- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Intestinal atony
The content of the article:
- Causes
- Forms
- Intestinal atony symptoms
- Features of the course of intestinal atony in the elderly and children
- Diagnostics
- Intestinal atony treatment
- Prevention
- Consequences and complications
Intestinal atony is a pathological condition of the large intestine caused by a low tone of the smooth muscles of the intestinal walls, which leads to a slowdown or complete disappearance of peristaltic movements at a rate of 15-18 contractions per minute. The main manifestation of intestinal atony is frequent prolonged constipation, which is difficult to cope with with conventional laxatives.
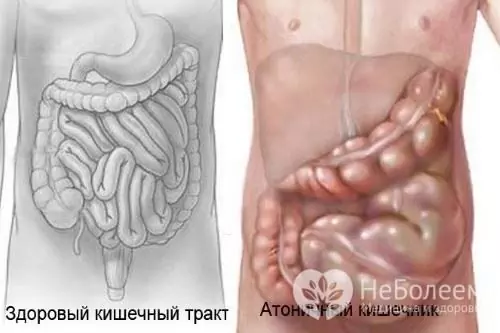
With intestinal atony, there is a low tone of its smooth muscles
Causes
Most often, intestinal atony develops against the background of general muscle weakness and impaired conduction of impulses, under the influence of which there is a reduction in the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall with a sedentary lifestyle, after abdominal operations, long-term adherence to bed rest.
Another common cause of atonic constipation is an unbalanced diet, in particular a lack of fiber and other coarse fiber in the diet against a background of excess calories, as well as non-compliance with the water regime. The systematic lack of fluid intake is compensated by the active absorption of moisture, which leads to the compaction of feces. The formation of a large number of toxic compounds during the putrefactive decay of undigested food debris, in turn, prevents the perception of impulses by muscle cells. Sometimes the movement of feces is limited by mechanical obstacles: diverticula, additional pockets of the large intestine, adhesions, coprolites (fecal stones), neoplasms, squeezing of the rectal wall by other organs, etc.

A common cause of atonic constipation is eating foods that are low in fiber.
Also, a number of factors are involved in the development of intestinal atony, which affect the processes of neurohumoral regulation of the functions of the gastrointestinal tract:
- laxative abuse;
- prolonged fasting;
- taking certain medications (pain relievers, antacids, antidepressants, antiulcer and antiepileptic drugs, etc.);
- prolonged stress;
- diseases of the anorectal region, prompting the patient to postpone going to the toilet;
- bad habits: smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, the use of morphine-type drugs;
- obesity;
- intestinal infections and changes in intestinal microbiocenosis;
- helminthiases (the waste products of some helminths contain substances that inhibit peristalsis);
- endocrine disorders and electrolyte imbalance;
- traumatic injuries or degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine and spinal cord, as well as traumatic brain injury;
- pregnancy. Bowel atony in pregnant women is a side effect of the relaxing effect of progesterone on smooth muscle.
Sometimes the tendency to atonic constipation is hereditary. Cases of intestinal atony in close relatives are a reason to think about prevention.
Forms
Depending on the degree of inhibition of the motor-evacuation function of the large intestine, there are full and partial forms of intestinal atony. The most common partial atony of the intestine is a slowdown and weakening of peristaltic movements, which leads to chronic constipation. Complete intestinal atony is characterized by an absolute absence of peristalsis and paralytic intestinal obstruction.
If acute abdominal pain is observed against the background of stool retention and gas, there is reason to suspect a surgical pathology - diverticulosis, volvulus, intestinal infarction and other pathological conditions that threaten the patient's life. The patient should be taken to a hospital as soon as possible.
Intestinal atony symptoms
A specific sign of intestinal atony is chronic constipation, which is characterized by a long and persistent course. In some cases, the "lazy bowel syndrome" develops, in which the patient is not able to defecate on his own.
In this case, constipation is not only a prolonged stool retention, in which there is no bowel movement for two or more days. The probable symptoms of intestinal atony with regular stool are quite diverse:
- feeling of discomfort and straining during bowel movements;
- insufficient bowel movement;
- streaks of blood in the stool;
- compaction and hardening of feces;
- t. n. sheep feces - the release of a small amount of dense dry excrement.

