- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
What makes the tongue hurt
The tongue hurts as a result of the following disorders:
-

Why does the tongue hurt: the main reasons Injuries;
- Inflammatory processes and infections;
- Neoplasms;
- Other pathologies of various origins.
Pain can be associated not only with direct lesions of the tongue, but also with diseases of neighboring organs - the larynx, pharynx, lymph nodes, tonsils and salivary glands.
Why does the tongue hurt with injuries
In traumatology, acute and chronic injuries are distinguished, in which the tongue hurts. Acute trauma to the tongue is a single effect of mechanical, thermal, chemical or other factors, leading to a violation of the structure, anatomical integrity of tissues and physiological functions of an organ. The tongue is protected by the teeth and jaws, so acute injuries are relatively rare. The following situations lead to them:
- Severe trauma to the face with crushing of tissues;
- A blow from below to the lower jaw, under the chin;
- Damage to the tongue with instruments during surgery and dental procedures;
- Epileptic seizure;
- Injury to the tongue with sharp objects, for example, while eating.
With minor injuries, the pain goes away on its own after a while, and with severe injuries, surgical intervention is necessary.
Chronic trauma to the tongue is a permanent micro-injury, as a result of which the tongue hurts, grows numb and swells a little, and its mucous membrane turns red. Chronic injury can be caused by the following:
- Broken teeth with sharp edges in the mouth;
- Wrong bite;
- Incorrectly installed implants, dentures or orthodontic structures;
- Using an overly sharp tongue scraper;
- An increase in the size of the tongue, for example, with diseases of the thyroid gland.
Mechanical damage also includes piercings. Why does the tongue hurt after piercing:
- Inflammatory process as a result of infection;
- Allergy to the material from which the bar is made;
- Nerve damage during manipulation.
To avoid such complications, you should use the services of professionals. In these cases, the procedure is either completely painless, or the puncture site heals quickly. If, after piercing, the tongue hurts for a long time, then the surgeon should prescribe treatment.
Pain and burning sensation in the tongue can provoke smoking due to the carcinogenic substances contained in tobacco smoke. During combustion, toxic components such as carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, acetone, benzene, acetaldehyde and much more are released.
Superficial burns are quite common, as a result of which the tongue hurts and grows numb. You can get burned by hot food or drinks, as well as by drinking low-quality alcohol or inhaling corrosive fumes at work. Burns, as a rule, go away on their own after a short time. However, in cases where they are combined with burns to the oral cavity and esophagus, you should immediately contact the trauma center.
Why does the tongue hurt during inflammation
Inflammatory diseases in which the tongue hurts can also spread to the tonsils, pharynx, larynx, salivary glands, and lymph nodes. There are several main inflammatory diseases localized in the area of the tongue:
- Glossitis;
- Submandibular lymphadenitis;
- Inflammation of the salivary glands;
- Salivary stone disease;
- Tonsillitis;
- Pharyngitis;
- Laryngitis.
