- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Oxodolin
Oxodolin: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. For violations of liver function
- 13. Use in the elderly
- 14. Drug interactions
- 15. Analogs
- 16. Terms and conditions of storage
- 17. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 18. Reviews
- 19. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Oxodolinum
ATX code: C03BA04
Active ingredient: Chlortalidone (Chlortalidonum)
Producer: JSC "Organika" (Russia)
Description and photo update: 2019-04-10

Oxodolin is a diuretic drug.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - tablets: white with a slightly yellowish tinge or white (in a cardboard pack: 1 can of polymer or light-protective glass containing 50 tablets; 5 packs of cell contour, containing 10 tablets, as well as instructions for the use of Oxodolin).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active substance: oxodoline (chlorthalidone) - 50 mg;
- auxiliary components: calcium stearate, low molecular weight povidone, potato starch, lactose.
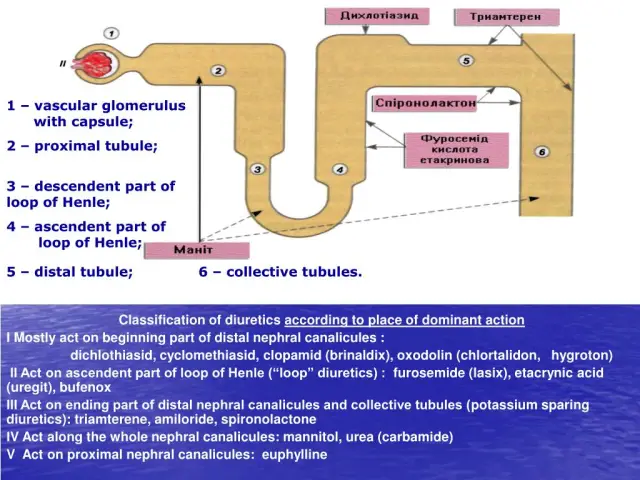
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Oxodoline is a diuretic drug. The use of the drug helps to suppress the active reabsorption of sodium ions (Na +), mostly in the peripheral renal tubules (cortical segment of Henle's loop), increasing the excretion of water and chlorine ions (Cl -). The excretion of calcium ions (Ca 2+) decreases, while the excretion of magnesium (Mg 2+) and potassium (K +) ions through the urinary system, on the contrary, increases.
Against the background of the use of the drug, blood pressure slightly decreases. The severity of the hypotensive effect of oxodoline increases gradually and is fully manifested after 14-28 days after the start of taking the tablets.
At the beginning of treatment, Oxodolin causes a significant decrease in the minute blood volume, the volume of circulating blood and extracellular fluid. After several weeks of therapy, these indicators return to a level close to the initial one.
In patients with renal diabetes mellitus, Oxodolin, similar to thiazide diuretics, causes a decrease in polyuria.
After oral administration, the diuretic effect is observed after 2-4 hours, the maximum effect occurs after 12 hours. The duration of the drug's effect is from 2 to 3 days.
Pharmacokinetics
Oxodoline absorption is 50% and is achieved within 2.6 hours after oral administration. The bioavailability of the substance is 64%.
After oral administration of 1-2 tablets (50-100 mg of oxodoline), the maximum concentration is observed after 12 hours and is, respectively, 9.4 and 16.5 mmol per 1 liter. The connection of the drug with plasma proteins is 76%.
The half-life of the drug varies from 40 to 50 hours. It is excreted unchanged through the kidneys.
Oxodoline passes into breast milk. Against the background of chronic renal failure, it can accumulate.
Indications for use
- obesity;
- chronic heart failure II degree;
- dysproteinemic edema;
- arterial hypertension;
- renal diabetes insipidus;
- nephritis;
- nephrosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver with portal hypertension.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- acute hepatitis;
- hypokalemia;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- acute renal failure with anuria;
- hepatic coma;
- severe progressive forms of nephritis and nephrosis with a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate;
- violations of water and electrolyte balance;
- gout;
- period of breastfeeding;
- children under the age of 18;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug, including sulfonamide derivatives.
Relative (Oxodolin is prescribed under medical supervision):
- allergic reactions;
- hepatic and / or renal failure;
- bronchial asthma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- elderly age.
Oxodolin, instructions for use: method and dosage
Oxodolin tablets are taken orally, usually in the morning (before breakfast).
The dosage of chlorthalidone is selected by the doctor on an individual basis, depending on the severity and nature of the pathology and the therapeutic effect obtained. With a long course of treatment, it is recommended to take tablets in the minimum effective dose, sufficient to maintain the optimal therapeutic effect, especially in elderly patients.
