- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Language

The tongue is a muscular organ in the oral cavity that is involved in mixing food, swallowing, and forming speech sounds. There are taste buds on the tongue that allow you to recognize the taste of food.
Language structure
The body and the root are distinguished in the language. The edge delimits the upper and lower surfaces of the tongue. The organ is based on striated muscle fibers covered with mucous membrane on top. Own muscles of the tongue:
- Vertical;
- Transverse;
- Longitudinal.
Paired skeletal muscles (awl-lingual, chin-lingual, sublingual-lingual) carry out the movements of the tongue and fix it.
The body of the tongue is separated from the root by a groove on the upper surface, consisting of 2 halves, converging at an obtuse angle. Below from it to the bottom of the oral cavity is a fold of the mucous membrane - the bridle.
On the back and along the edges of the tongue, the mucous membrane has many papillae, which are the organ of taste and touch. The papillae are distinguished by shape:
- Mushroom;
- Filiform;
- Conical;
- Leafy;
- Surrounded by a shaft.
The mushroom, leaf-shaped, and shaft-surrounded papillae contain taste buds, while the conical and filiform papillae are responsible for pain, temperature and tactile sensitivity.
In the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue, there are many lymphoid follicles, united under the name of the lingual tonsil. Small salivary glands are located between the muscle fibers of the tongue and under its mucous membrane.
Language functions
The language has a number of important functions:
- In breastfed children, participates in the act of sucking;
- Determines the taste, texture and temperature of food;
- Promotes mixing of food, the formation of a food lump;
- Participates in the production of saliva and swallowing food;
- The lingual amygdala is responsible for local immunity;
- Participates in the formation of speech sounds, some characteristics of the voice depend on it.
Tongue examination methods
There are few methods of examining the tongue - mainly complaints and external examination. The study of work begins with the collection of complaints. Defeat of the tongue is possible with the suffering of the whole organism from dehydration, poisoning, with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, gastroenteritis), cardiovascular (stroke, heart failure), central and peripheral nervous system (paralysis). The patient may complain of paresthesia, decreased mobility, or pain in the tongue.
On examination, attention is paid to the condition of the mucous membrane - its moisture, color, the presence of damage or rashes, erosion, foci of hyperkeratosis, the severity of the papillae, the degree of mobility of the tongue, the presence of teeth imprints on it.

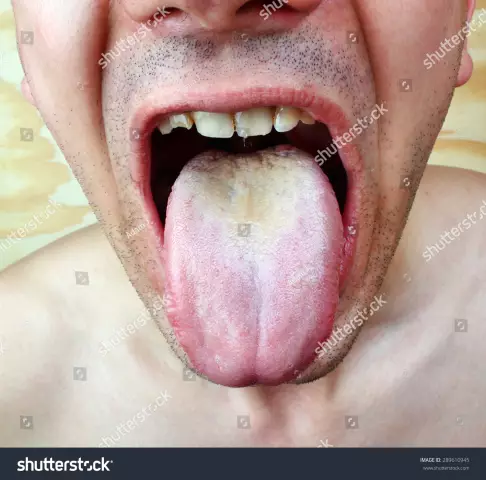
The tongue can have plaque of different colors and severity. White plaque on the tongue in its middle third with cracks of different sizes most likely indicates a lesion of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenteritis, ulcer). If plaque is found along the edges of the tongue in its front third, then most likely the person has a chronic pathology of the respiratory system (bronchitis, emphysema). White plaque on the tongue over its entire surface is often a symptom of the defeat of the tongue itself, candidal stomatitis. The plaque has a white cheesy character, is easily removed, and a bright red erosive surface is exposed under it.
A yellow coating on the tongue can indicate damage to the digestive system, in particular the pancreas, liver and biliary tract. This color is given to it by decay products or bilirubin. Yellow plaque on the tongue is also found in healthy people who drink a lot of tea, coffee or smokers. In this case, the teeth are also stained yellow, especially their back surface facing the tongue.
A brown coating on the tongue occurs with chronic alcohol abuse. The plaque acquires a greenish color when taking certain antibiotics, steroids and other drugs that suppress the work of the immune system. A gray bloom speaks of the ulcerative nature of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases of the tongue
Painful sensations in the language without visible external changes are called glossalgia. It is also accompanied by tingling, burning, tingling in the tongue, dryness of the mucous membrane. Glossagia is associated with endocrine, hormonal shifts, nervous disorders. The disease is rather difficult to treat.
Pain in the tongue can be the result of glossitis - inflammation of the tongue of a viral or bacterial nature, as well as mechanical or thermal reasons. The tongue then changes its color to bright red, becomes soft and swollen, and difficulty speaking and eating.
Severe pain under the tongue is one of the signs of salivary colic when stones from the salivary glands enter the salivary duct. The outlet openings of the salivary ducts on both sides of the frenum are somewhat swollen. When probing with a finger under the tongue, a focus of inflammation or a salivary stone the size of a pea is determined. Also, pain under the tongue occurs with injuries of the mucous membrane, stomatitis with localization at the bottom of the tongue.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.