- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Swollen gums - what to do?
The content of the article:
- Treatment of gum edema in various pathologies
- Recommendations for patients with gum edema
- Diet for dental diseases
- Traditional medicine
-
How does swelling in the oral cavity appear and what symptoms may be accompanied by?
- Caries
- Gingivitis
- Stomatitis
- Alveolitis
- Periodontitis
- Granulating periodontitis
-
Causes of gingival edema
- Teething wisdom tooth
- Removal of a tooth
- Caries and infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
- Improper care
- Video
If a person has swollen gums, the first thing he needs to do is contact a dentist, since there can be several reasons, and each of them requires a special approach. To determine the cause of the development of edema, in addition to examination, an X-ray examination may be required, and in some cases additional diagnostics (laboratory tests, etc.).

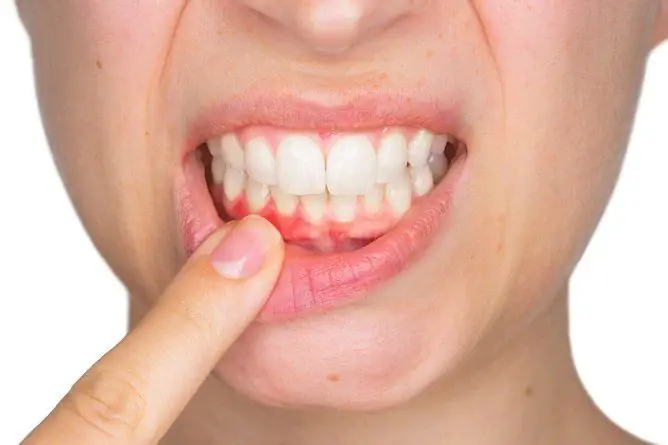
Gum swelling is most commonly caused by gingivitis, which can be due to various causes
Treatment of gum edema in various pathologies
In some cases, with swelling of the gums, rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic solution is enough to solve the problem, in others, serious treatment, including surgery, may be required.
| Pathology | Treatment |
| Teething wisdom tooth | It may be necessary to make an incision in the mucous membrane followed by rinsing with antiseptics. If the wisdom tooth is not able to take its proper place in the dentition, it may need to be removed. |
| Condition after tooth extraction | It may not require treatment, however, if inflammation develops, it is required to cleanse the hole from pus and plaque, and treat it with antiseptic agents. |
| Infectious and inflammatory process (gingivitis, periodontitis) | Sanitation, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, mainly local, but in some cases general. |
| The presence of hard dental plaque | Removal of hard dental plaque using curettage (an outdated method) or ultrasound. |
| Poor filling of a carious cavity | Grinding the filling or replacing it. |
| Poor quality prosthetics | Fitting the prosthesis. |
| Granuloma | Tooth root and granuloma resection. |
Recommendations for patients with gum edema
During treatment, a person is usually advised to use a softer toothbrush than usual, and during this period it is also recommended to choose a toothpaste without a sharp minty taste, otherwise the inflamed area will hurt more. At the same time, you cannot refuse to brush your teeth, oral hygiene is an important condition for the treatment of infectious inflammation.
If the gums are swollen, and there is no way to immediately consult a doctor, you can remove the swelling before the visit by rinsing your mouth with solutions of chamomile, sage, oak bark, which have an anti-inflammatory effect. You can rinse with a solution of table salt (1 teaspoon in a glass of water) after each meal.
Diet for dental diseases
Infectious and inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity may require the patient to follow a diet based on mechanical, chemical and thermal sparing. It is recommended to refuse spicy, spicy, sour, salty, hot dishes, as well as solid foods.
With the development of inflammation, it is recommended to drink vegetable and fruit juices (you should not choose sour fruits), eat soft, puréed foods, dairy products.
Traditional medicine
The main treatment can be supplemented with home remedies, but only after consulting a doctor:
- Gargle with aloe. Alcohol tincture of aloe is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10, the solution is rinsed in the mouth 2-3 times a day, 1 hour before meals. You can also cut off a leaf of indoor aloe and wipe it with the pulp of the gums 3 times a day.
- Rinses with an iodine-soda solution. Add 1 teaspoon of baking soda and 5 drops of iodine to a glass of hot water. Keep the solution in the mouth for about 1 minute, then spit it out and collect a new portion of the liquid. Such rinses should be carried out every hour for 3 days.
- Rinses with St. John's wort. 1 tablespoon of medicinal raw material is poured with 1 glass of boiling water, infused for 1 hour, filtered and used for rinsing the mouth 3 times a day.
- Gargle with lemon balm. 2 tablespoons of dry raw materials are poured with 1 glass of boiling water, insisted for 4 hours, rinse your mouth 3 times a day.
- Chamomile gargles. Pharmacy chamomile (1 tablespoon) is poured with boiling water (1 glass), insisted under the lid for about 30 minutes, filtered, used for rinsing the mouth 3 times a day.
- Gargle with horseradish juice. Grind 1 small horseradish root, squeeze out the juice, dilute in 1 glass of clean water, rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day. Used for severe gum swelling.
