- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Uric acid diathesis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms and stages of the disease
- Symptoms of uric acid diathesis
- Features of the course of the disease in children
- Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of uric acid diathesis
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Uric acid diathesis (neuro-arthric diathesis) is a constitutional feature of the body due to a violation, namely, an excessive intensity of purine and protein metabolism. An increased concentration of purines is found in the blood and urine, the acetylating properties of the liver are reduced.
With such metabolic disorders, an excessive formation of uric acid occurs, the salts of which can precipitate in tissues and affect the joints, digestive tract, respiratory system, cause allergic conditions, etc.

Source: mkb03.ru
Causes and risk factors
In the development of uric acid diathesis, a genetic predisposition is of great importance, multiplied by the action of aggressive environmental factors.
An unbalanced diet, overloading it with foods containing an increased amount of proteins and purine bases, greatly increases the likelihood of developing pathology.
So, the causes of uric acid diathesis include:
- genetic factor;
- eating disorders: unbalanced diet, prolonged refusal to eat;
- the use of an insufficient amount of fluid, which leads to the inability of the body to effectively remove the end products of metabolism;
- excessive consumption of alcohol;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- the presence in the body of pathogens of food toxicoinfections and other pathogenic bacteria;
- side effects of certain drugs (chemotherapy drugs, other highly toxic drugs);
- excessive physical activity;
- frequent stressful situations;
- endocrine system pathology (hepatitis; diabetes mellitus; pancreatitis, etc.);
- pathology of the structure or functioning of the kidneys, impaired protein production.
Forms and stages of the disease
There are four forms of manifestations of uric acid diathesis:
- neurasthenic;
- spastic;
- cutaneous;
- exchange (dismetabolic).
The first clinical manifestations of this condition usually arise from the nervous system, which is in constant overexcitation due to the irritating effect of urates. Such activation of nerve centers manifests itself in the occurrence of anxiety, causeless anxiety, sleep disturbances, depressive states, outbursts of aggression, and other neurotic symptoms.
Joints and kidneys can become target organs for uric acid diathesis. In the early stages, signs of morphological lesions are not yet noted, there are only complaints of joint pain, which are more often disturbing at night.
Sometimes in the early stages there are signs of damage to the digestive tract, allergic rashes. In laboratory studies, uraturia can be detected, the level of acetone and ketone bodies in the blood plasma increases.
With the appearance of acetone vomiting, violations of the water-electrolyte balance, dehydration of the body appear. In severe cases, this can lead to seizure and meningeal symptoms.
Symptoms of uric acid diathesis
The main signs of uric acid diathesis:
- neurotic syndrome (irritability, anxiety, aggression);
- metabolic disorders;
- transient (more often night) joint pain;
- dysuric disorders, urine acquires a pungent odor, dark color;
- manifestation of meningeal symptoms, severe migraine-like headaches;
- acetone vomiting, a feeling of the smell of acetone during breathing;
- convulsive syndrome;
- metabolic disorders;
- bronchospasm, asthma attacks;
- increased body temperature;
- intestinal and hepatic colic, constipation;
- drowsiness, loss of energy, loss of appetite;
- allergic skin rashes (eczema, urticaria).
Symptoms of uric acid diathesis usually occur periodically.
It is also worth noting that uric acid diathesis in women often first appears during menopause, while in men - after 40 years.
Features of the course of the disease in children
At the age of one year, uric acid diathesis in children is manifested by overexcitation of the central nervous system: the baby asks for his arms, falls asleep poorly, cries and screams. At the same time, the child does not lag behind in mental development from his peers, on the contrary, he is noticeably ahead. Such children often master speech faster, have excellent memory, and start reading early. However, they are anxious, quick-tempered, emotionally unstable, often suffer from enuresis, stuttering and phobias, their appetite is significantly reduced, and weight gain is very slow.
With an increase in the concentration of cell bodies in a child suffering from neuro-arthric diathesis, an acetone crisis may occur.
Attacks of acetone vomiting appear in children (more often in girls) at the age of 2-10 years and stop by the onset of puberty. An attack occurs suddenly or against the background of a previous malaise, lasts from several hours to several days, the reasons for its development can be both nutritional errors and mental or physical overload. But dysmetabolic syndrome occurs already in adolescence. It is manifested by pain and a burning sensation during urination and / or joint pain.

