- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Which doctor to see for high blood pressure, or which doctor treats hypertension
The content of the article:
- Which doctor treats hypertension
- What symptoms do you need to see a doctor
- Blood pressure measurement rules
- What is arterial hypertension and why does it occur?
- Video
Which doctor should i go to for high blood pressure? This question worries many people, because the prevalence of arterial hypertension has now increased significantly, in addition, there is a significant "rejuvenation" of the disease.
In order to prevent the aggravation of the disease and not to miss the development of complications, patients should promptly seek qualified medical help.

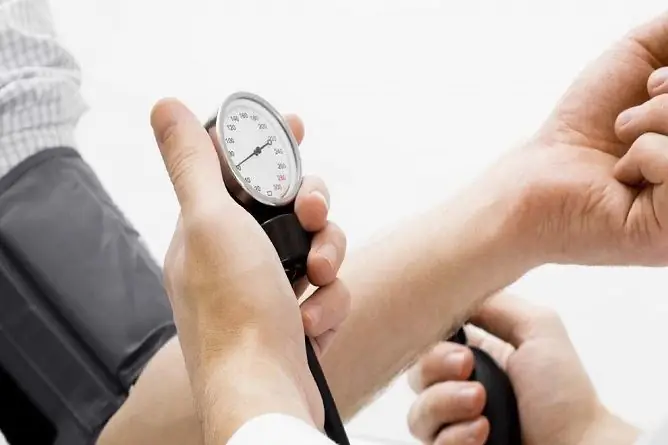
When signs of hypertension appear, you should first of all contact a therapist
Which doctor treats hypertension
If the patient notes the periodic appearance of symptoms of arterial hypertension, it is necessary to seek the advice of a therapist or cardiologist. These specialists deal with the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension. To clarify the diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen, the doctor will prescribe mandatory tests and instrumental studies (if necessary).
Laboratory research:
- complete blood count - will eliminate anemia, acute or chronic inflammation, increased allergic readiness;
- biochemical blood test - will give an idea of the performance of the kidneys, liver, blood glucose, cholesterol, thyroid hormones. With the help of this study, the doctor will be able to assess the functional state of the organs most often suffering from increased blood pressure (blood pressure).
Instrumental research:
- measurement of blood pressure. Blood pressure for the diagnosis of "arterial hypertension" must be recorded at least twice, with 2-3 measurements taken with an interval of 7-10 minutes, with each treatment. Repeated measurement can rule out "white coat hypertension" when, as a result of excitement at the hospital visit, the patient shows high blood pressure. Also, a 2 or 3-fold pressure measurement eliminates the error that occurs during physical or psycho-emotional stress (walking from a bus stop to a hospital, going up to the desired floor of a polyclinic, waiting for an appointment, etc.);
- chest x-ray. It will allow you to see left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy - one of the most common complications of hypertension;
- ECG. Electrocardiography will demonstrate the main characteristics of the heart: the rhythm and frequency of the heartbeat, the presence of disturbances in the conduction of excitation through its tissues. In addition, the ECG allows you to identify foci of ischemia and dystrophy with malnutrition of the myocardium, valve defects, signs of overload and congestion in the circulatory system;
- daily blood pressure monitoring. Allows you to establish a connection between pressure rises with the load or the impact of other provocateurs, reflects the distribution of "jumps" in blood pressure throughout the day;
- daily (Holter) ECG monitoring. A portable apparatus with electrodes is fixed on the patient's body for 24 hours. At regular intervals, it is activated and starts the process of recording ECG data. The obtained results most reliably confirm the presence of complications of hypertension from the circulatory system;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. One of the most common causes of secondary hypertension is renal neoplasms that affect the functioning of the pressure control system located in them. At the same time, ultrasound examination will allow to exclude or confirm this pathology with almost 100% certainty;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Quite often, the cause of these problems is an over-functioning thyroid gland. Ultrasound will help establish whether there are prerequisites for the development of hyperthyroidism;
- Ultrasound of the heart. It allows you to reliably, with an accuracy of a millimeter, determine the degree of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy and the thickness of the walls of other chambers, assess the ejection fraction of the heart, the coordination of all its structures, see the existing pathologies of the valves and cardiac chords, and evaluate all parameters of cardiac blood flow.
After receiving the results of all studies, the therapist, if necessary, will additionally appoint specialist consultations. A visit to a neurologist, ophthalmologist, psychotherapist is usually required. Based on the results, a detailed diagnosis is formulated with an indication of complications and possible risks, a treatment regimen is determined or the issue of hospitalization in a hospital for the purpose of additional examination is resolved.
