- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
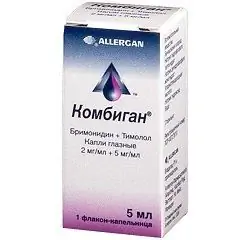
Combigan
Combigan: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. For violations of liver function
- 13. Use in the elderly
- 14. Drug interactions
- 15. Analogs
- 16. Terms and conditions of storage
- 17. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 18. Reviews
- 19. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Combigan
ATX code: S01ED51
Active ingredient: brimonidine + timolol (Brimonidine + Timolol)
Producer: Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland (Ireland)
Description and photo update: 2019-12-07
Prices in pharmacies: from 498 rubles.
Buy
Combigan is a combined ophthalmic drug with antiglaucoma action (nonselective beta-blocker + alpha 2-adrenergic agonist).
Release form and composition
The drug is available in the form of eye drops, which are a clear solution of greenish-yellow color (5 ml each in plastic dropper bottles with a capacity of 10 ml, 1 or 3 dropper bottles in a cardboard box and instructions for use of the Combigan).
Composition for 1 ml drops:
- active ingredients: timolol (in the form of timolol maleate) - 5 mg, brimonidine tartrate - 2 mg;
- auxiliary components: sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate, sodium hydroxide, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, benzalkonium chloride, hydrochloric acid, water.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The Kombigan contains two active components - timolol and brimonidine. Timolol is a beta-adrenergic receptor blocker, and brimonidine is an adrenergic agonist that stimulates alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Both substances are able to reduce increased IOP (intraocular pressure), but due to the combined interaction, a more pronounced hypotensive effect is achieved compared to the antihypertensive properties of these substances separately.
The properties of the active components of Kombigan, which determine its pharmacological effectiveness:
- timolol: refers to non-selective beta-blockers, it does not have internal membrane stabilizing and sympathomimetic activity. A decrease in IOP is provided by a decrease in the secretion of intraocular fluid, however, the exact mechanism of action of timolol has not been established. It is assumed that it is associated with the suppression of the synthesis of cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate) and is caused by endogenous stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors;
- brimonidine: is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist, acting primarily on alpha2-adrenergic receptors (selectivity for alpha1-adrenergic receptors is 1000 times lower). The selective effect of brimonidine is expressed in the absence of vasoconstriction in the microvasculature and in the absence of mydriasis. The hypotensive effect of the substance is due to a decrease in the formation of intraocular fluid and an increase in its uveoscleral outflow.
Pharmacokinetics
In the blood plasma, the average maximum concentrations of timolol and brimonidine after the use of Combigan eye drops were 0.406 and 0.0327 ng / ml, respectively.
About 80% of timolol, used in the form of eye drops, enters the systemic circulation. The absorption of the substance is carried out through the vessels of the lacrimal tract, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and the conjunctiva. After instillation of the drug, the maximum concentration of timolol in the aqueous humor of the eye is noted after 1-2 hours. T 1/2 from plasma is approximately 7 hours. Plasma protein binding is negligible. Timolol is partially metabolized in liver tissues; excreted by the kidneys unchanged and in the form of metabolites.
Plasma concentration of brimonidine after instillation of 0.2% solution of the drug is very low. Brimonidine is slightly metabolized in the tissues of the eye. About 29% of the substance binds to plasma proteins. After topical application of Combigan T 1/2 brimonidine is approximately 3 hours. More than 74% of the absorbed drug is excreted as metabolites within 5 days. Excretion is carried out by the kidneys. Unchanged brimonidine is not detected in urine. In vitro studies carried out on human and animal liver cells have shown that cytochrome P450 and aldehyde oxidase are actively involved in the metabolism of the drug, that is, systemic excretion of brimonidine is primarily determined by its hepatic metabolism.
