- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
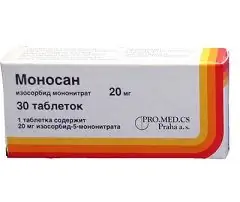
Monosan
Monosan: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. For violations of liver function
- 13. Use in the elderly
- 14. Drug interactions
- 15. Analogs
- 16. Terms and conditions of storage
- 17. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 18. Reviews
- 19. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Monosan
ATX code: C01DA14
Active ingredient: isosorbide mononitrate (isosorbide mononitrate)
Manufacturer: PRO. MED. TSS Praha a.o. (Czech Republic)
Description and photo update: 2019-20-08
Prices in pharmacies: from 64 rubles.
Buy
Monosan is a peripheral vasodilator with a predominant effect on venous vessels, an antianginal agent.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - tablets: flat, round, almost white or white, on one side of the risk (10 tablets in blisters, 3 blisters in a cardboard box).
Active ingredient: isosorbide-5-mononitrate, its content in 1 tablet is 20 or 40 mg.
Additional components: microcrystalline cellulose, granular lactose, corn starch, talc, magnesium stearate.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Monosan is a drug that has a vasodilator, antianginal, arteriodilatory and hypotensive effect.
The active ingredient of Monosan is isosorbide mononitrate, a peripheral vasodilator that affects mainly the venous vessels. In the vascular endothelium, it stimulates the formation of nitric oxide (an endothelial relaxing factor), which causes the activation of intracellular guanylate cyclase, as a result of which the mediator of vasodilation, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), increases.
Isosorbide mononitrate reduces pre- and afterload by decreasing myocardial oxygen demand. Possesses coronary dilating properties. Reduces blood flow to the right atrium and pressure in the pulmonary circulation, promotes the redistribution of coronary blood flow in areas with reduced blood circulation, as well as regression of symptoms in pulmonary edema.
With angina pectoris and coronary heart disease, it increases exercise tolerance. Expands the vessels of the brain and dura mater, which can lead to headaches. Reduces intraplatelet Tx synthesis, inhibits platelet aggregation.
As with other nitrates, cross-tolerance develops to isosorbide mononitrate. After the cancellation of Monosan (including after a temporary break in treatment), the body's sensitivity to the drug is quickly restored.
The antianginal effect develops within 30-45 minutes after taking Monosan and lasts for 8-10 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration of isosorbide, mononitrate is completely and rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
The drug does not have the effect of the first passage through the liver, therefore it is characterized by a very high bioavailability - about 100%. Does not bind to blood plasma proteins.
The maximum concentration in the blood reaches within 1 hour. Individual differences in patients do not significantly affect plasma concentration values. The effective blood level of isosorbide mononitrate is approximately 100 mg / ml.
When using Monosan in the dose range from 10 to 80 mg, the pharmacokinetics are linear. Unlike isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate is metabolized not in the liver, but in the kidneys to form isosorbide and two glucuronides isosorbide-5-mononitrate.
It is excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of glucuronic metabolites, unchanged - no more than 2%. The half-life is 4-5 hours. Renal clearance - 115 ml / min. In hepatocellular and renal failure, the pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug do not change significantly.
Indications for use
Combination therapy:
- Chronic heart failure;
- Pulmonary heart;
- Pulmonary hypertension.
Monosan is also used to prevent angina attacks in patients with coronary heart disease.
Contraindications
- Cardiac tamponade;
- Left ventricular failure with low diastolic pressure;
- Arterial hypotension and arterial hypovolemia (systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure below 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure below 4-5 mm Hg);
- Acute myocardial infarction, accompanied by severe arterial hypotension;
- Closed-angle glaucoma;
- Vascular collapse;
- Shock;
- Diseases accompanied by increased intracranial pressure (including hemorrhagic stroke, as well as traumatic brain injury);
- Toxic pulmonary edema;
- Age under 18;
- Hypersensitivity to the drug or other nitrates.
According to the instructions, according to indications, Monosan should be used with extreme caution in the following cases:
- Aortic and / or mitral stenosis;
- Tendency to orthostatic disorders of vascular regulation;
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- Constrictive pericarditis;
- Severe renal failure;
- Liver failure;
- Severe anemia;
- Thyrotoxicosis;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Elderly age.
Instructions for the use of Monosan: method and dosage
Monosan should be taken orally after meals: swallow the tablets whole and drink them with a sufficient amount of liquid.
The doctor sets the optimal dose individually for the patient, depending on the severity of the disease.
At the beginning of therapy, usually 10-20 mg is prescribed 1 to 3 times a day. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, from the 3-5th day of treatment, the pink dose is increased to 40-60 mg.
The highest permitted daily dose is 80 mg.
