- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Treatment of sinusitis in children 3 years and older: the most effective methods
The content of the article:
- The reasons for the development of sinusitis in children
- Symptoms of sinusitis
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment and prevention
- Home treatment
- Preventive measures
- Video
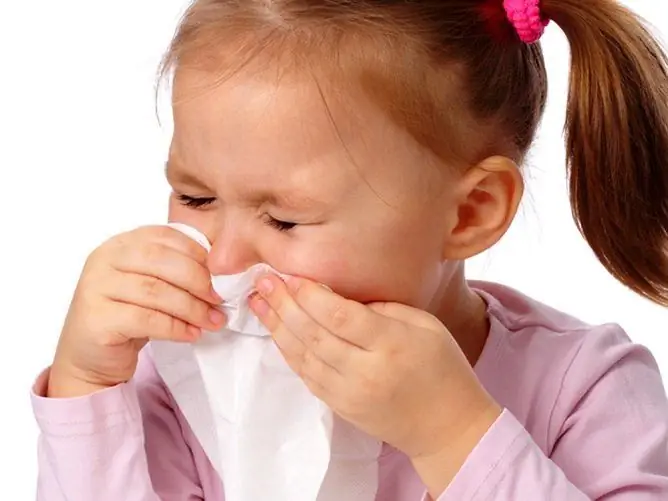
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses. The accumulation of thick, viscous mucus in the sinus cavity, which, when bacteria attaches, turns into pus, leads to the appearance of constant or periodic serous-purulent discharge from the nose.

Sinusitis is characterized by the appearance of serous-purulent discharge from the nose
In newborns, the maxillary sinuses are small in size, they represent a narrow gap (protrusion of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity). The cavities grow as the child grows, and only by 4-5 years do they acquire normal sizes. It is for this physiological reason that the disease in children under 3-4 years of age occurs in extremely rare cases.
In children, as in adults, the disease can occur in an acute, recurrent and chronic form. In this case, the course of sinusitis has a number of differences. The lower the functional maturity of the body, the brighter the clinical manifestations of pathology (high body temperature, general intoxication).

The formation of the maxillary sinuses lasts up to 4-5 years
Incomplete completion of the development of sinuses contributes to the spread of the inflammatory process in the orbit, meninges, leading to various complications.
The reasons for the development of sinusitis in children
Inflammation of the maxillary sinus most often occurs as a consequence of acute respiratory diseases, against the background of childhood infections (measles, scarlet fever, etc.). The entry of viral or bacterial flora occurs through natural messages, especially when sneezing, blowing your nose as a result of increased pressure in the nasal cavity. In the presence of carious teeth of the upper jaw, odontogenic inflammation may develop. The hematogenous pathway is also important (in the presence of chronic foci of infection).

One of the reasons for the development of sinusitis is polyps in the nose
It is necessary to take into account the anatomical features of the structure of the maxillary sinuses in children of different age groups, and under what conditions the risk of the onset and spread of inflammatory processes increases:
- abundant blood supply to the nose and paranasal sinuses;
- narrowness of the nasal passages;
- spongy structure of the upper jaw;
- increased vulnerability of the ciliated epithelium of the upper respiratory tract;
- immaturity of immunity and weakness of enzymatic systems, which reduces the body's resistance to infectious agents of the environment;
- the severity of allergic reactions;
- the presence of adenoids, fistulas or cysts in the nose, prone to inflammation and suppuration;
- deformation of the nasal septum;
- anomalies in the development of the paranasal sinuses;
- traumatic injuries of the nose, upper jaw, maxillary sinuses.
In infants, the close anatomical location of the tooth germs to the bottom of the orbit contributes to the development of intraocular complications in various dental diseases, which is rare in older children and adults.
Symptoms of sinusitis
The main symptoms that make it possible to determine the disease in a child in time and prevent complications are:
- headache localized in the forehead, temples, aggravated by coughing, sneezing, turning or tilting the head;
- viscous mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the nose;
- change in the timbre of the voice and nasal;
- pain in the nose, cheeks on the side of the affected sinus; pain sensations increase with pressure on the bridge of the nose;
- the rapid development of dermatitis in the vestibule of the nose from constant irritation with discharge;
- nasal congestion or difficulty breathing through the nose;
- an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C and above;
- redness and swelling of the cheeks on the affected side;
- unpleasant putrid odor from the corresponding half of the nose;
- cough during the day or night;
- ear congestion.
Sneezing and watery eyes are also possible. The child can respond to food, become irritable, whiny, apathetic.
Diagnostics
Most often, sinusitis develops against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), so parents first seek medical help from a pediatrician and, after initial diagnosis, are sent to an otorhinolaryngologist.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of complaints, examination data, results of laboratory and instrumental research methods. Appointed:
- clinical blood test;
- rhinoscopy;
- bacteriological culture of nasal discharge with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics;
- X-ray examination in the naso-chin, frontal-nasal and lateral projections;
- CT scan.
In the clinical analysis of blood, there may be moderate leukocytosis.

