- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
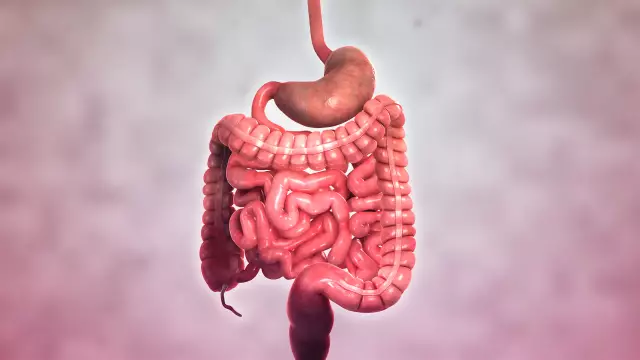
Crohn's disease

Crohn's disease is called a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, which is characterized by the formation of ulcerations on the intestinal mucosa, in the place of which granulomas subsequently grow, adhesions and strictures form, which narrows the intestinal lumen and disrupts its patency. Most often, Crohn's disease affects the small intestine, namely the ileal colon (terminal ileitis, regional ileitis, transmural ileitis), but can occur throughout the intestine (granulomatous enteritis, granulomatous colitis, regional enteritis, etc.). In addition, this disease has multiple extraintestinal manifestations.
Crohn's disease in children has a favorite localization in the duodenum and jejunum, often completely affecting the small intestine (jejunoileitis).
The disease affects men and women to the same extent, the average age of the sick is from 20 to 30 years. Crohn's disease in children usually manifests itself in adolescence - 12-12 years.
At the moment, the disease is considered incurable, the goal of treating Crohn's disease is to maintain the intestines in a state of long-term remission and relieve symptoms during an exacerbation, as well as prevent complications.
Crohn's disease causes
The causes of Crohn's disease are still unclear. Researchers have identified several factors that are important in the mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation, but the starting point in the pathological process is not known. Contributing factors include:
- Failure in the body's immune system. In the mechanism of maintaining inflammation, the autoimmune component plays an important role, that is, the pathological reaction of the immune system to the body's own tissues, as well as to those intestinal microorganisms that are not pathogenic and are necessary for the absorption of food:
- Hereditary predisposition. It is known that in people with Crohn's disease, relatives often suffer from chronic inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis;
- The damaging effect of external factors: unhealthy diet, bad habits, unhealthy lifestyle, infection.
Crohn's disease symptoms
The triad of main symptoms of Crohn's disease includes abdominal pain, chronic diarrhea, and weight loss.
Abdominal pain (abdominal pain) most often manifests itself in the lower right iliac region (Crohn's ileitis), is dull, aching in nature. Sometimes there is no pain, and an unpleasant heaviness and distension is felt in the lower right abdomen.
With Crohn's disease, appetite is often reduced, but even if it is not changed, weight loss is still noted, and often very significant.

In about 30% of patients, Crohn's disease symptoms are disorders of the anus and rectum: rectal fissures, swelling and irritation of the anus, which can cause pain during bowel movements, as well as the discharge of mucus and blood from the anus.
Crohn's disease in children has some features of the course. Children with this disease are characterized by severe weight loss, loss of appetite, sometimes complete, and developmental delay. One of the symptoms of Crohn's disease in children is a rise in temperature to high numbers, often accompanied by joint pain.
The extraintestinal symptoms of Crohn's disease can be misleading in diagnosis. These include: arthritis, arthrosis, cholelithiasis and kidney stones, hepatitis, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, as well as skin manifestations - dermatitis, eczema, rashes and ulcers that do not heal for a long time.
Crohn's disease diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in the presence of characteristic symptoms of Crohn's disease using the following studies:
- Endoscopy. A method consisting in the introduction into the intestine of an instrument consisting of a flexible tube equipped with a video camera and a light source, with the help of which the mucous membrane of the rectum and colon is examined.
- Intestinal fluoroscopy. Methods using a contrast agent are used to detect neoplasms, granulomas and areas of narrowing in the small intestine;
- Biopsy of the intestinal mucosa. The tissue for histological examination is taken during a colonoscopy. In laboratory conditions, changes in the mucous membrane are analyzed;
- Laboratory research methods. General and biochemical analyzes of blood, urine, analysis and bacterial culture of feces, as well as a detailed immunological blood test are performed.
Crohn's disease treatment
As mentioned above, Crohn's disease is one of the currently incurable diseases. However, treatment for Crohn's disease is not only necessary, but must be consistent and constant in order to maintain the patient's normal quality of life. In the absence of adequate treatment, Crohn's disease always has an unfavorable prognosis, as it leads to the development of one or more severe complications, and often not only from the intestines, many of which pose an immediate threat to life.
Treatment of Crohn's disease is conservative, with the development of complications, they resort to surgical intervention.
Drug treatment for Crohn's disease during an exacerbation consists in the use of antidiarrheal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs (hormonal therapy with corticosteroids), antibacterial drugs and drugs that suppress excessive activity of the immune system (immunosuppressants).
During the period of remission, treatment for Crohn's disease is reduced to adherence to a diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Diet for Crohn's disease limits the intake of heavy, rough foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa, as well as fat and milk. An easily digestible and easily digestible food is recommended, with a limited use of fermented milk products, sparing for the gastrointestinal tract. It is extremely important that the diet for Crohn's disease is balanced, as in this disease, anemia and vitamin deficiency are common due to poor absorption of food.

Gastroenterologists recommend an individual selection of dishes: during an exacerbation, a strictly limited diet of the first table, then the gradual introduction of individual products and monitoring the body's response to them. Aggravating foods are completely excluded from the diet. The Crohn's disease diet should be followed continuously, throughout life. It is especially important to follow these rules for Crohn's disease in children, as otherwise the disease can seriously affect the entire physical development of the child.
Complications of Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease can cause serious complications, which include: fistulas, fistulas and diverticula of the intestine, cancer of the intestine and biliary tract, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, intestinal abscesses, intestinal perforation. Most of these complications require urgent surgical attention.
Another group of complications is extraintestinal manifestations, which can reach any degree of severity.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!