The main symptom of intestinal atony is chronic constipation.
In the absence of stool for more than three days, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine develops, which prevents the absorption of nutrients. In parallel, the optimal balance of the intestinal microflora is disrupted: the active reproduction of putrefactive bacteria inhibits the vital activity of beneficial microorganisms. As a result, there are signs of indigestion and general intoxication of the body caused by the absorption of toxic products of putrefaction of intestinal contents:
- bloating;
- weakness and apathy;
- irritability and fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- anemia;
- frequent headaches;
- pallor and / or yellowish complexion;
- pain and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, disappearing after a bowel movement;
- purulent rashes on the skin.
Features of the course of intestinal atony in the elderly and children
Intoxication of the body with prolonged constipation is especially pronounced in children and the elderly: it is possible that the body temperature rises to 37 ° C or more, the appearance of nausea and vomiting. In the elderly, blood pressure rises sharply.
Intestinal atony is widespread in older age groups. The tendency towards muscle atrophy is one of the manifestations of aging, in addition, older people tend to lead a sedentary lifestyle, and dietary options for the elderly are limited. In particular, it is not recommended to increase your fiber intake without consulting your doctor, as in case of chronic constipation, eating large amounts of coarse fiber foods can worsen the patient's condition.
Atonic constipation, first manifested in old age, is sometimes the result of pathological lengthening of the sigmoid colon or sclerotic changes in the mesenteric arteries, which can lead to mesenteric thrombosis. To exclude surgical and vascular pathology with intestinal atony in the elderly, consultation with a phlebologist and a proctologist is required.

In a child, atonic constipation may be associated with weaning or stress
In young children, atonic constipation often occurs with a sharp change in diet during weaning, as well as on psychogenic grounds. In this case, intestinal atony must be differentiated from intestinal obstruction and congenital anomalies of the structure of the large intestine.
To prevent "lazy bowel syndrome" prescribe laxatives and enemas to children should be very careful and only as directed by a doctor. Irritants are contraindicated in young patients; usually prescribe osmotic drugs based on lactulose and glycerin suppositories that stimulate reflex bowel movements.
Diagnostics
Intestinal atony is diagnosed by a therapist or gastroenterologist based on anamnesis, study of the patient's diet and lifestyle, and clinical presentation. To identify the reasons for the weakening of the tone of the intestinal walls and to develop the most effective therapeutic strategy, a comprehensive examination of the intestine using instrumental and laboratory techniques is necessary.
The most informative method for examining the motor function of the large intestine is irrigoscopy - contrast radiography of the colon after a barium enema, which qualitatively visualizes hard-to-reach areas of the intestine that are inaccessible for colonoscopy (folds of the mucous membrane, bends of the colon and sigmoid colon, etc.). If perforation or obstruction of the colon is suspected, a water-soluble contrast agent is injected instead of barium suspension. After emptying the intestines, a study of the relief of the mucous membrane of the colon is carried out. If necessary, oxygen is injected into the intestinal lumen for better visualization of the inner wall of the intestine.
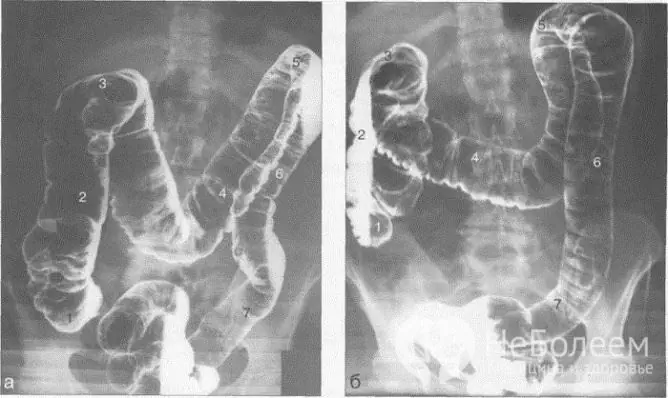
Irrigoscopy is the most informative method for diagnosing intestinal atony
Endoscopic examination of the large intestine with biopsy sampling is advisable for differential diagnosis with oncopathology, Crohn's disease and other diseases characterized by specific changes in the intestinal epithelium.
