- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Constipation in children
The content of the article:
- Forms of constipation in children
- Causes of constipation in children and risk factors
- Stages of constipation in children
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of constipation in children
- Diet for constipation in children
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Constipation in children is a difficulty in the process of defecation, the lack of self-emptying of the intestines throughout the day or longer, and for breastfed babies, defecation is less than 1-2 times a day.

Source: bolit.info
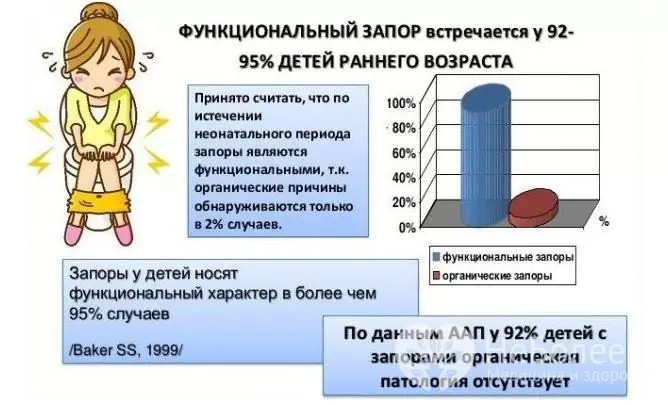
Constipation is registered in 15-30% of children, while children of preschool age are more susceptible to it. Regular constipation in children negatively affects the growth and development of the child, can lead to intoxication, hypovitaminosis, the development of other complications, and worsen the quality of life.
The main functions of the intestine are food digestion and absorption, as well as the excretion of unrealized products and substances toxic to the body. In children under 6 months of age, the act of defecation normally occurs 1-6 times a day, from half a year to 2 years - 1-3 times a day, over 2 years - at least 1 time a day. Approximately 40% of patients who had a tendency to constipation in childhood also suffer from it in adulthood.
In most cases of persistent constipation in children, there is no organic pathology. In patients with severe retardation of psychomotor development, constipation occurs in about 50% of cases.
Forms of constipation in children
Constipation in children can be true or false (pseudo-constipation).
Depending on the etiological factor:
- alimentary;
- functional dyskinetic (spastic and hypotonic);
- organic;
- conditioned reflex;
- intoxicating;
- endocrine;
- iatrogenic.
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture, acute and chronic constipation in children is distinguished.
Source: bolit.info
Causes of constipation in children and risk factors
Common causes of constipation in children in the first years of life include feeding errors and impaired absorption of nutrients.
A child can receive less breast milk than required in case of hypogalactia in the mother, as well as with sluggish sucking, regurgitation, clefts of the hard palate and upper lip. In the case of insufficient nutrition, the volume of feces in the child is accordingly insufficient to induce the urge to defecate. Such cases of delayed bowel movements are referred to as pseudo-constipation.
The occurrence of constipation in children who are breastfed is facilitated by a lack of fiber-rich foods in the mother's diet. At the same time, excessive consumption of fatty foods leads to an even greater hardening of the child's feces and aggravates constipation.
A temporary delay in defecation (transient constipation) is observed in children during periods of acute fever due to dehydration of the body against the background of an increase in body temperature, increased sweating, and vomiting.
Alimentary constipation in children occurs with nutritional disorders, which include inadequate nutrition, insufficient drinking regime, lack of vitamins in the body, dysfunction of the digestive glands, early transfer of the child to artificial feeding.
Constipation in a child can be a manifestation of diseases that are not directly related to pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Such diseases include hypothyroidism, rickets and other metabolic diseases. However, in most patients, constipation is still due to disorders of the digestive tract.
The organic form of constipation in children develops with ectopia of the anus, Hirschsprung's disease, rectal atresia, dolichosigma, intestinal neoplasms, anorectal scars, adhesive disease, helminthic invasions.
