- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Analyzes for vitamins and trace elements: how to prepare and where to take it, decoding
The content of the article:
- Indications for analysis for vitamins and minerals
- How to prepare for the study?
-
Minerals, their norms and deviations
- Cobalt
- Copper
- Molybdenum
- Selenium
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Vitamins, norm and deviations
An analysis for vitamins and trace elements is prescribed if there is a suspicion of their deficiency or excess. The type of research and the frequency with which it should be carried out is determined by the doctor.
Vitamins and trace elements play an important role in the regulation of biochemical processes in the human body. Their imbalance, especially if it persists for a long time, can cause many pathological processes. One should not think that only a lack of vitamins and minerals is fraught with danger to human health. Their excess is no less dangerous.
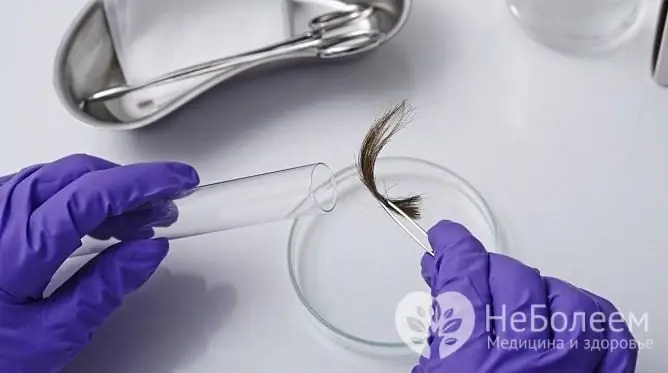
Blood, urine, hair and nails are examined for various analyzes for vitamins and minerals
If a person leads an active lifestyle, adheres to a proper diet, regularly visits the fresh air and does not have bad habits, then the development of a deficiency of vitamins and minerals is unlikely. Unfortunately, most of modern people live in ecologically unfavorable zones, suffer from excess weight due to inappropriate nutrition and physical inactivity. As a result, many complain of general weakness, increased fatigue, brittle hair and nails, sleep disturbances, frequent colds, anemia, and depressive conditions. In many cases, the cause of such ailments is not overwork, but a lack of vitamins and minerals. To identify it, a study is carried out for vitamins and trace elements (minerals).
Indications for analysis for vitamins and minerals
Experts recommend taking an analysis for vitamins and minerals on a regular basis, once a year, to the following categories of patients:
- people engaged in hard physical labor or professional sports;
- children and adolescents;
- To old people;
- suffering from chronic diseases;
- sticking to a mono diet for a long time.
In addition, it is desirable to pass such an analysis for women at the stage of pregnancy planning, breastfeeding mothers, as well as for patients with reduced immunity, signs of hypovitaminosis.
How to prepare for the study?
Depending on the content of which minerals and vitamins in the patient's body it is necessary to determine, different types of research are prescribed. The biological material used is whole blood, serum, urine, and sometimes nails or hair. Vitamin testing is usually done within one business day. A comprehensive study can last up to 10 days.
Blood for research is donated in the morning at 7-9 o'clock. After the last meal, at least eight hours should pass.
If hair is to be analyzed, it should be cut from the back of the head as close to the neck as possible. Strands are cut from several places. It is desirable that you get a small bundle of hair 3-5 cm long and 2-3 mm thick. If the hair is very short, then it should be cut just enough to fill a teaspoon. If, on the contrary, they are very long, then a piece 5 cm long, located closer to the roots, is cut from the cut strand and sent for research. Cut hair should be placed in a clean white paper envelope and taken to the laboratory. Do not store collected material in foil or plastic bag.
10-15 days before the study of hair, you should stop using medicinal shampoos, which include sulfur, zinc, selenium and other trace elements. During this period, it is recommended to use a mild baby shampoo that does not contain dyes and fragrances. Immediately before collecting the material, the hair should be washed and dried without using conditioner, serum, mask and styling products.
When collecting nails for analysis, the following rules should be observed:
- 7-10 days before the test, do not cover the nails with either medicinal or decorative varnishes;
- do not process nails with a metal file later than two days before the study;
- wash and dry hands well before cutting nails;
- nail scissors must have clean cutting surfaces;
- cut nails at least 2 mm long from all toes or hands;
- Place the cut nails in a clean white paper envelope and take them to the laboratory.