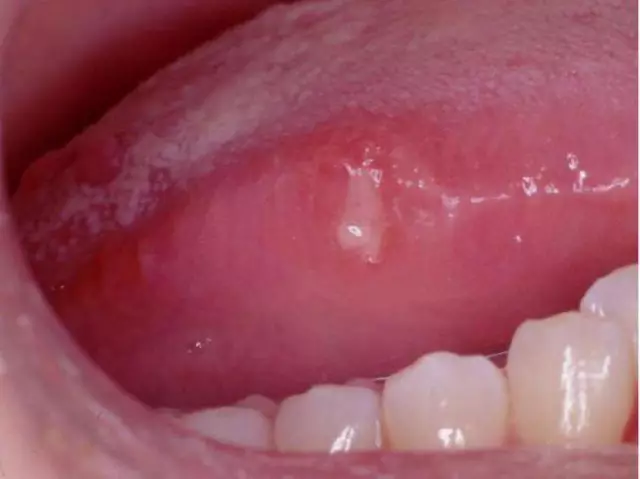
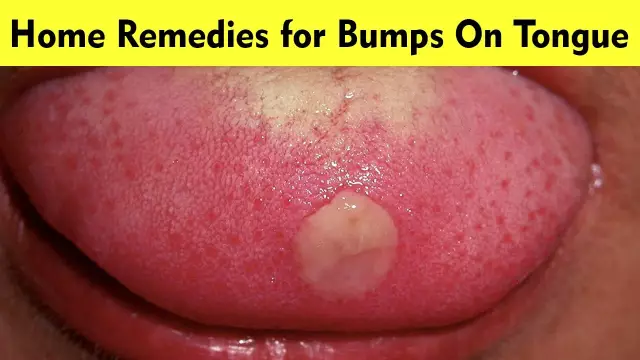
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue with different etiology and symptoms. Superficial glossitis mainly accompanies stomatitis and affects only the mucous membrane of the tongue, causing redness and swelling. This form of glossitis develops due to inadequate oral hygiene, smoking and alcohol consumption, as well as with various lesions of the teeth and gums.
Catarrhal glossitis also appears on the surface of the tongue. Compaction and swelling of this organ is observed, its mobility is sharply deteriorated. The tongue hurts constantly, this is accompanied by a burning sensation, the appearance of a white bloom, increased salivation and a violation of taste. A characteristic feature of catarrhal glossitis is the rejection of areas of the mucous membrane of the tongue, in place of which there are spots of bright red color.
Deep glossitis develops in the tissues of the tongue and proceeds as a purulent inflammation - phlegmon or abscess. The pain begins at the base of the tongue and can spread following the purulent process into the submandibular lymph nodes. At the same time, the general state of health worsens - the body temperature rises, headaches appear. In such situations, surgery is required.
Ulcerative glossitis is characterized by the appearance on the tongue of a gray plaque with an unpleasant odor, when removed, small bleeding ulcers remain on the mucous membrane. Pathology is caused by fungi and other pathogenic microflora.
With submandibular lymphadenitis, it hurts under the tongue due to inflammation and swollen lymph nodes. The disease can be caused by chronic tonsillitis, pulpitis or caries, as well as infectious gum disease.
The submandibular and sublingual salivary glands are located in the region of the root of the tongue, therefore, with their inflammation, just like with lymphadenitis, pain is localized under the tongue and intensifies when swallowing. The inflamed gland can be found by touch under the lower jaw.
Salivary stone disease is a rather rare pathology. When stones form in the submandibular and sublingual glands, the tongue does not hurt very much and only when a large amount of saliva is released, for example, from spicy food.
Sore throat causes pain at the base of the tongue and throat, which is worse when swallowing. Runny nose and cough, as well as fever, may disturb. Examination of the throat reveals enlarged scarlet tonsils with a bumpy surface, sometimes covered with plaque. Inflammation of nearby lymph nodes increases pain at the root of the tongue. A cavity with pus may form in the tonsils. This is the most severe complication of tonsillitis - a paratonsillar abscess, which is manifested by severe pain at the base of the tongue, fever and a significant deterioration in general well-being.
Pharyngitis and laryngitis can sometimes cause pain at the base of the tongue. Both of these conditions are characterized by malaise, fever, sore throat, and dry or moist coughs. If the inflammation covers the back of the larynx, then there is a pain in the throat and tongue during swallowing.
Pain in the tongue with tumors
If the tongue hurts sharply and strongly, then treatment should be started as soon as possible, since a diagnosis of a malignant tumor is possible. Cancer of the tongue is dangerous in that it has symptoms similar to glossitis, which are often ignored for this reason.

With cancer, the following clinical picture is observed:
- Lateral seal on the tongue;
- Redness and white spots on the mucous membrane;
- Bad breath;
- An increase in the submandibular lymph nodes;
- Bleeding painful ulcers on the lining of the tongue.
General symptoms include weakness, a slight increase in body temperature, drowsiness, and lethargy.
YouTube video related to the article:
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.