- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to get rid of edema in late pregnancy
The content of the article:
- Why does edema occur during pregnancy?
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Leg swelling in late pregnancy: what to do
- Compression of the pelvic veins
- Varicose veins
- Diseases of the heart and kidneys
- OPG-gestosis
- How to get rid of edema at home in late pregnancy
- Complications and prognosis
- Prevention
- Video
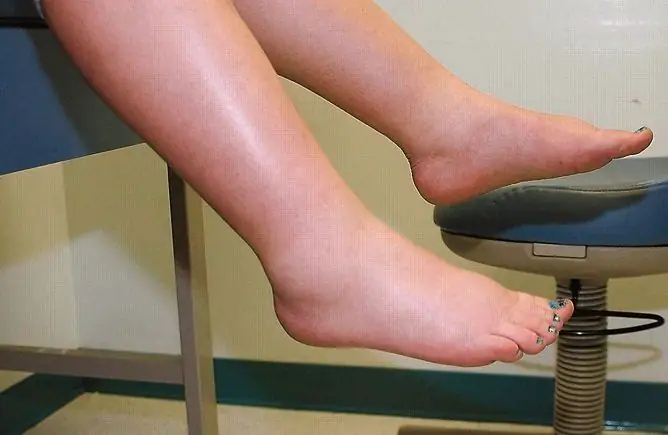
In the third trimester of pregnancy (28-40 weeks), women often face the problem of swelling of the arms and legs. It can arise under the influence of various reasons, so there is no single answer to the question of how to get rid of edema during pregnancy in the late stages.

In late pregnancy, edema is common, but not always requires treatment
Why does edema occur during pregnancy?
The appearance of edema is associated with excessive accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space. This process can be due to both physiological and pathological reasons:
- Compression of veins by an enlarged uterus. As the fetus grows and develops, the uterus rapidly enlarges. It begins to compress the pelvic veins and the outflow of blood from the lower extremities deteriorates. Stagnation of blood, in turn, promotes the sweating of plasma through the vascular walls into the intercellular space of soft tissues, which causes their edema.
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities. This disease is often exacerbated or is first diagnosed during pregnancy. This is due to stagnation of blood in the vessels of the legs.
- Chronic kidney disease. During pregnancy, the load on the kidneys increases significantly, which is associated with an increase in the volume of circulating blood in the body of the expectant mother by about 20%. In addition, a pregnant woman has a weakening of the ligamentous apparatus that supports the kidneys in the correct anatomical position. This becomes the cause of the pathological mobility of the urinary organs, impaired outflow of urine from the calyx-pelvis system through the ureters into the bladder. Against the background of chronic renal pathology, the excretory function of the kidneys deteriorates, and they cannot fully cope with the increased loads. Excess fluid accumulates in the body and edema appears.
- Heart defects. During pregnancy, complex changes occur in the circulatory system (the volume of circulating blood increases, the placental "third" circle of blood circulation appears, the contractile activity of the myocardium increases). These factors increase the risk of heart disease decompensation and the development of heart failure, the first symptom of which may be swelling of the lower extremities and fingers.
- OPG-gestosis. A complication of the second half of a normal pregnancy, characterized by the occurrence of edema, increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine (proteinuria). The reasons for the development are currently not fully understood. OPG-gestosis is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of both a pregnant woman and her unborn child.
Symptoms
Edema in pregnant women at a later date is always combined with other symptoms, the analysis of which in many cases allows a correct diagnosis to be made:
| Cause of occurrence | Clinical manifestations |
| Compression of the pelvic veins by an enlarged uterus | The general condition of the woman does not suffer. Swelling of the feet and legs is noted at the end of the day and disappears after a night's rest. There are no changes in urine tests. Blood pressure does not rise. |
| Varicose veins of the lower extremities | Patients note a feeling of heaviness in the legs, pain along the affected veins, swelling. Often, convulsions occur at night. With varicose veins, only one leg can swell. |
| Chronic glomerulonephritis |
From the early stages of pregnancy, urinalysis reveals proteinuria of varying severity. Some pregnant women have anemia, increased blood pressure, hematuria, and pain in the lumbar region. With a significant violation of the renal excretory function, swelling of soft tissues appears, the rate of glomerular filtration decreases and azotemia increases. |
| Heart defects | Increased fatigue, heaviness in the legs, swelling of the feet and legs, cyanotic skin, shortness of breath, cardiac arrhythmias. |
| OPG-gestosis | The first manifestation of the disease is the appearance of initially latent, and then overt edema. The general condition worsens, there are complaints of weakness, drowsiness. In the absence of treatment, after 1-2 weeks, the woman's blood pressure begins to rise, and protein appears in the urine. Attachment to the described symptoms of such signs as headache, visual impairment, nausea and vomiting indicate the development of preeclampsia. If a woman does not receive urgent medical attention, there is a high risk of developing eclampsia - a seizure, after which the patient falls into a coma. |
Diagnostics
If puffiness appears, a pregnant woman should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, measure blood pressure and prescribe the examination necessary in each case, which may include:
- general urine analysis;
- test of Nechiporenko;
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- biochemical blood test to determine the concentration of glucose, total protein, urea, creatinine;
- Rehberg's test;
- USDG of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- ECG and Echo-KG.
