- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to get rid of sweating and unpleasant foot odor: effective methods
The content of the article:
- Sweating functions
- Trigger factors for excessive leg sweating
-
Methods for eliminating leg hyperhidrosis
- Hygiene aspects
- Selection of suitable shoes
- Requirements for hosiery
-
Therapeutic methods
- Formagel
- Pasta Teymurov
- Borozin
- Dry dry
- Anticholinergics
- Botulinum toxin therapy for hyperhidrosis
- Folk remedies in the therapy of sweating feet
- Video
How to get rid of sweaty feet and an unpleasant smell - this question is most often of interest to men, but it can also bother women. Sweating (or hyperhidrosis) of the legs is a common problem that affects one in three people.
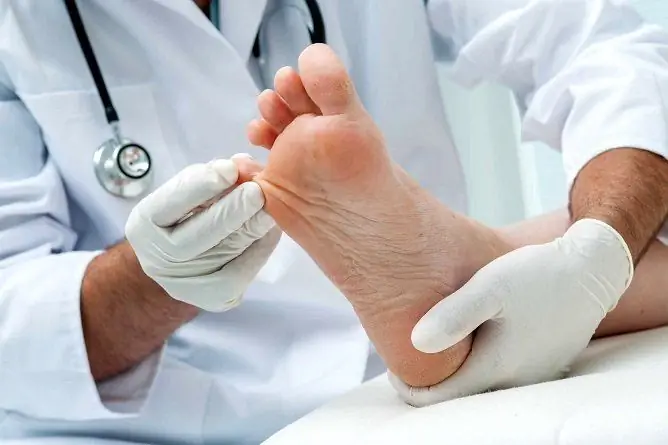
Excessive sweating of the feet is a fairly common problem
Excessive sweat on the legs leads to discomfort, the appearance of an unpleasant odor and, if simple care rules are not followed and a number of other factors are present, fungal, bacterial and other lesions of the lower extremities.
Sweating functions
Sweating is a natural process necessary to maintain a stable body temperature.
In addition to the thermoregulatory function, perspiration has other important functions in the human body:
| Function | Description |
| Protective function | The secreted sweat on the surface of the skin has bactericidal properties |
| Detoxification function | Together with sweat, many harmful substances are excreted from the body. |
| Maintenance of water-salt metabolism | If it is violated, weight loss, dry skin are noted, and the volume of circulating blood is reduced |
However, in some cases, perspiration is not aimed at maintaining normal life, but, on the contrary, leads to the development of fungal or bacterial skin lesions, which in turn causes an unpleasant odor. This is often associated with provoking factors.
Trigger factors for excessive leg sweating
It is believed that one provoking factor, or a combination of both, can increase leg sweating. These include:
- Improper foot care.
- Rare change of socks or tights.
- Use of socks or tights made of low-quality synthetic materials.
- Wearing uncomfortable, low-quality shoes that do not have sufficient convection (in a simple way - shoes do not breathe), which is why warm air is not emitted, humidity increases, which in the cold season can lead to frostbite of a limb, and in summer - create optimal conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic flora (bacteria, fungi).
- Lack of care or improper care of shoes.
- Professional activity that requires a long load on the legs.
- Some pathologies (endocrine, cardiovascular, nervous systems, flat feet, infectious diseases, neurocirculatory dystonia, etc.).
- Local factors (the presence of maceration on the feet, cracks, peeling, softening and swelling of certain areas of the skin, a change in its acidity).
- Fungal infections of the nails and skin of the feet.
Separately, there is a physiological generalized (whole body) or local (palms and feet) hyperhidrosis, which can be observed during stress, overexertion, physical or emotional experiences. It is short-lived and passes along with the external stimulus that caused such a reaction.
Also, general hyperhidrosis or hyperhidrosis of some areas may be due to a genetic predisposition.
Methods for eliminating leg hyperhidrosis
Increased perspiration in the feet area and unpleasant odor are primarily associated with poor hygiene and some external factors. Therefore, to get rid of this problem, you must follow certain recommendations for the care of the skin of the feet.
Hygiene aspects
People with excessive sweating of the feet should carry out hygienic procedures using detergent substances (soap, shower gel). The water should be at room temperature.

