- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
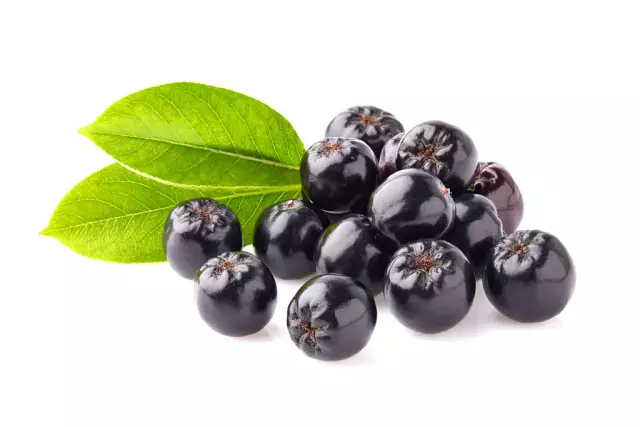
Chokeberry (chokeberry)
Instructions for use:
- 1. Description
- 2. Chemical composition
- 3. What is useful for the human body?
- 4. Contraindications and warnings

Aronia is a deciduous tree belonging to the Rosaceae family.
Description
The plant reaches a height of 10 meters. The bark is smooth, gray. Felt-fluffy buds on the branches. The leaves are alternate, with pubescent petioles, almost sessile. In the upper part, the leaves are serrate along the edge, dull green above, grayish below. Inflorescences are located at the ends of the branches. The plant blooms in May-June with white flowers. The fruits are berry-shaped, ripen in August-September and remain until frost.
The homeland of the chokeberry is North America. In the 18th century, chokeberry was brought to Europe, and in the 19th century - to Russia. Until the beginning of the 20th century, chokeberry was considered an exclusively decorative culture.
Later, chokeberry was used in different forms: the berries are eaten fresh, dried, ground with sugar. They make jam, jelly, jam, marmalade. Also, juices, tinctures, wines and liqueurs are prepared from the plant.
For medicinal purposes, the fruits of mountain ash are used. They have a pleasant sour-sweet, slightly tart flavor. They contain a large amount of vital trace elements and vitamins.
The medicinal properties of chokeberry are not lost during processing.
Chemical composition
The beneficial properties of chokeberry are due to the content of carbohydrates in it (10%), a whole complex of vitamins (B6, B2, B1, A, E, K, C, P), flavonoids, organic acids, pectins, tannins.
In addition, berries contain a large amount of iodine (four times more than gooseberries, raspberries and strawberries) and other trace elements (chromium, nickel, molybdenum, zinc, manganese, cobalt, boron, copper, iron, fluorine, and others).
Why chokeberry is useful is its high content of vitamin P (first place among vegetable and fruit crops). One kilogram of fresh berries can satisfy a person's daily need for this vitamin. In terms of vitamin C content, chokeberry also surpasses many fruit plants.
What is useful for the human body?
Aronia improves the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, strengthens the walls of blood vessels. Due to the medicinal properties of chokeberry, its juice is used in the treatment of atherosclerosis and the initial stage of hypertension.
Another benefit of chokeberry is that it can lower high blood pressure while keeping normal blood pressure at the same level.
Recommended combined use with black chokeberry rosehip and black currant. These plants are rich in ascorbic acid, which promotes better absorption of vitamin P.
Outwardly, black chokeberry has found application for burns and for allergic skin lesions (dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis).
With diffuse toxic goiter, in particular, with thyrotoxicosis, this plant is used as part of complex therapy.

The beneficial properties of chokeberry increase the body's resistance to infections, so that it is a powerful immunostimulant, increasing the tone of the body and improving the general condition.
The use of chokeberry helps to improve digestion, increase appetite, and increase gastric secretion. It is an excellent remedy for combating low stomach acidity and gastritis.
Chokeberry berries have a choleretic and diuretic effect. And the leaves of the plant normalize the liver, promote the formation and secretion of bile.
Chokeberry water infusion is indicated for patients with diabetes mellitus. And cancer patients use chokeberry because of the anthocyanins it contains.
Contraindications and warnings
Due to the high content of ascorbic acid in berries, chokeberry is contraindicated in hypertension and angina pectoris. Excessive use of them leads to hypercoagulability, and, as a result, to the formation of blood clots.
Chokeberry is categorically contraindicated for people with increased blood clotting and a tendency to thrombophlebitis.
The use of chokeberry berries is also undesirable for duodenal ulcer and stomach ulcers, with gastritis with high acidity.
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!