Side effects
- Allergic reactions: skin rash; in rare cases - exfoliative dermatitis;
- From the side of the central nervous system: blurred vision, drowsiness, stiffness, decreased speed of mental and motor reactions (especially at the beginning of treatment); in rare cases - cerebral ischemia;
- From the digestive system: a slight burning sensation of the tongue, dry mouth, nausea and / or vomiting;
- From the side of the cardiovascular system: transient hyperemia of the facial skin, "nitrate" headache, vertigo, a marked decrease in blood pressure, a feeling of fever, tachycardia; in rare cases - orthostatic collapse, paradoxical intensification of angina attacks;
- Others: tolerance, including cross-tolerance to other nitrates.
Overdose
Overdose symptoms: hyperthermia, increased sweating, skin redness, weakness, headache, lethargy, dizziness, visual disturbances, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, reflex tachycardia, fainting, collapse, increased intracranial pressure, dyspnoea, hypoderpnoea,; more often in case of chronic overdose), convulsions, paralysis, coma.
First of all, the usual first aid measures are taken: they do a gastric lavage, the patient is laid in a horizontal position and his legs are raised. The indicators of vital body functions should be monitored and adjusted if necessary. With severe arterial hypotension and / or shock, the replenishment of the circulating blood volume is indicated. In exceptional cases, norepinephrine and / or dopamine are administered to improve blood circulation. Administration of adrenaline (epinephrine) and related compounds is contraindicated. With methemoglobinemia, depending on its severity, ascorbic acid in the form of sodium salt is prescribed intravenously, hemodialysis, oxygen therapy, exchange transfusion.
special instructions
Monosan is not intended to relieve angina attacks.
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor blood pressure and heart rate.
Patients with arterial hypertension should be prescribed Monosan in combination with drugs with a positive inotropic effect.
In the case of frequent intake and / or use of high doses of the drug, tolerance may develop. If this happens, after 3-6 weeks of treatment, it is recommended to temporarily (for 24-48 hours) cancellation of Monosan or a break in therapy for 3-5 days with replacement of isosorbide-5-mononitrate at this time with another antianginal agent.
It is not recommended to abruptly cancel the drug, you should gradually reduce its dose.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
Since the drug can affect the rate of psychophysical reactions, care must be taken when driving a car and working in potentially hazardous industries.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
The data on the use of isosorbide mononitrate in pregnant and lactating women is not enough to establish the degree of its safety, therefore, Monosan during pregnancy and lactation can only be used as directed by a doctor, who must first assess the ratio of benefits to the woman and possible risks to the fetus / child. Children whose mothers take the drug during breastfeeding should be under constant medical supervision in order to identify the possible development of side effects in time.
Pediatric use
Monosan is contraindicated for the treatment of children and adolescents under the age of 18.
With impaired renal function
With severe renal failure, Monosan should be used with caution.
For violations of liver function
In patients with concomitant hepatic insufficiency, the risk of developing methemoglobinemia is increased, therefore, Monosan, if indicated, should be taken with caution, under the supervision of the attending physician.
Use in the elderly
Monosan should be used with caution in old age.
Drug interactions
- Dihydroergotamine: its concentration in blood plasma increases;
- Barbiturates: biotransformation is accelerated and the concentration of isosorbide-5-mononitrate in the blood decreases;
- Antihypertensive drugs, peripheral vasodilators, tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics, slow calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, quinidine, sildenafil, novocainamide, dihydroergotamine, ethanol: increased hypotensive effect;
- Slow calcium channel blockers, propranolol, amiodarone, acetylsalicylic acid: increased antianginal effect;
- Alpha-blockers, beta-adrenostimulants: the severity of the antianginal action of Monosan decreases, as a result of which an excessive decrease in blood pressure and the development of tachycardia are possible;
- M-anticholinergics (for example, atropine): the risk of increased intraocular pressure increases;
- Adsorbents, coating and astringent preparations: the absorption of isosorbide-5-mononitrate from the gastrointestinal tract is reduced.
Analogs
Monosan analogs are: Monocinque, Cardiket, Isoket, Pectrol, Efoks 20, Efoks long.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store at temperatures from 15 to 25 ºС out of reach of children, dry and protected from light.
Shelf life is 4 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Monosan
Reviews about Monosan are positive. Patients note that the drug significantly reduces the frequency of angina attacks and increases exercise tolerance, as a result of which shortness of breath decreases, the feeling of lack of air disappears, and the quality of life improves. Monosan is well tolerated and rarely causes side effects.
Price for Monosan in pharmacies
Approximate prices of Monosan: 30 tablets of 20 mg - 70-90 rubles, 30 tablets of 40 mg - 140-179 rubles.
Monosan: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Monosan 20 mg tablets 30 pcs. RUB 64 Buy |
|
Monosan 20mg tablets 30 pcs. RUB 85 Buy |
|
Monosan 40 mg tablets 30 pcs. RUB 90 Buy |

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!