- Lemon ointment. The zest of 1 lemon is crushed, placed in a small saucepan or other suitable container, poured with olive or sunflower oil (so that it completely covers the crushed zest), the mixture is kept in a water bath for 10 minutes, after which it is infused for 3 days, the gum is lubricated with a ready-made product 3 times a day after meals.
- Banana peel and sea salt ointment. Grind (for example, with a coffee grinder) 3 tablespoons of sea salt and dried banana peel, add 2 tablespoons of chopped peel to the salt, pour a little olive oil into the mixture (to the consistency of a cream), rub the affected area in the morning and evening with the finished product.
How does swelling in the oral cavity appear and what symptoms may be accompanied by?
Caries
When the gums are swollen against the background of caries, the pain can be both acute and aching, usually a large carious cavity is noticeable. If the cavity is not visible, its presence can be suspected by food particles constantly stuck in this area.
Gingivitis
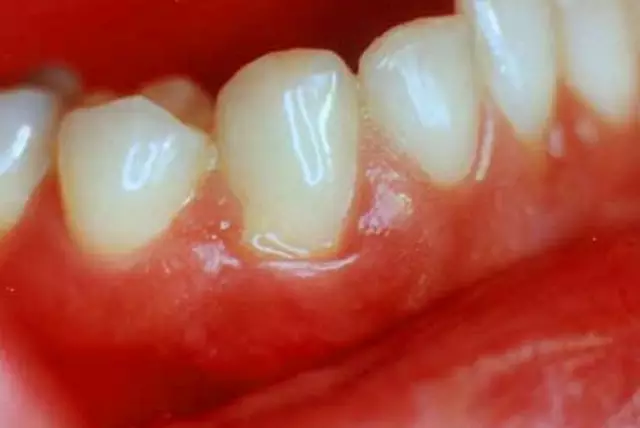
In addition to edema, patients may experience an unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth, discharge of pus from the gum pocket. With the catarrhal form of gingivitis, the mucous membrane swells, bleeds, hyperemia and pain are noted. In the case of the development of a hypertrophic form of the disease, there is an increase in the gingival papillae, bleeding.
With gingivitis, which causes vitamin C deficiency, patients experience pallor, cyanosis and / or bleeding of the gums, loose teeth, and may fall out. The general condition suffers (weakness, fatigue, susceptibility to infections).
Stomatitis
In the acute form of stomatitis, the gum tissue may become swollen, hyperemic, painful. In children, body temperature often rises, numerous aphthae appear.
Alveolitis
Alveolitis is an inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth. You can suspect a complication after tooth extraction by the following signs:
- tissue swelling lasts longer than a week, after three days it does not subside, but increases;
- body temperature rises;
- pus is released from the gum in the place of the extracted tooth;
- there is redness of the skin and / or mucous membranes;
- the general condition worsens.
Periodontitis
In case of periodontitis, in addition to soreness, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane is noted, and hard dental deposits are often visible.
Granulating periodontitis
In the presence of a fistula, the mucous membrane can not only swell, but also acquire a crimson color; near the fistulous passage, you can sometimes notice the discharge of pus. Acute pain in this pathology is usually absent.
Causes of gingival edema
Teething wisdom tooth
Severe inflammation and swelling of the gingival margin is often observed when a wisdom tooth erupts. This can happen if there is not enough space in the dentition or the tooth is in the wrong position.
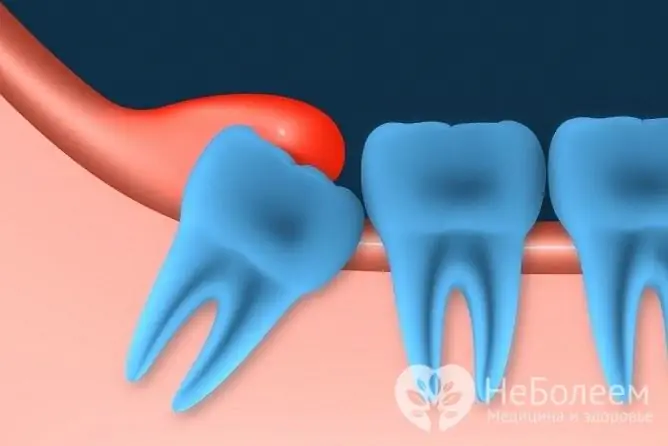
Eruption of a wisdom tooth can be painful and accompanied by swelling of the gums due to improper tooth placement
Removal of a tooth
Removal of a tooth is almost always accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane, but normally the swelling subsides no later than after 7 days. Normally, the edema does not spread to the soft tissues of the face, and there are also no strong pain sensations. In patients, a small amount of blood may be released from the well.
Caries and infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
In addition, the gums can swell if the patient has advanced caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis.
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity can swell after an injury, in the presence of a tooth cyst, fistula.
Risk factors for the development of inflammation and edema of the mucous membrane are:
- lack of oral care or lack thereof;
- the presence of allergic reactions, systemic diseases;
- stressful situations;
- chronic fatigue;
- excessive physical activity.
The inflammatory process can develop under the influence of thermal and / or chemical effects on the oral mucosa.
Improper care
The reason that the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and swollen may be due to improper oral care (both insufficient and excessive). So, a pathological process can occur when using too hard a toothbrush, excessive use of whitening toothpastes, too much pressure with a brush on the mucous membrane while brushing teeth.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.