Patients with mild (I) degree of arterial hypertension are prescribed 50 mg of chlorthalidone 1 time per day 3 times every 7 days. The initial dose for edematous syndrome is 100 mg every other day (in most cases, taking more than 100 mg of chlorthalidone per day does not lead to an increase in its diuretic effect). In the future, the patient is transferred to a maintenance dose - from 100 to 120 mg per day 3 times in 7 days.
The initial dose of Oxodolin for renal diabetes insipidus is 100 mg 2 times a day, the maintenance daily dose is 50 mg.
Side effects
- digestive system: pancreatitis, jaundice, intrahepatic cholestasis, constipation / diarrhea, nausea, gastrospasm, vomiting;
- nervous system: apathy, disorientation, asthenia (unusual fatigue or weakness), paresthesia, dizziness;
- sense organs: visual impairment, xanthopsia;
- hematopoietic organs: aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia;
- cardiovascular system: arrhythmia (due to hypokalemia), orthostatic hypotension (its intensification is possible under the influence of sedatives, anesthetics and ethanol);
- laboratory parameters: hyperlipidemia, glucosuria, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia (gout), hypercalcemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia, including accompanied by neurological symptoms (nausea), hypokalemia;
- allergic reactions: photosensitivity, urticaria;
- others: decreased potency, muscle spasm.
Overdose
The main symptoms of a chlorthalidone overdose: drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, excessive lowering of blood pressure, convulsions, arrhythmia, hypovolemia.
Therapy: gastric lavage, oral administration of activated charcoal, symptomatic treatment, including intravenous administration of saline solutions (in order to restore the electrolyte balance of the blood).
special instructions
It is important during the period of taking the drug to periodically determine the content of electrolytes in the blood plasma, especially in patients receiving simultaneously digitalis drugs.
Patients are advised not to follow a very strict salt-free diet. In cases of development of signs of hypokalemia (heart rhythm disturbance, myasthenia gravis) or in the presence of an additional risk of potassium loss (while taking glucocorticosteroids, adrenocorticotropic hormone therapy, hyperaldosteronism, cirrhosis of the liver, as well as in case of malnutrition, diarrhea or vomiting), substitution treatment with potassium preparations is indicated.
With hyperlipidemia, constant monitoring of serum lipids is necessary. Cancellation of Oxodoline is required when an increase in their concentration is detected.
There have been reports of exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus while taking thiazide diuretics. Despite the fact that no such phenomena were observed during the treatment with chlorthalidone, its use against the background of systemic lupus erythematosus requires medical supervision.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
In the course of studies carried out on animals (rats, rabbits), which received chlorthalidone in doses exceeding the recommended therapeutic for humans up to 420 times, no adverse effect on the fetus was found.
During pregnancy, chlorthalidone is prescribed according to strict indications. As a result of therapy, it is possible to develop such adverse consequences for the fetus or newborn as jaundice, and in infants - thrombocytopenia and hypokalemia.
Since chlorthalidone passes into breast milk, Oxodolin is not used during lactation.
Pediatric use
Oxodolin is not prescribed for patients under 18 years of age, since the safety and effectiveness of its use in this age group have not been established.
With impaired renal function
The drug is not used for the treatment of patients with acute renal failure with anuria.
With caution, Oxodolin tablets are prescribed for renal failure.
For violations of liver function
- use is contraindicated: hepatic coma;
- use requires medical supervision: liver failure.
Use in the elderly
Elderly patients are prescribed Oxodolin with caution.
Drug interactions
Possible interactions of oxodoline with other substances / drugs:
- lithium preparations: the concentration of lithium ions (Li +) in the blood increases, which leads to an increased risk of intoxication with Li + preparations. If Li + causes polyuria, antidiuretic action may develop;
- carbenoxolone, amphotericin, glucocorticosteroids: enhance the hypoglycemic effect of oxodoline;
- curariform muscle relaxants, antihypertensive drugs, including monoamine oxidase inhibitors, slow calcium channel blockers, vasodilators, beta-blockers, methyldopa, guanethidine: chlorthalidone increases their clinical efficacy;
- cardiac glycosides: possible aggravation of cardiac arrhythmias resulting from digitalis intoxication;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: weaken the hypotensive and diuretic effect of oxodoline.
With the simultaneous use of Oxodoline with insulin, an increase / decrease in the dose of the second may be required; with oral hypoglycemic agents - increasing their dose.
Analogs
Oxodolin analogs are Acripamide, Arifon retard, Hypothiazide, Hygroton, Veroshpiron, Indapamide, Apo-triazide, Lasix, Furosemide, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store in a place protected from light and moisture at temperatures up to 30 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
The shelf life is 5 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Oxodolin
Since the drug is practically not on sale, reviews about Oxodolin are very rare on specialized sites. But all the patients who used the drug indicate its effectiveness.
Price for Oxodolin in pharmacies
The approximate price for Oxodolin (in a package of 1 can, containing 50 tablets) is 2,490 rubles.

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!