- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Reflux

Reflux is the movement of the contents of the hollow organs of a person, the opposite of its normal movement. In certain physiological processes, reflux is the norm; the main cause of pathological reflux may be disruption of the sphincters.
Refluxes are conventionally divided into the following groups:
- Upper gastric tract;
- Ducts of the gallbladder, pancreas, liver;
- Urinary organs;
- Female reproductive organs.
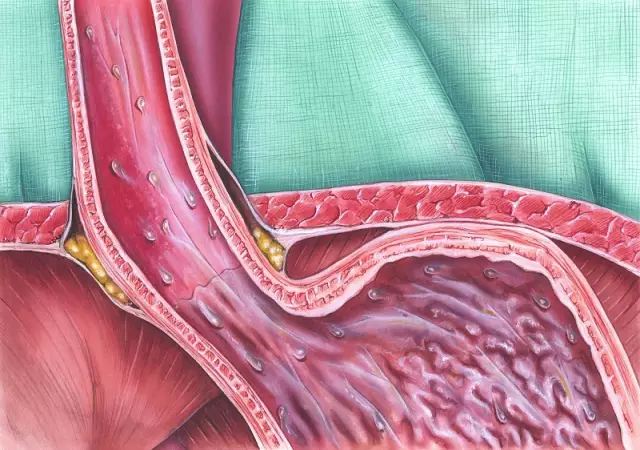
Gastric reflux
Gastric reflux is a functional disorder of the digestive system in which the contents of the duodenum (half-digested food mixed with digestive enzymes and bile) are thrown back into the stomach. Bile and digestive enzymes, entering the stomach, begin to corrode the mucous membrane, which is not designed for contact with highly corrosive substances. Gastric reflux causes severe inflammation of the stomach lining and, in some cases, even burns.
The full name of this syndrome is duodeno-gastric reflux, since the process occurs in the duodenum and stomach.
The symptoms of duodeno-gastric reflux are as follows:
- A constant feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- Yellow-coated tongue;
- Dyspepsia and belching;
- Constant pain in the stomach;
- Pain in the abdomen some time after eating.
The presence of such symptoms is a serious reason to see a doctor.
Erosive reflux
In the case of deeper lesions of the walls of the esophagus with the formation of erosions and ulcers on the mucous membrane, erosive reflux is formed. The consequence of erosive reflux, if not started on time, can be a chronic ulcer of the esophagus.
In order to avoid the development of complications with reflux of the upper gastric tract, the following dietary recommendations must be strictly observed:
- Complete cessation of smoking and alcohol;
- Eating often, but in small portions;
- Thorough chewing of food;
- Refusal of foods that increase acidity in the stomach;
- Avoiding fried, smoked, salty and spicy foods;
- Refusal from coffee, chocolate, strong tea;
- Eating soft foods that are soft;
- Eating vegetarian meals.
It is not recommended to go to bed or simply rest for at least an hour after eating, and you should also not wear tight clothing that would squeeze the abdominal cavity.
Ureteral reflux

Ureteral reflux is a functional disorder of the urinary tract that causes urine to flow back into the ureters and kidneys from the bladder. Anatomical defects or inflammation form obstructions in the urinary system for the normal flow of urine. Stagnation of urine, its excessive accumulation significantly stretches the walls of the bladder, urine under pressure returns back to the ureter, bending and deforming it. If the obstruction to the outflow of urine is not removed, the process spreads through the ureter, reaching the kidneys.
The main causes of ureteral reflux are:
- Congenital anomaly of the mouth of the ureter, which interferes or impedes the process of urine excretion;
- Dysfunction of the bladder, leading to an increase in urine pressure inside it;
- Chronic cystitis, which disrupts the elasticity of the internal tissues of the ureter.
Ureteral reflux does not have typical and specific symptoms, it begins to manifest itself at the stage of development of concomitant diseases, such as pyelonephritis. With a sharp rise in temperature, often above 39 degrees, without signs of a cold, severe pain in the lumbar and abdominal region, urinary disorders, it is necessary to undergo an examination and begin treatment as soon as possible. The danger of progression of ureteral reflux is a secondary damage to the kidneys, which in advanced cases can lead to their removal.
Reflux treatment
A timely diagnosis and a correctly chosen treatment regimen play a very important role in the treatment of reflux, since any type of reflux provokes diseases that develop over time.
Typically, refluxes are detected during examination of patients suffering from diseases of the urinary or digestive organs. In such cases, reflux treatment is carried out either simultaneously with the diseases caused by them, or after these diseases have been treated.
Reflux treatment is carried out exclusively as directed by a doctor and under his supervision in order to minimize all possible complications and consequences.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!