- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Arterial hypertension. Causes and treatment
The content of the article:
- Why arterial hypertension occurs
- Basic approaches to the treatment of arterial hypertension
High blood pressure, or arterial hypertension, is recorded in every fifth adult in the world. In Russia, about 40% of the adult population suffers from hypertension! Imagine almost half of the country's adult population has blood pressure problems.
Blood pressure is considered normal below 140/90 mm Hg. A repeated recorded increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. considered arterial hypertension or, as the disease was called before, hypertension.
The high prevalence and such dangerous complications as stroke and heart attack make arterial hypertension one of the most important problems in medicine.

Why arterial hypertension occurs
There are a number of triggers for hypertension:
- heredity;
- age (over 45 for men, over 55 for women);
- gender (men under 50 are more prone to the disease than women);
- overweight;
- chronic stress;
- passive lifestyle;
- bad habits (smoking, excessive alcohol consumption);
- excessive salt intake;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- unhealthy diet, vitamin and microelement deficiency;
- unfavorable working conditions.
It has been proven that social conditions and psychoemotional stress are the most significant triggering factors in blood pressure imbalance. Prolonged excessive stress of mental activity under the influence of psychoemotional situations causes a disorder in the regulation of vascular tone and blood pressure control.
Basic approaches to the treatment of arterial hypertension
Treatment of arterial hypertension should be comprehensive and consist of a drug and non-drug part. This is the only way to achieve a stable normalization of the patient's blood pressure figures. Lifestyle changes are of prime importance in therapy.
Non-drug treatment means:
- adherence to a diet with a clear calculation of the amount of table salt consumed (less than 5 grams per day), fats and carbohydrates (the content of these substances should be reduced); DASH diet
- normalization of the work and rest regime;
- exclusion of smoking and alcohol abuse;
- moderate physical activity, repetitive from day to day (at least 150 minutes per week);
- avoidance of stress;
- normalization of body weight.
The goal of drug therapy is to achieve and maintain target blood pressure levels, protect target organs and ensure the longest possible long-term reduction in the risk of complications. For treatment, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium antagonists and angiotensin-2 receptor antagonists are used.
One of the most effective representatives of drug therapy is bisoprolol. The essence of its action is to reduce the "toxic" effect of adrenaline and norepinephrine on the heart receptors. Bisoprolol has a high ability to selectively block beta1-receptors located in the heart muscle, due to which the drug does not cause bronchial spasm and respiratory failure in patients with lung pathologies, in contrast to its less selective, "congeners" of the first generation. Also, the drug does not affect carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, therefore it does not increase the level of cholesterol and glucose in the blood.
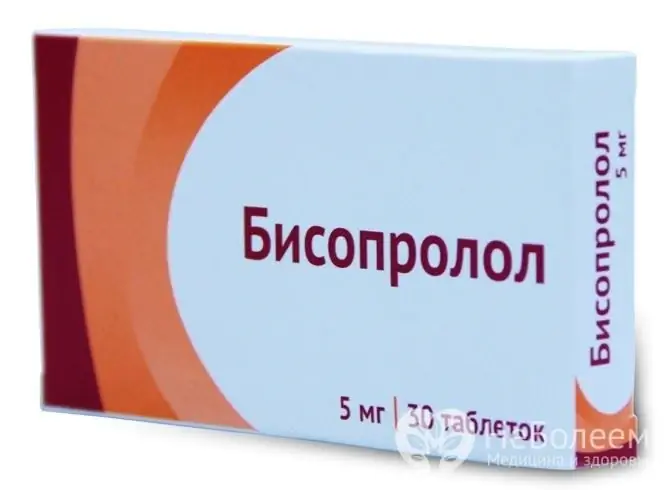
The main directions of action of bisoprolol:
- lowering blood pressure;
- slow heartbeat;
- prevention of the development of arrhythmias, due to a decrease in the excitability and automatism of the heart muscle;
- decreased cardiac output;
- reducing the load on the heart;
- decrease in myocardial oxygen demand;
- reducing the likelihood of SS catastrophes;
- increased load tolerance;
- slowing the progression of chronic heart failure;
- has a cardioprotective effect
An important fact is that bisoprolol monotherapy in terms of effectiveness is not inferior to representatives of other groups of antihypertensive drugs, and in some cases even surpasses them in terms of the effect of reducing pressure. Bisoprolol can be used in combination with other drugs without inhibiting or enhancing their effect.
Bisoprolol has unique pharmacokinetic properties
- the drug is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, regardless of food intake;
- metabolism does not change depending on the level of physical activity and the volume of adipose tissue;
In addition, bisoprolol can be used only once a day, which, of course, is very convenient for the patient.
Bisoprolol is generally well tolerated, does not interfere with sexual function, and improves overall quality of life.
Independent use of bisoprolol is not allowed. To prescribe therapy, you need to consult with a cardiologist, who will draw up an individual treatment regimen for hypertension and prescribe the drug that is right for you.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.