- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
First aid for bleeding

Since trauma, and thus bleeding due to it, can happen anywhere and anytime, every adult should know how to provide first aid for bleeding.
Types of bleeding and their features
Depending on the type of injured vessel, the following types of bleeding are distinguished:
- Arterial;
- Venous;
- Capillary.
Also, bleeding is distinguished by location. The hands are most often injured - upper limb bleeding is the most common type. In second place are leg injuries, in third place are nosebleeds. The most dangerous type is bleeding of internal organs, since it is difficult to notice them in time, it is even more difficult to keep the situation under control. Below we will consider the principles of first aid for arterial, venous, nasal and internal bleeding.
First aid for arterial and venous bleeding
Many vaguely remember that first aid for arterial bleeding consists in applying a tourniquet to the vessel, but few know how to do it correctly. Doctors warn: the imposition of a tourniquet can be no less dangerous than the loss of blood, an ineptly applied tourniquet can lead to the need for limb amputation, and, alas, it often does. How to provide first aid for arterial bleeding without causing harm? Remember, when a large artery is injured, there is little time left, only 3-5 minutes. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Do not rinse or in any other way try to disinfect the wound, do not remove small fragments that have got there;
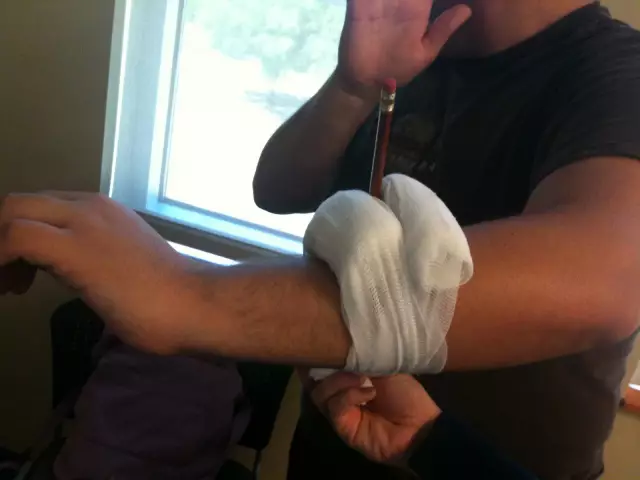
- Apply a pressure bandage as follows: apply a sterile bandage or a clean cloth folded in several layers directly to the wound (it is advisable that the dressing be sterile, if one is not at hand, use any). Place another roller made of fabric on top. Then everything is tightly bandaged, after which the limb must be placed above the level of the body. If done correctly, bleeding should stop;
- If there is nothing at hand that could serve as a dressing, you can try to stop the bleeding by maximally flexing the joint located above the wound;
First aid for bleeding and injuries using a tourniquet. This method is resorted to in the event that it was not possible to stop the blood in another way. The rules are as follows:
- A tourniquet (or any long piece of rubber, for example a rubber hose) is applied 5-7 cm above the wound, but not on bare skin, but on the fabric that should be wrapped around the limb, it can be on the sleeve or leg;
- After stretching the tourniquet, apply it in several turns without gaps between them, the first is not too tight, each subsequent turn is tighter. A sign of a correctly applied tourniquet is the stop of bleeding;
- The tourniquet should not be applied too tightly so as not to injure the nerves. If severe pain arises from the tourniquet, press the injured vessel with your finger, and remove the tourniquet, give the victim a break from the tourniquet, then apply again;
- It is imperative to record the application time of the harness! This is an extremely important condition that can save a person from possible disability. It is advisable to write the time of the tourniquet application with a pen directly on the victim's skin or clothing. The maximum time a tourniquet can be applied is one and a half to two hours in summer and one hour in winter. During this time, the patient must be taken to the hospital, if this is not possible, and the time has expired, the tourniquet must be very carefully and slowly removed, if bleeding has resumed, press the vessel with a finger above the wound.
First aid for venous bleeding occurs according to a similar algorithm, the only difference is that the vessel should be pressed below the wound.
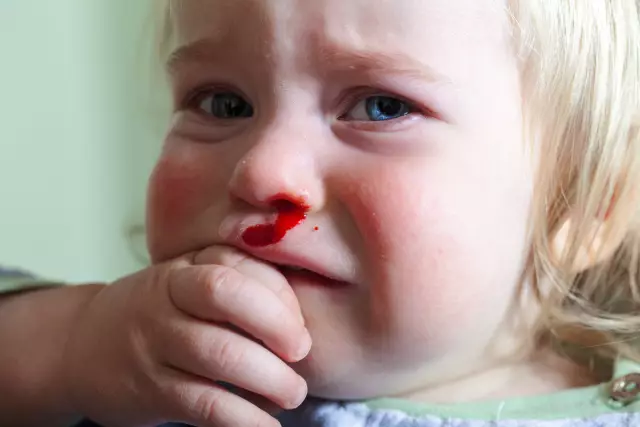
First aid for nosebleeds
As a rule, nosebleeds are not life-threatening, although they look intimidating. However, blood loss can be significant. To prevent this, you need to take the following actions:
- A small cotton swab, bandage, napkin or handkerchief should be inserted into the nostril from which blood flows. The tampon should not hurt;
- The person must be seated, slightly tilting his head down. A common mistake is made by people who, as a first aid for nosebleeds, put a person on their back or make them throw their head back. This can cause blood to drain down the back of the throat;
- Put a cold compress or any cold object on the nose area;
- Slightly compress the wings of the nose.
First aid for internal bleeding

Internal bleeding is difficult to recognize on your own. An indirect sign of it after an injury that has happened is a deterioration in a person's condition, pale skin, cold sweat that has emerged, darkening in the eyes. In this case, blood can be excreted with vomiting or with feces, but not necessarily. If you notice such signs, the following should be done as first aid for internal bleeding:
- With a chest injury, give a person a semi-sitting position, with an abdominal injury - recumbency;
- Provide fresh air supply;
- Apply cold to the stomach or chest;
- Forbid the victim to eat, drink, move and talk;
- Take the person to the hospital immediately.
The last point is relevant not only for internal injuries. In case of massive blood loss, the main point of first aid for bleeding of any kind will be the delivery of the victim to the clinic for the provision of qualified medical care.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.