In most patients of this age group, constipation is of a functional nature. Dyskinetic constipation in children is caused by traumatic or hypoxic-ischemic lesions of the central nervous system. A conditioned reflex form of constipation in children occurs with painful bowel movements (with anal fissures, rectal fistulas, paraproctitis, diaper dermatitis). Hypotonic constipation in children develops against the background of insufficient physical activity, prolonged bed rest, chronic gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer, rickets. Spastic constipation can occur in children with neuro-arthritic diathesis, infantile cerebral palsy, lactase deficiency.
Other reasons for the development of constipation in children include intestinal dysbiosis, diabetes mellitus, gigantism, pheochromocytoma, adrenal insufficiency.
Risk factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- uncontrolled use of a number of drugs (enzymes, diuretics, enterosorbents, antibacterial agents, antispasmodics, iron preparations);
- abuse of enemas;
- food allergy;
- muscle hypotension;
- unbalanced diet;
- underweight;
- a sharp change in climatic conditions;
- improper potty training;
- psychological problems;
- long-term (up to 3-4 years of age) wearing diapers.
Source: sitemedical.ru
Stages of constipation in children
During constipation in children, the following stages are distinguished:
- compensated - defecation occurs 1 time in 2-3 days;
- subcompensated - defecation occurs 1 time in 3-5 days;
- decompensated - defecation delay can reach 10 or more days.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of constipation in children include local (intestinal) and general (extraintestinal) symptoms. Local include: a rare rhythm or prolonged absence of defecation, a change in the consistency of feces, pain in the abdomen, bloating, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the intestines after a bowel movement, an admixture of blood in stool, pain during bowel movements, flatulence, a feeling of pressure in the anus.
In children under six months, the consistency of feces is normally pasty, from six months to one and a half to two years, the feces have a pasty or shaped consistency, and later - formalized.
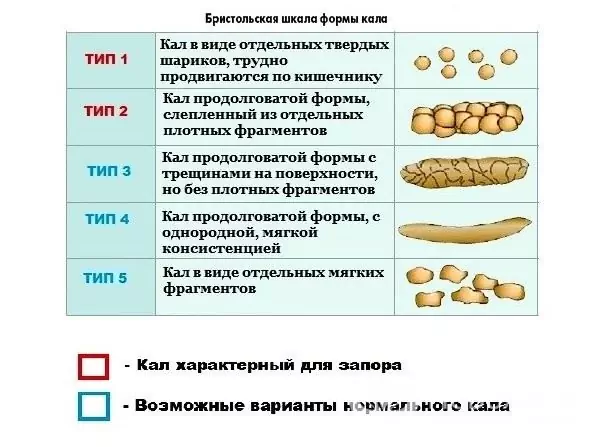
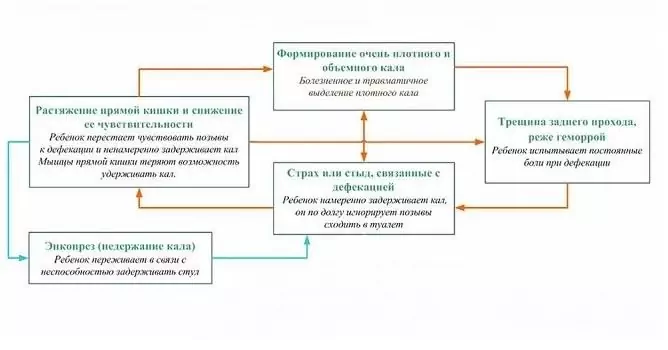
Overstretching of the intestinal wall with dense feces, which, moreover, can injure the mucous membrane of the anal canal, causes pain and anxiety in the child during bowel movements. In children with constipation, encopresis is often observed, usually after a long delay in bowel movements.
The extraintestinal manifestations of constipation in children include general weakness, fatigue, irritability, headaches, pallor of the skin, anorexia, anemia, a tendency to develop pustular rashes on the skin, loss of appetite.
