- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How plaque forms on teeth

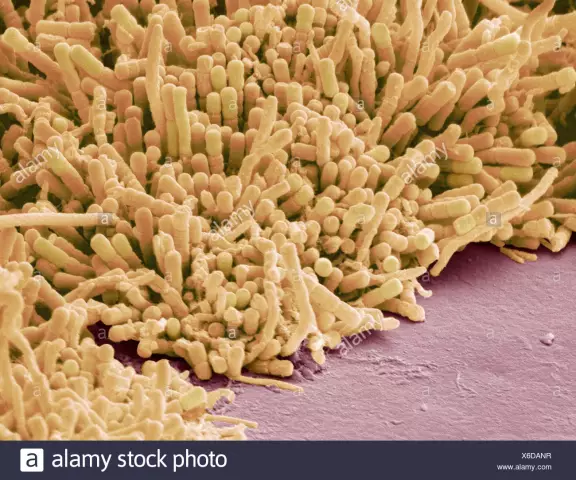
Toothpastes promise us effective plaque removal. What is this plaque on the teeth and where does it come from? Plaque on teeth, or dental plaque, is of two types - soft and hard. Toothpaste promises apply to soft dental plaque. Soft plaque, or dental plaque, under the microscope is a conglomerate of food debris, bacteria, desquamated epithelium of the villi of the tongue and their decay products, held together by viscous saliva. The color of soft plaque is usually white or light yellow.
A large amount of dental plaque is contained in fissures (grooves on the chewing side of the teeth), in the interdental spaces; dental prosthetics also creates favorable places for the accumulation of soft deposits, since there is always a gap between the artificial material and the natural tissues of the oral cavity. Soft dental plaque can be easily removed with conventional oral hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste.
By itself, the soft plaque on the teeth does not damage the tooth tissue, but creates a favorable environment for the activity of bacteria, which are always present in large numbers in the oral cavity. Bacteria, decomposing organic substances contained in soft dental plaque, secrete proteolytic enzymes that have a destructive effect on tooth enamel, despite the fact that it belongs to the hardest tissues of the body. Often at the reception, the dentist, brushing off the soft plaque formed as a result of poor-quality teeth cleaning, discovers a chalky spot under it - the initial stage of caries.
Hard dental plaque or tartar is calcified soft dental plaque. This is the next stage in the development of soft plaque. Two factors are decisive in the formation of hard dental plaque: the presence of dental plaque and the individual chemical properties of saliva. Some people are more prone to tartar formation, some less precisely because of the quality of saliva. But it should be

borne in mind that even if due to saliva there is an increased risk of calculus deposition, it will not form if the second main component is absent - soft plaque.
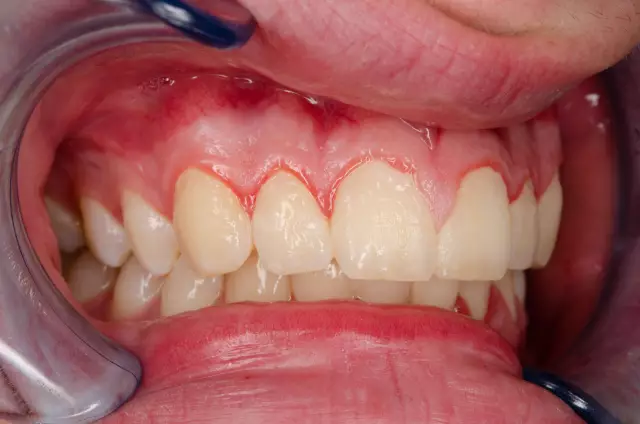
Hard plaque on the teeth is formed mainly at the neck of the tooth, in the place where the gum passes into the tooth, as well as in the interdental spaces on the lingual side, therefore, we may not notice it for a long time. Its color varies from light yellow to brown-black, depending on food preferences and tobacco smoking. Tartar contributes to the formation of periodontitis and periodontal disease, so it must be removed. This can only be done by a dentist using special devices for professional teeth cleaning.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.