- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Bone fractures

Bone fractures - various damage to their integrity as a result of traumatic impact. During injury, the force of impact exceeds the resistance of the bone tissue and the bone breaks. For reasons of occurrence, all bone fractures are divided into two main groups: those arising as a result of a strong mechanical effect on healthy bone and fractures of a pathological nature.
Traumatic bone fractures occur as a result of road accidents, falls, strong impacts and other mechanical effects on the bones.
With pathological bone fractures, the physical force of the impact can be quite insignificant, the real reason lies in the presence of any pathological process that occurs in the bone tissue.
A common cause of pathological bone fractures is the disease osteoporosis (bone loss), due to which the bone tissue becomes extremely fragile and breaks down with virtually no external force acting on it, for example, during awkward movements, abrupt standing, etc.
Types of bone fractures
The classification of bone fractures by type is extremely diverse. This circumstance is due to the fact that each specific case of a fracture combines a large number of factors accompanying its occurrence - the causes of the fracture, the localization of the injury, the nature of the injury to soft tissues, etc. displacement of bone fragments, the nature of the fracture and other parameters.
Nevertheless, with all the variety of types of bone fractures, there is an urgent need to accurately identify the site of bone tissue that is the center of the fracture.
The most common classification of bone fractures is:
- simple;
- complex (otherwise referred to as wedge-shaped bone fractures, in which multiple comminuted bone fragments are formed);
- extra-articular fractures;
- intra-articular fractures.
There is also the following classification of fractures:
- closed bone fractures, in which there is no damage to the outer skin;
- open bone fractures, in which there is a violation of the integrity of the skin in the area of injury and there is a risk of infection.
Bone fracture symptoms
Traumatologists consider the presence of external bruising and swelling in the area of injury to the mandatory signs of bone fracture. As a rule, when it comes to a limb, its functional mobility is significantly limited. When trying to move, pain is pronounced. In rare cases (for example, with a punctured fracture of the femoral neck), some victims can continue to move independently, but this fact leads to further injury and displacement of bone fragments. With impacted, subperiosteal, periarticular, intraarticular fractures and bone fractures, some of the above symptoms may be completely absent or not too pronounced.
Diagnosis of bone fractures
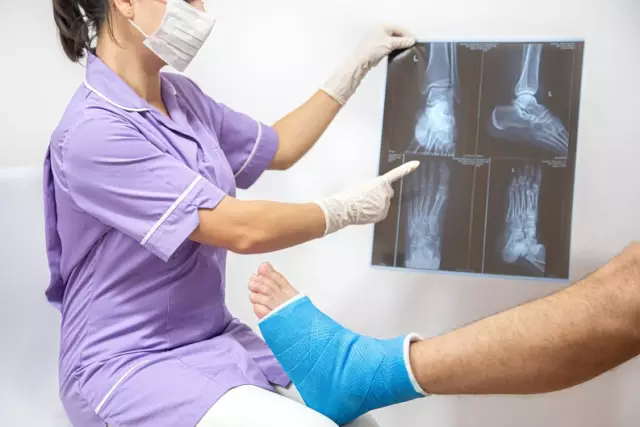
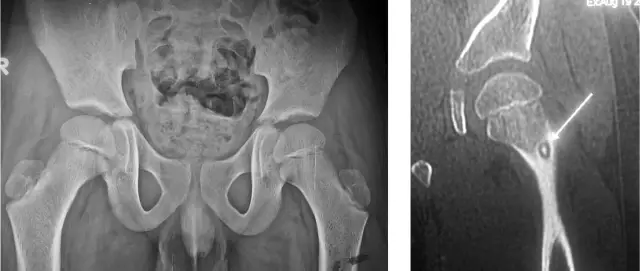
Before taking measures to apply plaster (or other options for fixing bone fragments) within the walls of a medical institution, an X-ray examination of the victim with a bone fracture is mandatory. X-rays are always taken in several projections for detailed examination of the bone fracture site from several different angles.
X-ray examination is the most accurate tool that allows traumatologists to create a complete picture of a bone fracture - its type, localization, direction and nature of the fragments displacement.
Then control X-rays are taken to the patient after conservative or surgical fixation of the broken bone. In the future, an X-ray examination is prescribed after about 14 days (in each case - in different ways) to monitor the progress of the fusion of the broken bone and the formation of callus at the site of the fracture.
Bone fracture treatment

Bone fracture treatment should begin at the scene of the accident. The most urgent help in the first minutes after injury should be measures to eliminate pain shock, especially when it comes to bone fractures in children.
Next, you need to take action to stop bleeding (if any). Immediately after the above first aid measures, immobilization (creation of conditions for complete immobility) of the bone fracture site should be ensured with the help of special means or improvised materials.
In the case of an open bone fracture, a sterile gauze pad and a pressure bandage should be applied on top of the wound surface to prevent the possibility of further bleeding and wound infection. In no case should you try to set bone fragments sticking out of an open wound on your own, thereby you can only cause severe pain to the victim, but also cause significant harm to his health.
First aid for a closed fracture of bones consists primarily in immobilizing the damaged area of the body to prevent the possibility of displacement of fragments and the occurrence of internal bleeding.
Timely and competent first aid provided to the victim significantly reduces the subsequent rehabilitation period for bone fractures and guarantees full restoration of the motor functions of the damaged area of the body.
In a hospital setting, the main medical methods for treating bone fractures include the following:
- the imposition of a plaster cast;
- skeletal traction;
- endoprosthetics;
- external hardware compression-distraction osteosynthesis;
- internal osteosynthesis, etc.
In order for the victim not to lose their ability to work in the future and can, as soon as possible, return to their usual way of life, special attention should be paid to the rehabilitation period after a bone fracture. The list of rehabilitation measures after a bone fracture (and especially after prolonged immobilization) must certainly include therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy procedures.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!