With chronic constipation in children, an increase in the volume of feces occurs. This form of pathology is characterized by a persistent long-term (3 months or longer) decrease in bowel movements, which is accompanied by difficulty in emptying the intestines and an increase in the density of feces.
Diagnostics
To diagnose constipation in children, it may be necessary to consult not only a pediatrician, but also a pediatric gastroenterologist or proctologist. When collecting complaints and anamnesis, the time of onset and dynamics of the pathological process, the frequency of bowel movements and the consistency of feces are specified. When carrying out an objective examination, the color of the skin, the state of the tongue, tissue turgor, bloating and soreness of the abdomen are determined; palpation can determine the presence of fecal stones along the sigmoid colon. During the digital rectal examination, the state of the ampoule, the sphincter is assessed, organic malformations can be detected.
From the methods of laboratory diagnostics, a general and biochemical blood test, a coprogram, a study of feces for helminth eggs, for dysbiosis are usually carried out.
In order to exclude somatic pathology, an ultrasound examination of the liver, pancreas, stomach, large intestine, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, plain radiography of the abdominal cavity, irrigography, enterocolonoscintigraphy may be required. To examine the mucous membranes of different parts of the intestine, they resort to sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy.
In some cases, consultation of a pediatric neurologist with electroencephalography, echoencephalography is required.
Treatment of constipation in children
When treating constipation in children, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the causative factor. In some cases, normalization of the child's nutrition is sufficient, including an increase in the amount of fluid consumed. Of no small importance for constipation in children is the development of a conditioned reflex to defecate.
Medical treatment of constipation in children is carried out if necessary and consists in the appointment of laxatives, antispasmodic drugs, prokinetics. In some cases, short courses of cleansing, hypertensive or oil enemas are indicated.
The most convenient and safe option for solving the problem of constipation in children are topical agents - rectal glycerin suppositories Glycelax®. The active ingredient of Glycelax® suppositories is glycerin. It has a double effect: it softens stool and stimulates intestinal motility, thereby accelerating bowel movements. As a result, the intestines are emptied without pain or discomfort. Glycelax® suppositories do not require division: the dosage and size are designed for children, the use of suppositories is possible from three months.

Glycelax
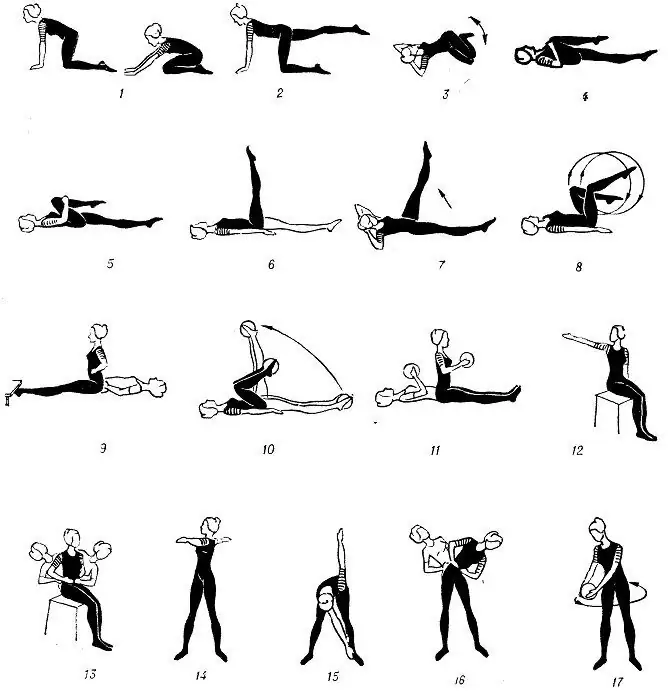
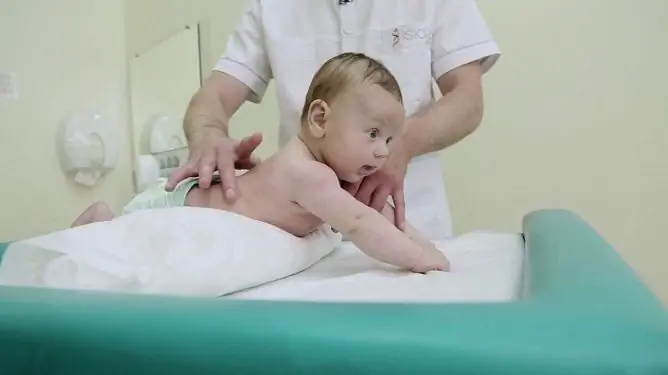
In some cases, physical therapy is effective. Electrophoresis, pulse currents, galvanization (with hypotension) and paraffin applications (with hypertonicity) can be used. With functional constipation in children, exercise therapy provides a good therapeutic effect. Massage for constipation in a child is used in case of intestinal hypotension after each meal. In the absence of contraindications, herbal medicine can be used (tea with fennel, dill water).
