- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Tachycardia

Tachycardia is a condition in which the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute. Tachycardia can occur as a result of an increase in heart rate due to physical exertion, stressful situations or excitement, or be a consequence of an increase in heart rate at rest.
In some cases, tachycardia can be uncomplicated, however, it can seriously disrupt the normal function of the heart, increase the risk of stroke, or can lead to sudden cardiac arrest and death. Risk factors for developing tachycardia are obesity and type 2 diabetes. Allocate sinus tachycardia, paroxysmal and ventricular fibrillation.
Sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is a condition when impulse conduction from the sinus node to the ventricles is disturbed or the generation of impulses by the sinus nodes that control the heart rhythm is disturbed. It is detected using an electrocardiogram, and its causes can be both external factors and malfunctioning of the sinus node.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
Paroxysmal tachycardia is a condition in which an attack of a rapid heartbeat suddenly occurs and stops, with a frequency of 150-300 beats per minute. There are three forms of paroxysmal tachycardia:
- Ventricular;
- Atrial;
- Nodal.
The immediate causes of this type of tachycardia are increased activity of the nervous system and dystrophic changes in the myocardium.
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation is a condition in which a chaotic contraction of myocardial fibers occurs with a frequency of 250-480 beats per minute, which leads to the absence of ventricular contractions and cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation is often a consequence of complications caused by extensive myocardial infarction.
Causes of tachycardia
The most common causes of tachycardia are disorders of the autonomic nervous system and hemodynamics, various forms of arrhythmias and disorders of the endocrine system.
Often, tachycardia is a consequence of hypertension, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and heart defects. Also, one of the causes of tachycardia is excessive consumption of caffeine, alcoholic beverages and tobacco smoking. Diseases of the thyroid gland and various infectious diseases contribute to the development of tachycardia.
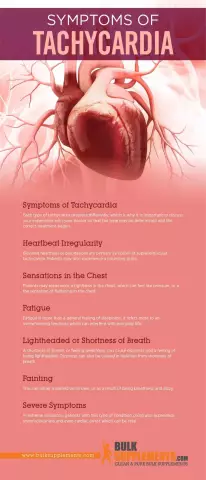
Tachycardia symptoms
The symptoms of tachycardia are:
- Chest pain;
- Confusion of consciousness;
- Dizziness;
- Hypotension;
- Heart palpitations (pulse);
- Dyspnea;
- Weakness;
- Fainting.

In some cases, tachycardia can occur without the above symptoms. In such cases, as a rule, the condition is detected by physical examination or heart monitoring.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
Diagnosis of tachycardia occurs through a medical examination, a series of examinations, analyzes and tests. Common tests for making a diagnosis are:
- Electrophysiological study, with the help of which it becomes possible to determine the source of problems of the cardiac system;
- Electrocardiography, which determines the type of tachycardia and its effect on the heart rate;
- Holter monitoring, on the basis of which it becomes possible to obtain a complete symptomatic picture of the disease.
Tachycardia treatment
The main directions of the treatment of tachycardia are to prevent its attacks in the future, to minimize the complications caused and to bring the heart rate to a normal state. Treatment of tachycardia can be medication, with the prescription of special medications, or it can consist in changing the patient's lifestyle, avoiding stressful situations and good rest.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!