Indications for use
Combigan is used in patients with open-angle glaucoma, as well as in ophthalmic hypertension (increased IOP), if local therapy with beta-blockers is not effective enough.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- heart failure;
- sinus bradycardia;
- cardiogenic shock;
- AV block II-III degree (if there is no implanted artificial pacemaker);
- severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, episodes of bronchial obstruction, bronchial asthma and other cases of increased airway reactivity;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years old;
- lactation period;
- simultaneous administration of tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants, as well as MAO (monoamine oxidase) inhibitors;
- hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary components of eye drops.
Relative (Combigan is used with caution):
- hepatic and / or renal failure;
- unstable severe cardiovascular pathologies;
- metabolic acidosis (violation of the acid-base state of the blood);
- pheochromocytoma (untreated);
- diabetes mellitus and cases of hypoglycemia (if there is no appropriate therapy);
- orthostatic hypotension;
- coronary or cerebral insufficiency;
- Buerger's disease (thromboangiitis obliterans);
- Raynaud's syndrome;
- depression;
- intravenous administration of slow calcium channel blockers or lidocaine (due to the risk of heart failure, bradycardia, inhibition of AV conduction and a drop in blood pressure);
- combined use with X-ray contrast agents;
- simultaneous prescribing or changing the doses of drugs taken from the groups of adrenergic blockers, adrenomimetics and other drugs that affect adrenergic transmission (due to the risk of possible drug interactions or changes in their medicinal properties).
Combigan, instructions for use: method and dosage
Combigan eye drops are intended for topical use. The drug is instilled into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye. A single dose for adults (including the elderly) is 1 drop, the frequency of application is twice a day. The interval between instillations is at least 12 hours.
Combigan can be used in conjunction with other ophthalmic agents to lower IOP. When using more than two drugs at the same time, instillations should be carried out at intervals of at least 5 minutes.
After instillation of the product, as with any other eye drops, it is recommended to press on the area in the area of the lacrimal sac projection (at the inner corner of the eye) for one minute. This reduces the possible systemic absorption of the Combigan.
Side effects
Most often, after the use of Combigan, hyperemia of the conjunctiva of the eye (in about 15% of patients) and a burning sensation of the mucous membrane (in 11% of patients) occurred. The severity of the listed adverse reactions was insignificant, treatment cancellation was required only in 3.4% and 0.5% of cases (with hyperemia and burning sensation, respectively).
In addition, side effects from the following systems and organs have been noted:
- gastrointestinal tract: often - dryness of the oral mucosa; infrequently - dysgeusia (perverted taste perception);
- respiratory system: infrequently - dryness of the nasal mucosa, rhinitis;
- cardiovascular system: often - increased blood pressure; infrequently - palpitations, congestive heart failure;
- nervous system and psyche: often - headache, drowsiness, depression; infrequently - fainting, dizziness;
- organ of vision: very often - a burning sensation of the mucous membrane of the eye, conjunctival hyperemia; often - itching of the eyelid skin, irritation and dryness of the mucous membrane, acute stabbing or burning pain in the eye, superficial keratitis, blepharitis, discharge from the eye, foreign body sensation, lacrimation, corneal erosion, conjunctival folliculosis, allergic conjunctivitis, visual impairment; infrequently - conjunctivitis, photophobia, edema of the conjunctiva, soreness of the eyelids, follicular conjunctivitis, floating precipitates in the vitreous body, decreased visual acuity, corneal edema, pallor of the conjunctiva, allergic blepharitis, visual fatigue, eye muscle rupture, vitreous hypertrophy
- skin and subcutaneous fat: often - redness and itching of the eyelid skin, eyelid edema; infrequently - allergic contact dermatitis;
- laboratory tests: often - increased activity of hepatic transaminases;
- other reactions: often - asthenia.
Since the advent of the Combigan on the market, additional side effects from the cardiovascular system have also been reported in post-marketing studies: tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia and a decrease in blood pressure. The frequency of their occurrence is unknown.
The likelihood of the appearance of undesirable side effects that were observed when using the active ingredients separately cannot be ruled out. So, brimonidine can cause side effects from the following systems and organs:
- gastrointestinal tract: dyspeptic disorders, dysgeusia;
- respiratory system: shortness of breath, inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- nervous system and psyche: insomnia;
- organ of vision: constriction of the pupil, iridocyclitis;
- other effects: systemic allergic reactions.