An important part of treating excessive sweating of the feet is personal hygiene.
After the end of the procedure, the legs need to be dried with a towel, sometimes it is necessary to apply a moisturizer. It is also recommended to have regular pedicure.
Selection of suitable shoes
Another important component is the correct selection of shoes. It is necessary to take into account the quality of the material from which it is made, its air and moisture permeability. It is necessary to wear shoes taking into account the season and weather conditions (to avoid hypothermia, wetting, overheating of the lower limbs).

With hyperhidrosis of the legs, special attention should be paid to shoes
Shoe care consists in regular, as it gets dirty, cleaning the outer and inner surfaces of the shoe and changing the insoles.
Requirements for hosiery

Socks for hyperhidrosis need to be changed frequently
If the above recommendations are ineffective, you should contact a dermatologist to find out the cause of the pathology and select the correct measures that will help cure it.
Therapeutic methods
If somatic causes (problems with internal organs and systems) are excluded, you can use a variety of pharmacological agents for topical application, which are aimed at solving this problem.
Formagel
This is a gel for external use, the main component is formaldehyde. The tool reduces sweat hypersecretion and suppresses excessive bacterial growth.
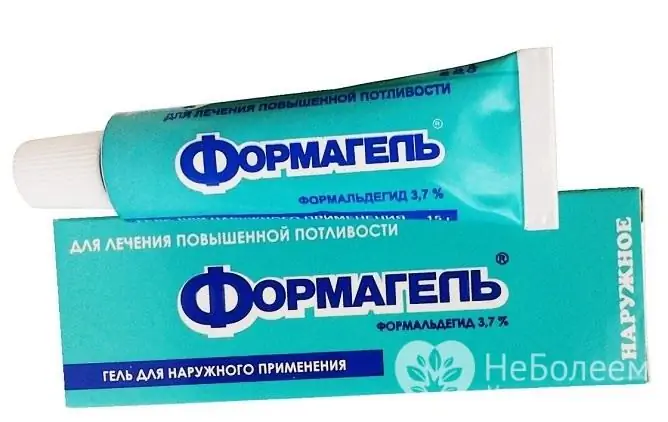

Formagel may be prescribed for treatment
Formagel is applied once every 7-14 days (depending on the degree of sweating), in severe cases - every day for 2-3 days.
Before applying the product, you must thoroughly rinse and dry your feet. Then, apply a small layer of Formagel to the desired area of the skin, then after 30-40 minutes wash off the gel with warm running water, dry your feet with a towel and dust them with baby powder or talcum powder.
Contraindications for use include cases of allergic reactions to formaldehyde (including formalin), inflammatory skin diseases.
Pasta Teymurov
Teymurov's paste is a remedy used for hyperhidrosis of the feet, sweating and diaper rash of the epidermis.
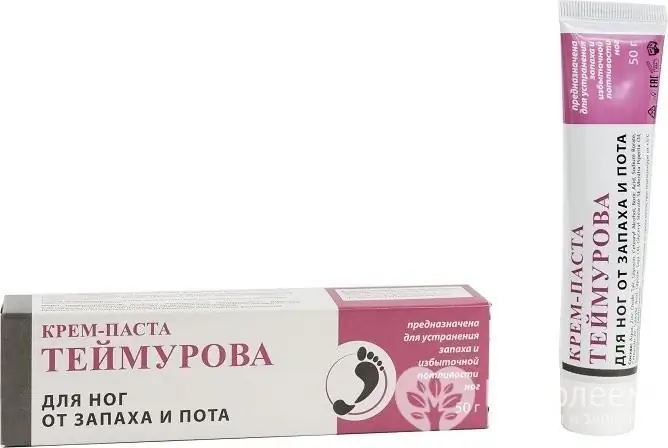

