- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Typhus
Brief description of the disease

Typhus belongs to the category of acute anthroponotic diseases. It is characterized by severe intoxication of the body, feverish conditions, damage to the cardiovascular, nervous and other vital systems of the body.
The causative agent of epidemic typhus is Provacek's rickettsia. It enters the human body through the skin. The initial accumulation of harmful microorganisms occurs in the lymph nodes, then they enter the circulatory system and spread to other organs. The most severe complications of typhus disease are in the activity of the brain, adrenal glands and myocardium.
Epidemiology of infection
The carrier of the causative agents of epidemic typhus is an infected person, and the carriers are head and body lice, which multiply rapidly in unsanitary conditions. It is for this reason that epidemic typhus is also known to us as "war fever", because soldiers, often unable to wash themselves, have suffered from this infection for several millennia. The transmission mechanism of typhus is extremely simple. The lice move to the body of the new host and, when bitten, inject a large amount of rickettsia into it, which are then rubbed even deeper into the skin when scratching the itchy area. The rapid spread of lice, and the short incubation period of the disease often lead to epidemics, however, in the territory of the Russian Federation, outbreaks of infection have not been recorded for more than half a century. In part, this fact explains the effective prevention of typhus. It also exerts its influence on a noticeable increase in the quality of life of ordinary people.
Symptoms of typhus and the clinical picture
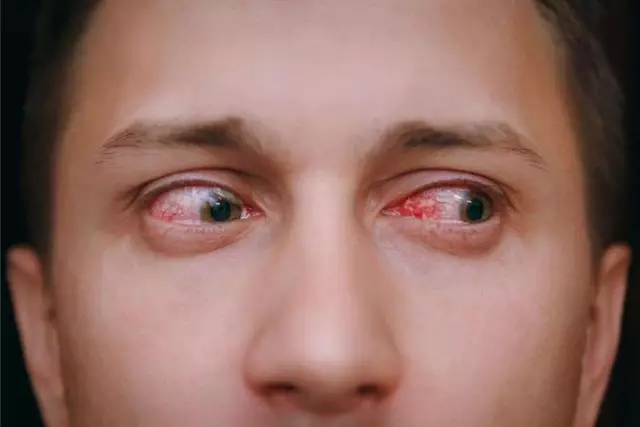
Epidemic typhus begins acutely. Within a few days, the patient's body temperature rises to critical levels. Typhus sufferers feel severe headache, insomnia, and constant vomiting. Sometimes they have neuropsychiatric disorders, manifested in a darkening of consciousness and euphoria. The skin of the face of infected people is hyperactive, the injection of the sclera vessels is pronounced. Already in the first days after the first symptoms of typhus appear, patients have heart problems. Typhoid fever leads to hypotension, severe tachycardia, muffled heart rhythms.
Palpation of internal organs in patients with typhus reveals an increase in the liver and spleen. In some cases, the development of typhus is accompanied by suppression of urinary reflexes. Urine is excreted literally drop by drop, which causes a person severe suffering and worsens his psychological state.
On the 5-6th day of illness, a characteristic rash appears on the skin of sick people. The most large-scale accumulations of it are observed on the lateral surfaces of the trunk and limbs. The severe course of the disease contributes to the spread of rashes to the face and neck, and can lead to the development of meningeal syndrome. With adequate treatment, epidemic typhus is completely cured within 1-2 weeks after the first symptoms appear.
Diagnosis of typhus
To make a correct diagnosis of typhus, specialists use differential and laboratory methods. In the first case, the doctor must separate the symptoms of typhoid from similar manifestations of other diseases - influenza, pneumonia, measles, syphilis, meningococcal infection and sepsis. Serological tests are used to detect parasites in the blood. It should only be noted that positive results can be obtained no earlier than 2 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Possible complications
Since, when diagnosed with typhus, the symptoms indicate damage to the heart, lungs and genitourinary system, complications, first of all, are localized in these organs. The most dangerous of them are adrenal insufficiency and infectious toxic shock. In addition, the development of pneumonia, thromboembolism and thrombophlebitis is possible.
Treatment for typhus

If there is any suspicion of epidemiological typhus, patients are subject to immediate hospitalization. They are assigned to bed rest, which remains until the patient has a normal temperature for at least 5-6 days. Patients with typhus are prescribed tetracycline drugs and chloramphenicol. Simultaneously with etiotropic therapy, detoxification therapy is performed by introducing infusion solutions.
Prevention of typhus
The main measures for the prevention of typhus are aimed at registering cases of lice, hospitalization of patients with fever of unknown etiology, and timely serological examinations. Children's groups and people living in hostels deserve special attention. When typhus is detected, patients are subject to isolation with disinfection and disinsection of their personal belongings.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!