If there are signs of perinatal damage to the central nervous system, treatment is carried out with the participation of a pediatric neurologist. In this case, neurometabolic stimulants, B vitamins, drugs to improve cerebral circulation are prescribed. With the development of conditioned reflex constipation in children, it may be necessary to consult a child psychologist.
Follow-up and supportive care is usually given for 6-24 months.
Diet for constipation in children
With the development of constipation in a breastfed baby, first of all, it is necessary to analyze and correct the nature of the feeding of the nursing mother. It is recommended to limit the consumption of foods that contribute to increased gas production (black bread, onions, tomatoes, cabbage, rice, legumes, mushrooms, grapes, pears, spicy, smoked foods, spices).
For constipation in children who are bottle-fed, it is recommended to use mixtures containing lactulose or dietary fiber. Young children need up to 5 g of dietary fiber per day (excess content of dietary fiber in the diet can cause impaired digestion and poor absorption of calcium, zinc, iron).
For constipation in children, it is recommended to include sour cream, cream, milk, yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese, mild cheese, soft-boiled eggs or steam omelets, juices, dried fruit compotes, berries, fruits, beets, carrots, zucchini, wheat bran, cereals in their diet on milk and water. From sweets, honey, marmalade, marshmallow, marshmallow are acceptable. Turnip, radish, radish, mushrooms, green peas, strong broths, strong tea, baked goods, industrial confectionery are excluded from the diet. Limit the use of pasta, semolina. Products are recommended to be boiled, steamed, baked.
With the development of constipation in children with celiac disease, patients are shown an agliadin diet. Rye, barley, wheat, oat flour, cereals and cereals from them, semolina, starch, pasta and confectionery, boiled sausages, fish and canned meat, as well as products to which there is an individual intolerance or hypersensitivity are excluded from the diet. The diet includes buckwheat, rice, corn, vegetables, fruits, berries, eggs, meat, vegetable oil.
In case of constipation in children with cystic fibrosis, it is recommended to increase the calorie content of the diet by 50-90%. The diet should include meat, poultry, fish, cottage cheese, eggs, milk and dairy products, honey, fruits. The use of cereals from whole grains, legumes, bran is limited.
With constipation against the background of lactose intolerance, milk and dairy products are excluded from the diet. In milder forms of hypolactasia, it is permissible to include butter, hard cheese, yogurt, kefir in the diet.
Possible complications and consequences
Constipation in children contributes to colitis, which in turn aggravates the course of constipation, creating a vicious circle. Persistent constipation in children can lead to rectal prolapse.
Forecast
When the cause of constipation is eliminated and the recommendations of the attending physician are followed, the prognosis is favorable. In the absence of timely adequate treatment, the prognosis worsens, and constipation can become chronic and persist into adulthood.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of constipation in children, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of diseases that can lead to constipation;
- avoidance of irrational use of medicines;
- balanced diet;
- sufficient physical activity;
- correct potty training.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!