- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Annular granuloma

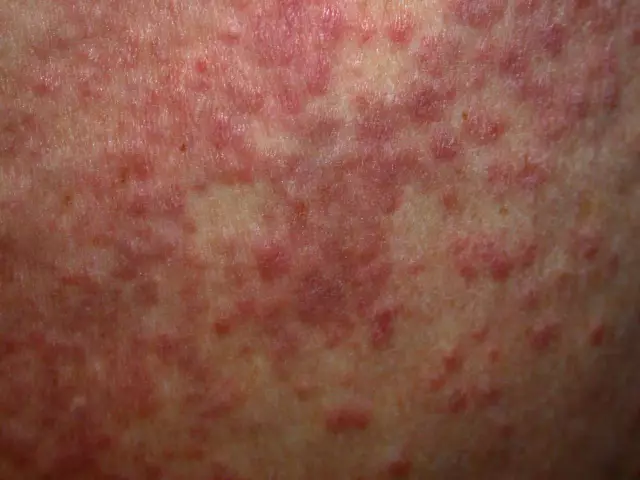
A chronic skin disorder characterized by the appearance of raised, dense nodules that form a ring with slightly receding or normal skin in the center is called granuloma annulus.
The disease in most cases is asymptomatic and does not require special treatment, however, to speed up the healing of nodules, the doctor may prescribe corticosteroid creams or subcutaneous administration of corticosteroids. According to statistics, granuloma annular occurs in 0.4% of patients with dermatological diseases.
The cause of the granuloma remains unknown, however, pathologies of the immune system are assumed, against the background of which delayed-type allergic reactions develop and cellular immunity is impaired. Factors predisposing to annular granuloma are:
- Sarcoidosis and Tuberculosis;
- Conducting tuberculin tests;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Autoimmune thyroiditis;
- Rheumatism and vasculitis;
- Long-term vitamin D intake;
- Skin trauma, sunburn and insect bites;
- Diabetes.
The following forms of annular granulomas are distinguished:
- Disseminated;
- Subcutaneous;
- Perforating;
- Localized.
In medical practice, there are often cases when the annular granuloma developed at the site of scars and tattoos, after shingles and warts.
Symptoms of granuloma annulare
The main symptom of annular granuloma is the appearance of yellowish nodules on the patient's skin, or the shade of the skin surrounding the affected area. These nodules can form one or more rings and often appear on the feet, hands, arms and legs of adults and children. Granuloma annulare usually does not cause itching or pain at the site of occurrence.
Annular granuloma in children
The most common form of granuloma among children is localized, it occurs in 90% of cases. One or more foci with dense dermal papules appear on the extensor surfaces of the hands, arms, feet and legs, less often in the periorbital region. The color of the formations usually coincides with the tone of the surrounding skin, or is slightly reddish, papules are located in the form of an arc or ring 2-5 cm or more in size, the central area of the focus and the epidermis usually remain unaffected.
The local annular granuloma in children spreads along the periphery, partially recurring or resolving in the same place. In medical practice, there have been cases when children have rings nested one inside another, resembling erythema multiforme exudative.
The subcutaneous form of annular granuloma occurs exclusively in children under the age of 6 years, it has the appearance of single or multiple deep, clinically unexpressed, subcutaneous or dermal nodules on the elbows, periorbital zone, forearms, legs, fingers, the back of the hands and on the scalp. A feature of this type of granuloma is that the nodes that form on the scalp are in all cases tightly connected to the periosteum, while the nodes on the limbs are mobile, and only in rare cases are associated with the fascia.
Disseminated granuloma annulare in children is extremely rare, mainly in adults aged 50 and older. The manifestations of the disease are widespread throughout the body, and more often in the distal parts of the limbs and trunk, papules of a purple hue or skin color. The tendency to annularity in such skin formations is absent; polyformism of the rash is noted.
Perforating granuloma annulus occurs mainly in children and adults under the age of 30. On the hands or fingers of patients, papules with plugs appear in the center, which secrete a gelatin-like content, after which foci and crusts with an umbilical depression in the center are formed. These formations develop over time into large plaques, with atrophic hyper- or hypopigmented scars.
Diagnostics of the annular granuloma
When nodules appear, the patient needs to seek help from a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist, who, according to the clinical picture, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. Only in the most doubtful cases, a patient can take a skin sample in the affected granuloma site.
Treatment of granuloma annulare
Usually, the disease does not require special treatment and goes away by itself. For faster skin healing, your doctor may prescribe creams that contain corticosteroids, or intradermal corticosteroid medications. It is important to apply an occlusive dressing on top of the skin after applying the ointment.
The funds must be applied daily for two weeks, then applied every two days for 2-3 weeks.
Also, the treatment of annular granuloma can be carried out through superficial scarification, sometimes a biopsy leads to the resolution of the focus.

Phototherapy, Puva therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, the use of retinoids and antimalarial drugs are included in the list of possible systemic effects in granuloma, but none of them is reliably effective and is not recommended for the treatment of children.
It has been clinically confirmed that cryodestruction, which is used for the treatment of annular granulomas in cosmetology, leads to the progression of the disease and the proliferation of lesions along the periphery.
For the treatment of localized granuloma annulare in children, the fourth generation corticosteroid ointment Psoriderm is a safe remedy, the effectiveness of which is confirmed by clinical studies. Due to the fact that the agent is used in a small dose and is applied to a local area of the skin, the likelihood of side effects is very low, no cases of such have been reported.
A granuloma annulus is a benign skin formation of ring-forming nodules that do not cause pain or itching. Usually, the formations go away by themselves after a while, but if the patient has manifestations atypical for granulomas, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!