Source: cf.ppt-online.org
Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
The appearance of uric acid diathesis in pregnant women in most cases speaks only of a predisposition to it. As a rule, the symptoms of uric acid diathesis, which appeared in the first months of pregnancy, disappear without a trace during the second trimester.
Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests are prescribed:
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test to determine the level of uric acid, urates, oxalates and phosphates;
- daily urine analysis, determination of urine output;
- pH (blood test for pH).
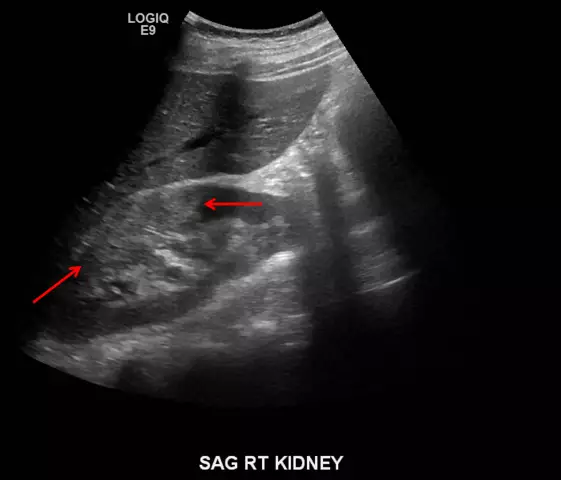
Ultrasound of the urinary system is also prescribed.
Laboratory symptoms of uric acid diathesis are predisposition to acidosis, constant or periodic increase in blood levels of acetone and ketone bodies, uraturia.
If there are signs of acid-base imbalance, an examination of the liver and lungs, blood tests for bicarbonates, buffer bases, and corticosteroids are prescribed.
Treatment of uric acid diathesis
The main method of treatment of urine acid diathesis is lifestyle correction, including strict adherence to the diet.
In the diet, they limit the intake of salt and proteins, completely exclude broths, offal, chocolate, coffee, limit the consumption of meat and products containing animal fats. Increase the content of vegetables and fruits, as well as fluid intake. This diet is designed to help reduce the formation of urates, to prevent the excretion of calcium in the urine.

Source: street-sport.com
Important in the treatment of uric acid diathesis is the competent distribution of physical and emotional stress, the establishment of a work and rest regimen, and hardening.
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing the content of uric acid in the urine and alkalizing it, stimulating urinary excretion and metabolic processes. As symptomatic treatment, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic), hepatoprotectors, sedatives and vitamin-mineral complexes containing potassium and calcium are prescribed.
Physiotherapy is effective at some stages (ultrasound therapy, ultraviolet radiation, laser therapy, darsonvalization, magnetotherapy).

Source: cf.ppt-online.org
Possible complications and consequences
With the transition of uric acid diathesis to pathological forms, arthritis, gout, urate nephropathy, urolithiasis (urolithiasis) may develop.
Gout is an articular form of uric acid diathesis resulting from hyperuricemia (excess urate in the blood). Its main symptom is the appearance of seals and growths in the joints, causing severe pain, and then deformation of the joint. The clinic of gouty arthritis is characterized by edema, hyperemia in the area of the affected joint, and then by its deformation and dysfunction.
Uric acid metabolic disorders can also lead to the development of urate nephropathy. Deposits of urate crystals appear in the kidney tissue, a sediment forms in the distal tubules and collecting ducts, clogging the tubular system, an inflammatory process begins, urine acquires a brick tint, and renal function decreases.
With the progression of these symptoms, urate nephropathy leads to the development of urolithiasis, the formation of sand and calculi (solid formations in the form of stones) in the urinary system. In the acute course, the disease is manifested by colic and pain in the lower back.
Forecast
If pathology is detected in the early stages, the prognosis is positive. Timely correction helps to normalize metabolism and avoids the development of serious diseases.
Prevention
Preventive measures involve adherence to the daily routine, work and rest regimen, a decrease in psychological stress and a decrease in the likelihood of stressful situations, strict adherence to a special diet, refusal from alcohol (prevention of urine acid diathesis in adults), timely treatment of chronic liver and gastrointestinal diseases.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!