What is the name of the study for minerals and vitamins and where to take it? This type of laboratory diagnostics does not have a special name, the working name is analysis for a certain substance (vitamin or mineral). You can take it in medical laboratories, both public and private.
A comprehensive analysis includes the determination of the content of 13 vitamins and 16 minerals in the body.
Such important for the body trace elements as iron, iodine, chlorine, sodium, potassium and calcium are determined during an extended biochemical blood test, therefore, they are not considered in this article.
If acute or chronic poisoning with arsenic, heavy metals (lead, mercury, nickel, cadmium) or their compounds is suspected, their content in the body is determined during toxicological analysis. For this, blood is examined, but also urine, hair, nails. These trace elements should not normally be present in the body.
Minerals, their norms and deviations
Mineral elements are found in the human body in different concentrations, depending on which they are divided into three groups:
- Ultramicroelements - no more than 0.000009%.
- Trace elements - from 0.000009% to 0.001%.
- Macronutrients - from 0.001% to 9%.
Cobalt
It is necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous and hematopoietic systems, the synthesis of DNA molecules. Normally, its content in the blood is 0.00045-0.001 mcg / ml. The deficiency leads to the development of megaloblastic anemia, funicular myelosis, pernicious anemia. Excess has a toxic effect on the body.
Copper
Participates in the synthesis of certain proteins and enzymes. Its content in blood serum in men is normally 0.75-1.5 μg / ml, in women - 0.85-1.8 μg / ml. A lack of copper leads to damage to the musculoskeletal system and a violation of hair pigmentation, and an excess causes intoxication, manifested by nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Molybdenum
It is necessary for the synthesis of a number of enzymes. The literature describes isolated cases of its deficiency, all of them were observed in patients who had been on parenteral nutrition for a long time. Serum of an adult normally contains molybdenum 0.0004-0.0015 µg / ml.
Selenium
It is part of the enzyme that converts thyroxine into triiodothyronine. Regulates the functions of the nervous, cardiovascular and immune systems. Selenium deficiency increases susceptibility to infectious diseases and some types of cancer, and provokes mental disorders. Excess is toxic to the body. Normally, the serum selenium content is 0.07-0.12 μg / l.
Zinc
Participates in the synthesis of nucleic acids and protein, is part of more than three hundred enzymes. The concentration in the blood is from 0.75 to 1.5 μg / l.
Manganese
It is necessary for the normal development and growth of connective and bone tissue, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. The excess is clinically manifested by hypothyroidism, rickets, increased fatigue and general weakness, and neurotic syndrome. The deficiency is characteristic of diabetes mellitus, vitiligo, multiple sclerosis. The normal content of manganese in the blood is 0.007-0.015 μg / l.
Vitamins, norm and deviations
Vitamins are divided into two large groups: water-soluble and fat-soluble. The most studied of them are vitamins A, groups B, C, D, E. Both deficiency and their excess can lead to serious consequences.
Lack of vitamin A leads to the development of "night blindness", and its excess in the body of pregnant women can cause fetal development disorders. There are also indications of the role of excess vitamin A in the development of cancer.
Lack of B vitamins leads to mental disorders, liver dysfunction, memory and vision impairment, joint pain, hair loss, metabolic disorders. Vitamin B 12 deficiency leads to impaired blood formation.
Deficiency of vitamin C is manifested by bleeding gums, scurvy, nosebleeds, and decreased immunity.

For the body, both a deficiency and an excess of vitamins and minerals are equally undesirable.
Vitamin D not only enters the body with food, but is also formed in it under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Its deficiency is accompanied by softening of bone tissue (osteomalacia), and in children of the first years of life it leads to the development of rickets.
Vitamin E deficiency causes myopathy, neuromuscular disorders, as well as reproductive disorders such as infertility, spontaneous abortion in the early stages.
In clinical practice, an analysis is most often prescribed to determine the following vitamins in the blood serum:
- vitamin B 9 (norm 3.1-20.5 ng / ml);
- vitamin B 12 (norm 187-883 ng / ml);
- vitamin D (norm 25-80 ng / ml).
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.