The following systemic organ side effects have been reported with timolol:
- gastrointestinal tract: dyspepsia, nausea, loose stools;
- respiratory system: cough, shortness of breath, bronchospasm (most often in patients with a history of broncho-obstructive diseases), respiratory failure;
- cardiovascular system: Raynaud's syndrome, complete transverse heart block, cerebrovascular accident, cold extremities, intermittent claudication, cardiac arrest;
- nervous system and psyche: cerebral ischemia, nightmares, memory loss, insomnia, paresthesia, decreased libido, worsening of symptoms of myasthenia gravis;
- organ of vision: diplopia, changes in refraction (usually due to the cancellation of miotic therapy), decreased sensitivity of the cornea of the eye, drooping of the upper eyelid, rupture of the choroid (after filtration surgery);
- organ of hearing: tinnitus;
- connective tissue: systemic lupus erythematosus;
- skin and subcutaneous fat: exacerbation of psoriasis or psoriasis-like rash, pathological hair loss;
- other reactions: chest pain, peripheral edema, fibrosis of the tunica albuginea of the cavernous bodies of the penis.
Overdose
In case of an overdose of brimonidine, when applied topically, the patient has a decrease in body temperature, cyanosis, bradycardia, apnea, a decrease in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
The classic symptoms of an overdose of brimonidine with its accidental ingestion include: lowering blood pressure, apnea, bradycardia, depression of the central nervous system, lower body temperature, short-term confusion or loss of consciousness, coma. When these symptoms appear, an urgent hospitalization of the patient is required (in some situations, the patient was intubated). In all reported cases of brimonidine poisoning, full recovery of functions was noted in the period from 6 to 24 hours.
In addition to the signs described above, in case of an overdose of drugs from the group of alpha2-adrenergic agonists, the following disorders may also occur: vomiting, arrhythmias, asthenia, drowsiness, pupil constriction, sedation, convulsions and respiratory depression.
Dizziness, headache, bradycardia, bronchospasm, decreased blood pressure, and cardiac arrest have been reported with timolol overdose. Hemodialysis is not effective enough to eliminate timolol.
In the case of a diagnosed overdose of Combigan, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
special instructions
To avoid infection of the contents of the vial and the eye, it is forbidden to touch the tip of the vial with the drug to any surfaces or the cornea.
Like other topical ophthalmic agents, Combigan eye drops can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Treatment with the drug should be discontinued if any allergic reactions occur.
In patients with severe impairment of renal function, who are on hemodialysis, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is observed during therapy with timolol.
Beta-blockers can reduce or completely block the effect of epinephrine administration in patients with severe anaphylactic reactions and atopic manifestations of allergens. In addition, beta-blockers can worsen the course of vascular diseases, Prinzmetal angina pectoris, arterial hypotension, hide the signs of hyperthyroidism and mask the symptoms of acute hypoglycemia (palpitations, tachycardia, sweating).
Drugs from the group of beta-blockers, including Kombigan, should be canceled gradually, since abrupt cancellation increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction and sudden death.
Benzalkonium chloride, which is part of the drops as an auxiliary component, can irritate the mucous membrane of the eye. Before instilling Kombigan, contact lenses must be removed. They can be put back on 15 minutes after instillation.
The drops should be used within 28 days after opening the bottle. After the specified period, the drug should be disposed of, even if a sufficient amount of solution remains in the vial. Such measures avoid contamination of the droplets. The patient is advised to write down the date of opening the dropper bottle on the carton.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
After instillation of the Combigan, the patient may experience temporary blurred vision, weakness and drowsiness. When these symptoms appear, one should refuse to perform work that requires a high concentration of attention and a quick reaction (driving a car, controlling other mechanisms, the work of a dispatcher, etc.).