If necessary, the woman is referred for a consultation with a nephrologist, cardiologist or vascular surgeon.
Leg swelling in late pregnancy: what to do
Therapy for puffiness in pregnant women should be aimed at the underlying pathology that caused its appearance.
Compression of the pelvic veins
For leg edema associated with compression of the enlarged uterus of the pelvic veins, no treatment is required. To eliminate this phenomenon, it is enough:
- Observe the regime of alternation of work and rest.
- Lead an active lifestyle (swimming, walking, Pilates, yoga), provided there are no contraindications.
- Adhere to the principles of healthy eating.
Several times a day, it is recommended for a pregnant woman to take a horizontal position for 15-20 minutes with raised legs.

Sometimes, to get rid of edema, it is enough to lie down for 20 minutes with your legs raised.
Varicose veins
In case of varicose veins of the lower extremities, the doctor may recommend wearing compression hosiery, local application of Heparin ointment or Lyoton gel.
Diseases of the heart and kidneys
Treatment of edema caused by diseases of the heart or kidneys is carried out jointly by a doctor of the appropriate profile and a gynecologist. With the decompensation of a heart defect, the issue of abortion is resolved. Moreover, in most cases, natural childbirth is contraindicated.
OPG-gestosis
Patients with OPG-gestosis are hospitalized in the department of pathology of pregnancy (for preeclampsia and eclampsia - in the intensive care unit).
Therapeutic measures are aimed at normalizing:
- hemostasis;
- water and electrolyte balance;
- permeability of vascular walls
- blood pressure;
- metabolic processes;
- blood rheology;
- functions of the central nervous system.
If, despite the ongoing therapy, the patient's condition does not improve or she develops an attack of eclampsia, then urgent delivery is necessary.
How to get rid of edema at home in late pregnancy
Treatment of puffiness during pregnancy at home is possible only if they are caused by:
- compression of the pelvic veins by an enlarged uterus;
- varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- dropsy (the initial stage of OPG-gestosis).
In this case, a woman should carefully follow all the recommendations received from her doctor. In agreement with him, alternative methods of treatment can also be used:
- Foot baths with sea salt. Pour 2-3 liters of warm water into a basin (temperature not higher than 37 ° C) and dissolve 4 tablespoons of sea salt in it. Baths relieve swelling well, feeling tired legs. The procedure is carried out for 15-20 minutes 2-3 times a day.
- Decoctions of herbs with a sedative effect (motherwort, valerian). They normalize the activity of the central nervous system, relieve the negative effects of stressful influences, and help to normalize night sleep.
- Rosehip infusion. Contains substances that reduce the permeability of the vascular walls, due to which it has an anti-edema effect.
Complications and prognosis
Complications and prognosis for puffiness in late pregnancy are determined by the cause of their occurrence. So, when the pelvic veins are compressed by the enlarged uterus, the prognosis is favorable. Varicose veins can be complicated by the occurrence of trophic ulcers.
The progression of OPG-gestosis can cause a number of serious complications:
- development of HELLP syndrome;
- placental insufficiency;
- placental abruption;
- death of the fetus and / or pregnant woman;
- pulmonary and / or cerebral edema;
- hemorrhage in the brain and internal organs (kidneys, pancreas, intestines, adrenal glands, intestines);
- acute renal failure;
- acute heart failure;
- retinal disinsertion.
Prevention
Prevention of leg edema in late pregnancy includes:
- maintaining an active lifestyle (walking, gymnastics, swimming, yoga), provided there are no contraindications;
- a full night's sleep lasting at least 8-9 hours;
- observance of the regime of work and rest;
- balanced diet;
- timely detection and active treatment of any gynecological and extragenital diseases.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.