- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Increased temperature with bronchitis in children and adults
The content of the article:
- What is the temperature with various forms of bronchitis
- Treatment of bronchitis with fever
- General information about bronchitis
- Video
Fever with bronchitis is one of the most common symptoms, but it is not always observed. What temperature for bronchitis depends on the cause and form of the disease, as well as the state of the patient's immunity. To a greater extent, increased body temperature is characteristic of acute bronchitis. Its increase is a reaction of the body aimed at curbing the spread of the infectious agent.
The temperature in children with bronchitis rises more than in adults, this is due to the peculiarities of the immune system of the child's body. Nevertheless, acute bronchitis without an increase in body temperature in adult patients is quite rare; it may indicate an allergic nature of the disease or reduced immunity.

With an increase in temperature, acute bronchitis of viral etiology usually occurs
With a prolonged increase in body temperature to 39 ° C and above, the patient may experience disorders of the cardiovascular, central nervous system, and kidneys. If the fever persists for more than 7 days, this may indicate the development of complications.
What is the temperature with various forms of bronchitis
How many days the temperature lasts for bronchitis depends on the infectious agent, the form of the disease, the patient's age, the state of his immune system, and also on the adequacy of the treatment.
Most often, the causative agents of infectious bronchitis are viruses, much less often - bacteria. Bronchitis caused by microscopic fungi is rare, usually in immunocompromised patients.
Typically, bronchitis develops as a complication of acute respiratory viral infections. Body temperature with bronchitis of viral etiology is rarely high, usually it does not exceed 37.5 ° C (degrees Celsius). With bronchitis caused by the influenza virus, the temperature can reach 38 ° C. It is accompanied by the usual symptoms for such a condition - weakness, aching muscles and joints, headache, and lasts no more than 2-3 days. If an adenovirus is the infectious agent, fever may persist for about a week. In the case of complications, it is increased for a long time, two weeks or more.
With bronchitis of bacterial etiology, the patient's body temperature is also kept within the subfebrile range, the residual (about 37 ° C) can persist for several weeks. When taking antibiotics, the patient's condition usually returns to normal within 3-4 days. What does it mean if it doesn't happen? This may mean an incorrect identification of the pathogen (non-bacterial pathogen), the wrong choice of the drug, the development of complications.
Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. In acute bronchitis, an increase in temperature occurs from the first days of the disease. In the chronic form of the disease, the temperature rises during the exacerbation, usually slightly, to subfebrile values. This condition persists for no more than 5 days.
Bronchitis can be simple or obstructive. With obstructive bronchitis, an increase in body temperature occurs on the 2-3rd day after the onset of dry cough attacks, it can reach febrile values (38 ° C and above) and last for 3-7 days.
With allergic bronchitis, an increase in body temperature does not occur, in rare cases it rises slightly (up to 37 ° C).
With plastic bronchitis (a rare pathology in which the airways are clogged with large casts of the bronchi), the temperature sometimes does not rise, but, on the contrary, drops to 36 ° C and below.
Treatment of bronchitis with fever
Antipyretic drugs are prescribed for children with bronchitis to bring down temperatures exceeding 38 ° C. The temperature for bronchitis in adults is knocked down when it reaches 38.5 ° C or more.
When using the same antipyretic medication, 6-8 hour intervals must be observed between doses. If during these intervals the body temperature rises to high numbers, additional diagnostics or drug replacement may be required.
In addition to antipyretic drugs, if necessary, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mucolytic, expectorant drugs can be prescribed. Anti-infectious drugs are selected depending on the causative agent of the disease. If viruses are the causative agent, antiviral drugs can be used; antibiotics are used for bronchitis of bacterial etiology. In case of breathing difficulties, oxygen therapy can be used, which helps to combat oxygen deficiency in the tissues.
How long to take medicines for bronchitis is decided by the doctor, whose recommendations must be strictly adhered to. Do not change the dosage, do not stop treatment, even if the patient's condition improves, you need to undergo a full course of therapy.
The main treatment for bronchitis can be supplemented by traditional medicine. At elevated body temperature, you can use tea with dried raspberries, cranberries, infusion of chamomile flowers, linden blossom. It is recommended to drink mineral water, diluted juices, fruit drinks, green tea, especially since it is recommended to increase the drinking regime.
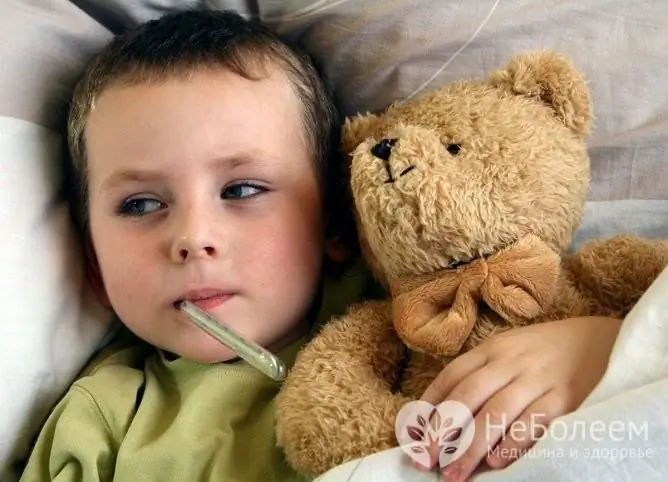

In children, the temperature with bronchitis is usually higher than in adults
You can reduce the heat with rubdowns or compresses.
Any methods of lowering body temperature with bronchitis should be used only after consulting your doctor.
Uncomplicated acute bronchitis is cured in 10-14 days, chronic bronchitis requires more prolonged therapy, sometimes several courses.
General information about bronchitis
The main symptom of bronchitis is a cough, which is dry at first and then becomes moist when a person begins to sputum. When listening to breathing, wheezing is usually detected. The sputum can be transparent, or, depending on the admixture of blood or mucus, acquire a brownish, greenish, yellow tint. In patients at the initial stage of the disease, there is a sore throat, discomfort along the trachea, discharge from the nasal cavity, nasal congestion. Patients complain of deterioration in general condition, weakness, lethargy, hoarseness, chills, fever, chest pain, difficulty breathing.
There are many reasons why bronchial inflammation can occur. The disease can have an infectious and non-infectious etiology. Most often, bronchitis is caused by influenza A and B viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, rhinoviruses. Staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae are isolated from bacteria that can be infectious agents in bronchitis. Atypical bronchitis is caused by mycoplasmas, chlamydia.
Risk factors for the development of bronchitis are genetic predisposition, smoking, inhalation of chemicals, hypothermia, unfavorable environmental conditions, harmful working conditions, as well as decreased immunity due to chronic diseases.
Diagnosis requires physical diagnostics, laboratory tests of blood and sputum, in some cases - X-ray examination, bronchoscopy. Differential diagnosis is carried out with pneumonia, aspiration of foreign bodies, tuberculosis.
In the absence of therapy or improper treatment of bronchitis, the risk of developing complications increases - pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary emphysema, bronchial asthma, pulmonary hypertension, etc.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.