Application during pregnancy and lactation
The effect of Kombigan on the course of pregnancy, as well as the growth and development of the fetus has not been studied.
There are no data on the use of brimonidine in women during pregnancy. Studies in animals have shown that high doses of the drug have reproductive toxicity, but the degree of this risk to humans has not been determined.
Ultra-high doses of timolol have also shown reproductive toxicity in animal studies. Congenital malformations of the fetus have not been identified, however, it is known that when taking beta-blockers inside, there is a risk of intrauterine growth retardation. Symptoms typical for drugs from the group of beta-blockers (respiratory dyspnea, bradycardia, hypoglycemia, low blood pressure) were identified in newborns whose mothers took beta-blockers until delivery.
If pregnant women used Combigan before the very beginning of labor, it is necessary to establish constant monitoring of the newborn during the first few days of life.
During pregnancy, Combigan should be prescribed only in special cases.
Preclinical studies of timolol and brimonidine have shown that these substances are secreted in breast milk, therefore, breastfeeding should be suspended during treatment.
Pediatric use
The combigan is contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under the age of 18 years.
With impaired renal function
Eye drops are used with caution in patients with renal failure.
For violations of liver function
Combigan is used with caution in patients with hepatic insufficiency.
Use in the elderly
Combigan is used according to the prescribed dosage regimen for the treatment of adult patients, including elderly patients.
Drug interactions
Studies aimed at studying the possible interaction of Combigan with other drugs have not been conducted. However, it must be borne in mind that when used simultaneously with drugs and substances that depress the central nervous system (barbiturates, general anesthetics, sedatives, alcohol and opium derivatives), the effects of the latter may increase.
Timolol can increase the risk of a serious decrease in blood pressure and aggravate compensatory tachycardia when used together with drugs for general anesthesia, so the anesthesiologist should be warned about the use of Combigan eye drops before the planned surgery.
Taking epinephrine and timolol together can cause pupil dilation (mydriasis).
Beta-blockers can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia and enhance the hypoglycemic effect of the corresponding drugs.
Against the background of treatment with beta-blockers, it is possible to increase the hypertensive reaction to abrupt withdrawal of clonidine.
Quinidine, slowing down the metabolism of timolol, can increase its hypotensive effect; ethanol, hydralazine and cimetidine are capable of increasing the plasma concentration of timolol.
Combigan should be used with caution together with drugs that affect the absorption and metabolism of circulating catecholamines (reserpine, methylphenidate, chlorpromazine, etc.). Combined use with MAO inhibitors is contraindicated (treatment with the drug can be started no earlier than 14 days after stopping therapy with MAO inhibitors).
Oral antiarrhythmics, slow calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers or guanethidine, parasympathomimetics or cardiac glycosides, when used simultaneously with eye drops containing timolol, caused severe bradycardia and / or a significant decrease in blood pressure, which is due to the potentiation of the effects of these drugs.
Analogs
Kombigan's analogs are Azarga, Alfagan R, Arutimol, Ganfort, Dorzopt Plus, Cosopt, Ksalak, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Keep out of the reach of children. Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C in a dark place.
The shelf life of eye drops is 1 year and 9 months.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Kombigan
In a few reviews of the Combigan, patients note its effectiveness, which is provided by the combined composition of the drops. They describe that the burning sensation is less than that from the use of pure timolol, and the effect is stronger than when its components are used in the form of separate drugs. To achieve the required therapeutic effect, it is enough to instill one drop of Combigan at a time.
In some cases, they indicate such adverse reactions as blurred vision, swelling of the upper eyelid, general weakness and a sharp drop in blood pressure. If undesirable side effects occur, both patients and doctors recommend discontinuing therapy and picking up similar drops for topical use.
Price for Combigan in pharmacies
The price of the Combigan in the form of eye drops (in dropper bottles of 5 ml, in a cardboard box 1 bottle) ranges from 710 to 800 rubles.
Combigan: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Combigan 2 mg + 5 mg / ml eye drops 5 ml 1 pc. 498 r Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!