula
Rectal fistula is a chronic inflammatory process of the anal gland, usually located in the area of morgan crypts (anal sinuses), as a result of which a passage forms in the rectal wall through which the products of inflammation (pus, mucus and ichor) are periodically excreted.
Causes of rectal fistula

In the overwhelming majority of cases, the cause of the formed fistula of the rectum is an acute paraproctitis (inflammation of the anal gland) that has not received adequate treatment. Acute paraproctitis leads to suppuration of the anal gland. The inflamed gland swells, and the outflow from it is disturbed, as a result, the resulting purulent contents find a way out through the loose tissue of the rectum, opening on the skin in the anus. The gland itself, as a rule, is melted by a purulent process. Its outlet into the rectum becomes the internal opening of the fistula, and the place where the pus has found its way out becomes the external inlet. Due to the constant infection with intestinal contents, the inflammatory process does not stop, but goes into a chronic phase. Scar tissue is formed around the fistula of the rectum, forming its walls.
Less common are post-traumatic and postoperative fistulas.
Rectal fistula symptoms
Rectal fistula can be complete (external) or incomplete (internal). These two forms have different clinical manifestations.
An internal fistula of the rectum is characterized by a chronic course with periodic exacerbations. In the period between exacerbations, the fistula may not manifest itself in any way, and not disturb the patient. During an exacerbation of the inflammatory process, pain appears in the anus, aggravated by bowel movements, a feeling of a foreign body appears in the anus, pus may be released from the anus, irritating the skin in this area. During exacerbations, the patient's general condition may worsen: fever, weakness, headache appear.
If the fistula of the rectum is external, then the patient is worried about a burning sensation in the area of the outlet of the fistula, periodic discharge of pus and ichor from there. In this place, the skin becomes denser, which can also create inconvenience, since there is constant injury during bowel movements.
Diagnosis of rectal fistula
The diagnosis of rectal fistula is made on the basis of digital rectal examination and sigmoidoscopy. With external fistulas, a probe is carried out, moving from the outer outlet to the inner one. Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum using a tube inserted into the anus. This method allows visualization of the rectal mucosa, as well as a biopsy, in order to differentiate a rectal fistula from a tumor, if suspected. In order to clarify the position of the rectal fistula and the presence of additional branches, ultrasonography is performed - an ultrasound examination of pararectal tissue.
Rectal fistula treatment

Treatment of rectal fistula is only operative. Due to a long-lasting chronic process, the fistulous course acquires dense walls and is not capable of independent scarring, even if anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. Therefore, conservative treatment of rectal fistula is always insufficient. The rectal fistula operation consists in excision of the internal, external inlet openings and walls of the fistulous tract. Drug treatment of rectal fistula is prescribed as an additional therapy in the postoperative period, to prevent relapse. Removal of the fistula of the rectum is carried out in the proctological hospital, under general anesthesia. The postoperative period lasts about a week, during which time the patient is in the hospital under medical supervision.
Alternative treatment of rectal fistula
Alternative treatment of rectal fistula consists in the use of natural anti-inflammatory drugs, mainly of plant origin, as well as general strengthening of the body, to combat the focus of chronic infection.
As a local anti-inflammatory treatment of rectal fistula, it is effective to use decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, in the form of baths, compresses and microclysters. For this purpose, St. John's wort, pharmaceutical chamomile, eucalyptus, sage, oak bark, plantain, calamus and other medicinal herbs with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are used. You can also use infusions and decoctions of these herbs to flush the fistulous tract with a small syringe.
Alternative treatment of rectal fistula also suggests the use of honey and other bee products, as well as ointments based on them.
For general strengthening of the body, it is recommended to daily use a tablespoon of honey on an empty stomach, or honey mixed with aloe juice in a 1: 1 ratio. Also, preparations from Echinacea purpurea, marshmallow root, and ginseng have a good immunostimulating effect.
It is hardly worth considering alternative therapy as an alternative to rectal fistula surgery due to the high risk of recurrence. Rather, the alternative treatment of rectal fistula is a good method of relieving exacerbation and inflammation with mild and at the same time effective means, as well as maintaining remission when surgical removal of the rectal fistula is impossible for any reason.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!