- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the terminal stage of severe liver disease, in which the liver structure degenerates, normal tissue is replaced by fibrous growths, the death of hepatocytes, as a result of which the liver gradually loses its functions. In this case, the most important signs of cirrhosis are the involvement of the entire liver tissue in the pathological process, a violation of its lobular structure and portal hypertension.
People of any age can be sick with cirrhosis, most often the disease affects people aged 35-55 years. Men get sick more often, which is associated with a large proportion of cirrhosis of alcoholic origin.
Causes of cirrhosis

Cirrhosis is a polyetiologic disease, which means that many reasons can lead to it. The most common causes of cirrhosis include the following:
- Chronic alcoholism;
- Viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C;
- Diabetes;
- Thyrotoxicosis;
- Violation of the outflow of bile from the bile ducts (chronic choleostasis);
- Hepatitis of non-viral origin (toxic-allergic);
- Chronic intoxication of the body with certain chemical compounds, including drugs.
In addition, the cause of cirrhosis can be some types of cardiovascular pathology, autoimmune processes, metabolic disorders (fatty degeneration of the liver), hemochromatosis and some other hereditary diseases, as well as a specific infection (syphilis, brucellosis, etc.). In addition, there are cirrhosis, the cause of which cannot be found.
Types and stages of cirrhosis
Depending on the cause of cirrhosis, it can be primary, developed as an independent pathology, or secondary, which is a symptom of a general disease, as in diabetes or syphilis.
Depending on the morphological signs of cirrhosis, there are:
- Portal cirrhosis;
- Biliary cirrhosis;
- Postnecrotic cirrhosis;
- Mixed.
According to the activity of the course of the process, cirrhosis are active and inactive.
Depending on the type of nodes:
- Small-nodular cirrhosis;
- Large nodular cirrhosis;
- Mixed.
In the chronic process, the following stages of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- The initial stage of cirrhosis, or the stage of compensation. The destruction of blood vessels and parenchyma is poorly expressed, the onset of the inflammatory-necrotic process;
- Subcompensation stage. The increase in destructive processes, the gradual replacement of the parenchyma with fibrous tissue, however, at this stage of cirrhosis, most of the liver functions are preserved due to the remaining hepatocytes;
- Decompensation. This is the terminal stage of cirrhosis, at which there is an almost complete degeneration of the liver with the loss of its functions.
Symptoms of cirrhosis

Cirrhosis develops for a long time, over months or years. The brightness of clinical manifestations depends on the stage of cirrhosis, as well as on the degree of activity of the process. At the same time, the early symptoms of cirrhosis, as a rule, go unnoticed, especially against the background of an existing pathology.
The early signs of cirrhosis include asthenic syndrome: increased fatigue, general malaise, weakness, difficulty concentrating, and decreased appetite. The first noticeable symptoms of cirrhosis are usually the following: jaundice of the skin, itching, redness of the palms, recurrent fevers, nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the stomach after a small amount of food, weight loss, susceptibility to infectious diseases. The characteristic signs of cirrhosis include a visible and tangible increase and hardening of the liver, sometimes even to the touch its dense bumpy structure is determined.
Another symptom of cirrhosis is abdominal enlargement due to the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Abdominal enlargement attracts attention also because it occurs against the background of significant weight loss.
As the process develops, symptoms of cirrhosis due to portal hypertension join. Veins appear on the body, nosebleeds appear, hemorrhoids may appear. There is a need to solve the question: how to treat hemorrhoids. A sign of cirrhosis in the developed stage is turbidity and darkening of urine, while feces, on the contrary, become lighter.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis
The diagnosis of cirrhosis is based on the collection of anamnesis, the study of the clinical picture of the disease, as well as laboratory and instrumental research data. The peculiarity of cirrhosis is that biochemical tests (liver function tests) may not show significant deviations from the norm for a long time.
The following hardware methods for diagnosing cirrhosis are used:
- X-ray examination of the liver;
- Ultrasound;
- Doppler ultrasonography of the hepatic, portal and splenic veins;
- Radionuclide liver scan;
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the liver;
- Percutaneous liver biopsy.
In doubtful cases, laparoscopic examination is used.
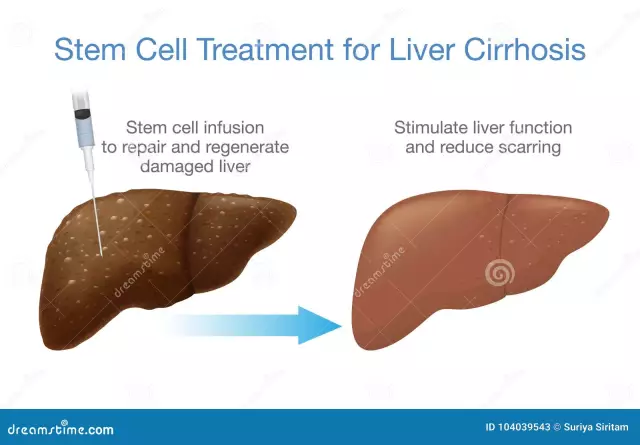
Cirrhosis treatment
Treatment of cirrhosis should be active and immediate, but cirrhotic changes in the liver are irreversible. The goal of cirrhosis treatment is to maintain an acceptable quality of life for the patient and stop disease progression.
Treatment of cirrhosis begins with the elimination of the main damaging factor, if possible (for example, complete cessation of alcohol intake). In the stage of acute symptoms, bed rest is necessary, in the future physical activity should be gentle. The fundamental principles of cirrhosis treatment are diet therapy and normalization of lifestyle.
The diet for cirrhosis consists in limiting protein products, animal proteins are replaced by plant proteins, one or two days a week should be protein-free. The use of salt is limited, as well as products containing soda or baking powder, fatty foods, canned food. Meals should be fractional, in small portions, 5-6 times a day.

Drug treatment of cirrhosis consists in the use of drugs that compensate for existing disorders to relieve exacerbation and reduce the activity of the process (symptomatic treatment of cirrhosis). In case of mechanical blockage of the biliary tract, surgical removal of the obstacle is performed (removal of stones, elimination of stenosis), in case of bleeding from dilated veins of the stomach and esophagus in the stage of subcompensation, surgical intervention is also used.
In case of inactive cirrhosis, sanatorium treatment, courses of general strengthening therapy once or twice a year, as well as regular medical supervision are recommended.
Cirrhosis prognosis
The prognosis depends on the stage of cirrhosis and the activity of the process, as well as on how seriously the patient takes the treatment of cirrhosis and adherence to the diet. In the case of the patient's discipline and the inactivity of the process, which was caught relatively early, it is possible to keep cirrhosis in the stage of compensation for many years. With active cirrhosis in the stage of subcompensation, as well as with decompensated cirrhosis, the prognosis is poor.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!