What symptoms do you need to see a doctor
Consultation of a therapist is necessary if the following symptoms are systematically recorded for a long time:
- headache or feeling of tightness (like a hoop), episodes of spontaneous dizziness;
- flickering of luminous points in front of the eyes, short-term transient deterioration of vision, a feeling of a veil;
- sudden attacks of palpitations, tachycardia;
- tinnitus;
- hot flashes, fever, redness of the skin of the face, neck and décolleté during physical or psycho-emotional stress;
- episodes of sweating;
- stitching pains in the left side of the chest;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- memory impairment, decreased vitality, feeling of weakness, "stale head", intolerance to habitual stress.
The listed signs are most common in adult patients. In a school-age child or adolescent, such symptoms can also occur in the norm, which is due to the instability of the functioning of the nervous and vascular regulation of a growing organism.
Blood pressure measurement rules
To find out whether there is a need to contact a specialist about an increase in blood pressure, it is necessary to take measurements at home in accordance with a certain algorithm. Violation of the methodology can provoke a significant error.
It is necessary:
- Before starting the procedure (approximately 30 minutes), refrain from intense physical activity, smoking, taking tonic drinks and alcohol.
- Prepare the device and all its accessories, empty the air bellows from the cuffs, then tighten the valve tightly.
- Take a comfortable position, while the arm with the cuff should be located at the level of the middle of the chest.
- Put on an overlay on the shoulder, just above the bend of the elbow (the exact location is indicated on the accessory itself as a pictogram), avoiding excessively tight or excessively loose overlap: the index finger should fit freely between the skin and the inner surface of the cuff.
- Under the edge of the accessory, fix the head of the phonendoscope (in the place of the most distinct pulsation), pump up the cuff and measure.
What is arterial hypertension and why does it occur?
Arterial hypertension is a systematic increase in blood pressure over 140/90 mm Hg. Art. Normally, its value ranges from 110/65 to 129/84 mm Hg. Art. In modern medicine, an unambiguous opinion is accepted: blood pressure exceeding 130/85 mm Hg. Art. is not normal. This threshold demonstrates the readiness of the body to develop hypertension, this condition is called prehypertension.

Normal pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. with the possibility of a slight deviation in one direction or another
High blood pressure can accompany any disease, being one of the symptoms, or it can develop independently, without any connection with another pathology. In the first case, hypertension is called secondary, or symptomatic, in the second - primary or essential.
Treatment and diagnosis of secondary hypertension is usually straightforward. In this case, complex therapy of the underlying disease leads to the normalization of blood pressure figures.
With essential hypertension, finding the cause is sometimes not possible. At the same time, a breakdown of the internal regulation mechanisms leads to a systemic increase in pressure. It is extremely difficult to isolate and eliminate its trigger factor.
A number of risk factors have been identified, under the influence of which the likelihood of developing hypertension increases significantly.
The main provocateurs:
- Overweight. With an increase in weight by 10 kg, the pressure increases by an average of 10 mm Hg. Art. A significant deterioration in well-being is explained not only by hypertension, but also by excessive stress on the joints, spine, and cardiovascular system.
- Smoking. Promotes the breakdown of receptors, which read information about the magnitude of pressure in the vascular bed and transmit it to the vasomotor center. Distortion of data leads to inadequate functioning of the higher centers of regulation.
- Alcohol abuse. In this case, episodes of hypotension that occur with the use of small doses of alcohol are replaced by an increase in blood pressure with an increase in the amount of ethanol. There is a colossal load on the heart and blood vessels. In addition, the products of C2H5OH metabolism have a destructive effect on the circulatory system.
- Sedentary lifestyle. A detrained heart, functioning in a low load mode, does not cope well with stress and various pathological influences. Systematic physical activity allows you to keep the myocardium and blood vessels in good shape, making them less vulnerable.
- Age over 45.
- A diet high in animal fats. The body accumulates high concentrations of cholesterol, which accumulates on the walls of the arteries. Vessels lose elasticity, the ability to actively relax and contract.
- Excessive salt intake. NaCl promotes fluid retention in the body, which increases the volume of circulating blood.
- Chronic psycho-emotional overload, unrealized stress. It is especially recommended to carefully monitor blood pressure figures for people who are hot-tempered, emotionally labile, prone to violent reactions: they are the ones who have the greatest risk of developing arterial hypertension.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Olesya Smolnyakova Therapy, clinical pharmacology and pharmacotherapy About the author
Education: higher, 2004 (GOU VPO "Kursk State Medical University"), specialty "General Medicine", qualification "Doctor". 2008-2012 - Postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty "Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacology"). 2014-2015 - professional retraining, specialty "Management in education", FSBEI HPE "KSU".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.