- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Coxsackie virus in children
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms of the disease caused by the Coxsackie virus in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of diseases caused by the Coxsackie virus in children
- Possible complications and consequences of the Coxsackie virus in a child
- Forecast
- Prevention of Coxsackie virus in children
Coxsackie virus in children - a virus of the enterovirus genus from the picornavirus family, contains single-stranded RNA that encodes a polyprotein, and is one of the main causes of aseptic meningitis. The human gastrointestinal tract serves as a favorable environment for the multiplication of the virus, however, with the blood flow, the infectious agent penetrates into other organs and tissues, causing inflammation in them. There are 30 known serological types of the Coxsackie virus, all of them are divided into two groups that have a common complement-binding antigen, as well as differences in type-specific antigens involved in the neutralization reaction.
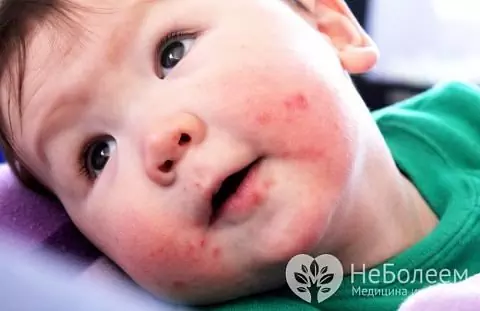
Skin rash with Coxsackie virus in children
Most often, diseases caused by the Coxsackie virus are recorded in children under ten years of age, older children usually carry a mild viral infection. Children under 3 months old do not become infected with this virus, which is due to the fact that maternal antibodies circulate in the child's blood during this period, protecting against viral infection.
After a disease, the patient develops a tense type-specific immunity. Virus-neutralizing antibodies in the blood of a person who has had the Coxsackie virus have been present for several years, complement-binding antibodies usually disappear a few months after the illness.
Causes and risk factors
The source of infection is a sick person or a virus carrier. The Coxsackie virus enters the external environment by airborne droplets, as well as with the feces of an infected person. It is quite stable and can persist in the external environment for two and a half years; it collapses when dried, boiled, or exposed to disinfectants. Most often (up to 97% of cases), infection occurs through contaminated food, water, household items, less often - in water bodies and pools. It can be carried by insects (flies, cockroaches). The fecal-oral route is predominant in children in the first years of life. The virus can also be transmitted through the placenta from an infected mother to her fetus during fetal development. The peak incidence of infection caused by the Coxsackie virus occurs in the summer and autumn period.