In the acute form of the disease, pneumococci, staphylococci and streptococci can be detected in bacteriological culture
In the bacteriological inoculation of the discharge from the sinuses, the following can be detected:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- pneumococci;
- intestinal, hemophilic or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
During rhinoscopy, hyperemia and edema of the mucous membrane of the nasal conchas, the presence of secretions on the walls and in the area of the natural anastomosis (messages between the sinus and the nasal cavity) are visualized.
The mucous membrane of the maxillary cavity in young children is much thicker than in adults; more intense changes are noted in it with any inflammation. In this regard, with acute or allergic rhinitis, the x-ray often reveals a darkening of the maxillary sinus in the absence of sinusitis. Therefore, if an inflammation of the maxillary sinus is suspected, in the diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account all the data as a whole, not relying solely on the radiograph. In children of the older age group, as well as in adults, a darkening of the sinus with a horizontal level of fluid in the presence of pus inside is determined on the roentgenogram.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of sinusitis in children is carried out taking into account the etiology and severity of the disease, the nature and localization of the process, the presence of complications.
Allergic sinusitis usually occurs as a consequence of allergic rhinitis. In most cases, it is quickly stopped by antihistamines and very rarely leads to the development of consequences.
Increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier causes an increase in intracranial pressure during an active process of inflammation, which can lead to compression of the medulla oblongata by edematous tissues. Therefore, when prescribing the treatment of sinusitis in children 3 years old and younger, lytic mixtures and antipyretics are widely used.
Therapy of uncomplicated acute sinusitis requires an integrated approach; medications should be selected by a doctor taking into account the age and body weight of the child. Usually appointed:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides; it is important not to interrupt the self-initiated course of treatment after the condition improves; children under 6-7 years of age are usually prescribed drugs in the form of syrups for accurate dosing, injectable forms are used only in cases of severe disease;
- vasoconstrictor drops to restore nasal breathing (Sanorin, Vibrocil, Nazivin); before their introduction, it is necessary to cleanse the nasal passages; for this purpose, nasal sprays based on sea or ocean water can be used (Aqualor, Aqua Maris, etc.);
- antihistamines to relieve edema (Loratadin, Tavegil);
- mucolytic agents for thinning mucus and facilitating its excretion from the sinuses (ACC, Sinupret).
Rinsing of the nasal cavity with antiseptic solutions may be prescribed to ensure the free outflow of the contents from the sinus (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine). A clear definition of microflora allows, after washing the cavity, to use bacteriophages (staphylococcal, streptococcal, etc.).

One of the effective methods of treatment is rinsing the nose with saline solutions.
Symptomatic treatment of sinusitis in children is usually aimed at lowering body temperature (drugs containing paracetamol, ibuprofen).
From the age of ten months, with a purulent form of the disease, diagnostic and therapeutic punctures of the sinus are performed. In contrast to the treatment of chronic sinusitis, in an acute process, it is recommended to refrain from active lavage of the sinus and limit ourselves to aspiration of the contents followed by the introduction of an antibiotic solution, a proteolytic enzyme or an immune preparation into the cavity.
With odontogenic inflammation, an active sanitation of the oral cavity is performed.

Physiotherapy is usually prescribed at the stage of sinusitis resolution
When treating sinusitis in a child 4 years old and older in the stage of resolving the disease, it is possible to prescribe physiotherapy: UHF currents (ultra-high frequency), magnetic field, ultrasound. This helps to enhance blood and lymph circulation, stimulates metabolic processes and adaptive mechanisms.
In severe and complicated forms, surgical interventions are performed. The indications for surgery are:
- orbital and intracranial complications;
- polyposis or polypoid-purulent forms of sinusitis;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
Home treatment
In addition to the main treatment, at home, you can rinse the nose with saline solutions and pump out mucus. This requires a syringe or rubber bulb.

During the treatment of sinusitis, it is necessary to strictly control the child's diet.
It is recommended to pay special attention to the air humidity in the room, periodically ventilate the room, and prevent too hot a house temperature. Food should be light, rich in vitamins and minerals. Proper child care is important: you need to promptly remove mucus, pus and the resulting crust from the nose.
You can also use folk remedies: pine oil, cedar, aloe juice, infusion of eucalyptus leaves, green tea. But even the most effective traditional medicine does not cancel the use of antibiotics.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of the disease, the following recommendations must be observed:
- timely treatment of viral and bacterial infections;
- regular examination by the dentist and oral cavity sanitation;
- hardening and other activities aimed at maintaining immunity;
- elimination of contact with the allergen (if the child is prone to allergies);
- ensuring an adequate stay in the fresh air, regular sports and outdoor games;
- adherence to the daily regimen, sleep and nutrition.
If symptoms of sinusitis appear, you should consult a pediatrician or an ENT specialist.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Alina Ervasova Obstetrician-gynecologist, consultant About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University. THEM. Sechenov.
Work experience: 4 years of work in private practice.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.