A detailed analysis of feces (coprogram) provides comprehensive information about the state of the secretory-resorptive function of the intestine and the hepatobiliary system. With severe symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis, bacteriological culture of feces is shown; to exclude parasitic invasion, feces are tested for helminthiases and protozoal diseases.
Intestinal atony treatment
The first step to restoring normal bowel motility should be nutritional correction. In case of atonic constipation, the study of the diet and lifestyle of the patient is shown therapeutic diet No. 3: the basis of the diet is dairy-vegetable, while it is necessary to exclude astringent products that stimulate gas formation from the menu, and also reduce the calorie content of dishes. First of all, the ban includes rich soups, meat and fish smoked meats and canned food, mushrooms, legumes, whole milk, hard-boiled eggs, strong tea and coffee, as well as some fruits and berries - dogwood, blueberries, pears, pomegranates, cabbage, radishes, onion and garlic. To fill the deficiency of fiber and pectin substances, the menu includes wheat bran, wholemeal bread, buckwheat porridge, fresh fruits and vegetables, vegetable oils and melons. Especially useful are apricots, plums, melons, apples,rhubarb and seaweed, which have a mild laxative effect.

Diet correction is the first step to restoring intestinal motility
In addition, you will have to seriously limit the consumption of instant carbohydrates - chocolate, white bread, baked goods and confectionery. It is recommended to replace sweet carbonated drinks and industrial juices with water, compote and fruit drinks; in this case, you should drink at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day. The normalization of peristalsis is also facilitated by a fractional diet with meals at the same time.
Increasing physical activity will help to quickly improve stool in sedentary patients. A good effect on intestinal atony is given by sports walking, swimming, dancing and yoga, as well as performing special exercises for the muscles of the abdominal wall and massage of the abdomen.
Drug treatment of intestinal atony involves the use of only mild laxatives. Preference is given to osmotic and prokinetic drugs and choleretic agents. According to indications, cholinesterase inhibitors can be included in the therapeutic regimen; with severe abdominal pain, antispasmodics are additionally prescribed. In order to prevent intestinal dysbiosis, the use of enemas for intestinal atony is not recommended; it is permissible to use oil candles and microclysters, which facilitate the evacuation of feces.
In case of severe intoxication, it is advisable to carry out detoxification therapy and deep lavage of the intestines through hydrocolonotherapy, subaquatic baths and intestinal irrigation. If intestinal obstruction, neoplasms, and anatomical abnormalities of the intestine are detected, surgical intervention may be required.
Prevention
Prevention of intestinal atony is not difficult. It is enough to lead an active lifestyle, control body weight, give up bad habits, avoid stress as much as possible and monitor nutrition, avoiding deficiency of ballast substances, vitamins and minerals. At the same time, it is important to eat food in small portions 5-6 times a day, adhere to the optimal drinking regimen and avoid large intervals between meals.
In order to prevent intestinal dysbiosis, you should not take antibiotics without talking to your doctor. It is advisable to teach children to go to the toilet at the same time and not suppress the urge to defecate out of false shame in school or kindergarten.
Consequences and complications
Persistent constipation caused by intestinal atony seriously impairs the patient's quality of life. Patients become lethargic and apathetic, or, on the contrary, irritable and touchy, the patient's emotional lability prevents full communication and social life. The patient's appearance also leaves much to be desired: the complexion worsens, rashes on the skin and bad breath appear, and skin diseases may worsen.
Putrefactive processes caused by coprostasis disrupt the balance of intestinal microflora and suppress the immune system, provoke allergic and atopic conditions, and due to a violation of the absorption process in the intestine in persons prone to atonic constipation, vitamin deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia are often noted. In the absence of adequate treatment against the background of intestinal atony, intestinal obstruction may develop, causing severe intoxication of the body.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!