The composition of Teymurov's paste contains components that have an antiseptic, keratolytic and adsorbing effect
In its composition, the drug contains components that have the following actions:
- antiseptic: boric and salicylic acids, sodium tetraborate;
- antimicrobial: methenamine;
- adsorbent: talc;
- keratolytic (removes the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis): salicylic acid.
Every day, for 4-5 days after washing and drying with a towel, the feet should be rubbed into the skin of the feet for three minutes.
Do not apply the paste to damaged and inflamed skin areas and apply it to people who are allergic to one or more of the components that make up the paste.
Borozin
Borozin is a hygienic product in the form of a powder, intended for the care of footwear of people with excessive sweating of the feet, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Borozin is intended for shoe care
It contains antiseptic, disinfectant, antimicrobial, antifungal, astringent, deodorant and other substances.
Borozin is used according to the following scheme: 1 sachet of powder must be divided equally (half for each shoe or other shoe) and distributed over the inner surfaces of the shoe. The tool is used daily for 5 days, in the morning, before putting on shoes.
Dry dry
Dry Dry Classic is a medical antiperspirant with a special applicator, which is used for increased perspiration in the areas of the soles, palms and armpits.

Medical antiperspirants, such as Dry Dry Classic, can be used to relieve symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
The mechanism of action is to block the sweat glands due to their interaction with the aluminum-protein components that make up Dry Dry. As a result, a redistribution of the perspiration surface occurs: the sweat that should have come out through the blocked glands evaporates through the free areas of the skin.
Dry Dry is applied 1 hour before bedtime with a frequency of application once every 4 days - 3 weeks.
Anticholinergics
The drugs that belong to this group have a hypohydrotic effect (reduce the secretion of sweat). However, they are rarely used in isolated hyperhidrosis, as they have many contraindications and side effects.
Anticholinergics are prescribed strictly by a physician and are available by prescription.
Botulinum toxin therapy for hyperhidrosis
Botulinum toxin blocks neuromuscular transmission, thanks to which it has found its application in some branches of aesthetic and classical medicine, including in the treatment of hyperhidrosis.

The effect of botulinum toxin therapy lasts for 6-9 months
The effect of botulinum toxin is similar to that of anticholinergic drugs, only it acts locally. The remedy removes hyperhidrosis a few minutes after intradermal injections in the sole area, the effect lasts up to 6-9 months.
Folk remedies in the therapy of sweating feet
Baths using some herbs (such as chamomile, oak bark, sage) or herbal preparations help to get rid of foot odor at home. They have antiseptic, tanning, antimicrobial, antifungal effects and are effective in the complex treatment of foot sweating.

Foot baths with herbal infusions are effective only with regular use
Examples of herbal baths that can help cure hyperhidrosis:
- chamomile bath. Steam 6-7 tablespoons of chamomile in two liters of boiled warm water (70-80 ° C), leave for 40-60 minutes, strain and put your feet in the finished broth for half an hour;
- bath with sage, plantain, chamomile and linden. Steam 3 tablespoons of each herb in 500 ml of boiling water (leave for 15 minutes). Mix the finished infusion with warm water in a container and immerse your feet in it for 30 minutes so that the solution is just below the ankle;
- soda bath. Mix 3 tablespoons of baking soda in a container of water, add a few drops of tea tree essential oil (this will give a pleasant aroma and help soften your feet). Stir the solution and place your feet there for 30 minutes, then dry them with a towel.
The help from herbal baths is noticeable only with regular use. In comparison with traditional methods of treatment, folk remedies are considered less effective, they do not act so quickly and for a long time.
When choosing ways to solve a problem, it is advisable to be guided by the principle from less aggressive means to more aggressive ones.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.