- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Insulin
Instructions for use:
- 1. Pharmacological action
- 2. Release form
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Method of application
- 5. Side effects
- 6. Contraindications to use

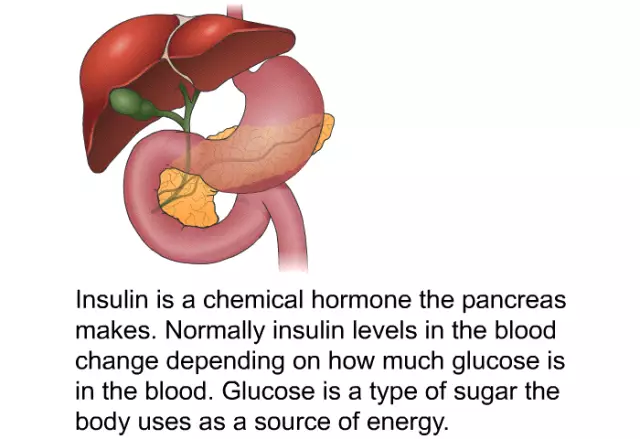
Insulin is a drug based on the pancreatic hormone.
pharmachologic effect
Insulin, which is found in our blood, is a hormone that regulates carbohydrate metabolism, lowers blood sugar levels, and helps metabolize glucose.
A person needs to receive insulin from the outside in cases where the pancreas stops producing it in sufficient quantity or produces too much. The level of insulin in the blood of a healthy person is 3-20 μU / ml. In case of deviations from the norm to the lower side, type 1 diabetes develops, and with increased insulin, type 2 diabetes develops.
Artificial insulin for medical purposes is produced from the glands of the pancreas of pigs, cattle, and genetic engineering is also used.
Release form
The drug is released in the form of a solution, 1 ml of which contains 20, 40, 80 U of insulin.
Indications for the use of Insulin
The main application of the drug is the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus. In some cases, it is also used for type 2 diabetes.
A small dose of insulin (5-10 units) is used to treat hepatitis, cirrhosis in the initial stage, with exhaustion, furunculosis, acidosis, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis.
The drug can be used for the depletion of the nervous system, for the treatment of alcoholism, some forms of schizophrenia.
Mode of application

Basically, the drug is injected into the muscle or under the skin, in severe cases with a diabetic coma, it is administered intravenously.
The required dose of the drug is determined individually according to the test results, incl. data on the level of sugar, insulin in the blood, so only the average allowable norms can be cited.
The required dose of insulin for diabetes mellitus ranges from 10-40 IU per day.
With a diabetic coma, no more than 100 U per day can be injected subcutaneously, and with intravenous administration, no more than 50 U per day.
For other indications, the drug is prescribed in small doses - 6-10 IU / day.
For insulin injections, a special syringe is used, with a built-in needle, the design of which provides for the introduction of all its contents without residue, which allows you to adhere to the exact dosage of the drug.
Before filling the syringe with insulin in the form of a suspension, the contents of the vial should be shaken to form a uniform suspension
Usually the daily dose is administered in two to three doses. The injection is done half an hour, an hour before meals. The action of insulin, its one-time dose, begins in half an hour, an hour and lasts 4-8 hours.
The effect of intravenous insulin begins after 20-30 minutes, the sugar level drops to the initial one after one to two hours.
Side effects
With the introduction of the drug subcutaneously, lipodystrophy may develop. Also, the drug can cause allergies.
Elevated insulin due to overdose can lead to hypoglycemic shock. Symptoms: increased salivation, sweating, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, palpitations, rarely - coma, convulsions, delirium, loss of consciousness.
Contraindications to the use of Insulin
Insulin is contraindicated in: acute hepatitis, hemolytic jaundice, liver cirrhosis, renal amyloidosis, urolithiasis, decompensated heart defects, duodenal ulcer, stomach, diseases accompanied by hypoglycemia.
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!