In most cases, Coxsackie virus infection occurs through contaminated food
Forms of the disease
There are two main groups:
- Coxsackie virus type A (group A) - consists of 24 serotypes, causes the development of a pathological process in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (erosive vesicular stomatitis), upper respiratory tract (herpangina), conjunctiva (acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis), dura mater (aseptic meningitis), however, most often it manifests itself only as a rash on the skin. The disease it causes usually proceeds without complications, in some cases the infection is asymptomatic (virus carrier).
- Coxsackie virus type B (group B) - includes 6 serological types and usually affects the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis), pleura (pleurodynia, or Broncholm disease), liver (hepatitis).
For both groups, multiple organ tropism is characteristic. Determine which of the groups the causative agent of a particular disease belongs to is possible only by a laboratory method.
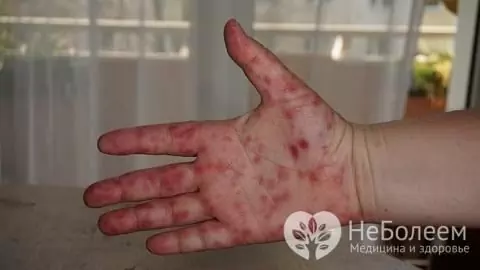
Coxsackie virus type A mainly affects the skin of children
An infectious disease caused by the Coxsackie virus can take a typical or atypical form. Typical forms include:
- isolated lesions (enteroviral angina, hepatitis, myalgia, gastroenteritis);
- lesions of the nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis);
- lesions of the urogenital tract (epididymitis, cystitis);
- eye damage (conjunctivitis);
- heart damage (myocarditis, pericarditis).
For atypical forms, an erased course is characteristic.
Depending on the severity of the course, the disease can be mild, moderate and severe, as well as complicated and uncomplicated.
Symptoms of the disease caused by the Coxsackie virus in children
The incubation period for infection with the Coxsackie virus lasts from several days to one and a half weeks. The first clinical manifestations of the disease are usually an increase in body temperature up to 39-40 ˚С, repeated vomiting and / or diarrhea. Patients have headache, increasing weakness, decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, sore throat, cough, and sometimes heart rhythm disturbances. With the course of the pathological process, the patient develops hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and / or pharynx, a yellowish coating on the tongue, an increase in the cervical lymph nodes. With damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx, food intake is difficult. In some cases, there is an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. These symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children precede the appearance of rashes on the skin of the upper and lower extremities (including on the soles of the feet and palms), chest and face. The rash may spread to the genital area. The elements of the rash have a diameter of 1-2 mm, are filled with serous contents and are surrounded by a hyperemic halo, they can open with subsequent ulceration. The appearance of a rash can be accompanied by itching, a feeling of discomfort in the affected areas. The late symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children include a change in the nail plates.a feeling of discomfort in the affected areas. The late symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children include a change in the nail plates.a feeling of discomfort in the affected areas. The late symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children include a change in the nail plates.
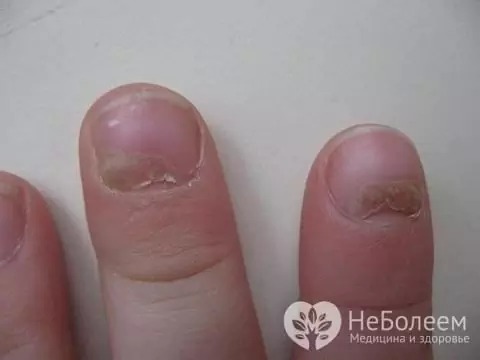
A late symptom of the Coxsackie virus in children is a change in the nail plates
The described manifestations can be both pronounced and slightly expressed. They usually last for 1-2 weeks and then fade away.
In the case of aseptic meningitis, the child develops meningeal symptoms: a sharp headache, photophobia, increased sensitivity to sounds, persistent nausea and vomiting, stiff neck muscles, positive Kernig and Brudzinsky symptoms. Body temperature rises to febrile values (38 ° C and above).
With the development of pleurodynia, compaction is observed in the intercostal muscles, which is accompanied by pain syndrome, as well as headache and fever.
In some cases, against the background of a child's infection with the Coxsackie virus, paralysis develops, which can manifest itself both at the peak of the temperature and when acute symptoms subside. Manifestations range from weakness in the upper and lower extremities to gait disturbance. Persistent severe paralysis is not caused by the Coxsackie virus.
With the development of pericarditis or myocarditis in children, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, edema of the lower extremities, deterioration of the general condition appear.
Herpetic sore throat, provoked by the Coxsackie virus, is characteristic of children 3-10 years old. The main signs of the disease are intense sore throat, aggravated by swallowing, the appearance of ulceration on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx, a significant increase in body temperature, headache and a decrease in general well-being. Because of a sore throat, children usually refuse to eat.
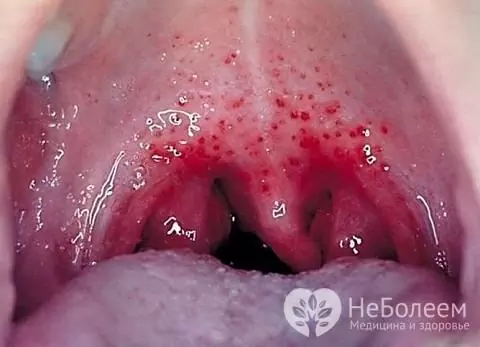
In children 3-10 years old, the Coxsackie virus often provokes the development of herpetic sore throat
Pleurodynia is characterized by sudden intense pain of a spastic nature in the chest and upper abdomen.
Hemorrhagic conjunctivitis is manifested by puffiness and severe pain in the eyes (the child often refuses to open his eyes, cries when trying to open his eyes), sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, hemorrhage in the sclera and conjunctiva, lacrimation and photophobia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the Coxsackie virus in children is based, first of all, on the data obtained during the collection of anamnesis and patient complaints, an objective examination of the patient, and the epidemic situation. The causative agent is established as a result of a number of laboratory tests.
In order to isolate the pathogen, the patient's blood, pathological discharge from the nasopharynx, feces, cerebrospinal fluid (with the development of meningitis) are examined by polymerase chain reaction, complement binding reaction, enzyme immunoassay, hemagglutination inhibition reaction.
Depending on the form of the lesion, you may need to consult an ophthalmologist, otorhinolaryngologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, neurologist, rheumatologist.

To diagnose the Coxsackie virus, the child's blood is examined
Differential diagnosis is carried out with acute respiratory viral infections, intestinal and skin infections of a different etiology, childhood diseases, which are characterized by skin rashes (measles, scarlet fever, rubella), scabies, streptoderma, etc.
Treatment of diseases caused by the Coxsackie virus in children
When a child develops symptoms that are characteristic of a viral infection, especially in a complicated epidemic situation in the region, in order to prevent the further spread of the virus, you should call a doctor at home, and not bring the child to a hospital. With a standard uncomplicated course, the treatment of the Coxsackie virus in children is carried out at home, and only in the case of a severe form of the disease (meningitis, pericarditis, etc.) or with the development of complications, hospitalization is indicated in the pediatric department of an infectious hospital.
An etiotropic treatment for the Coxsackie virus has not yet been developed. The main therapeutic measures are aimed at detoxification and elimination of the symptoms of the disease. The child needs plenty of drink. When the body temperature rises to high numbers, the administration of antipyretic drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol is indicated. The same funds are used to relieve pain. With pronounced signs of intoxication, enterosorbents can be prescribed (drugs of this group should be taken separately from all others, observing the time intervals).

For successful treatment of the Coxsackie virus, a child needs to drink plenty of fluids
For the treatment of ulcerations on the skin and / or mucous membranes, antiseptic preparations are used in the form of ointments, gels, sprays, rinsing solutions. With severe itching on the affected areas of the skin and / or mucous membranes, antihistamines are prescribed, which makes it possible to avoid scratching and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. If bacterial infection could not be avoided, local antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
With a severe course of the disease and the development of complications, the use of corticosteroids may be required, as well as intensive care measures.
Possible complications and consequences of the Coxsackie virus in a child
Diseases that arise when a child is infected with the Coxsackie virus most often proceed easily and do not have any serious complications. The consequences of the Coxsackie virus in a child, especially in the first year of life, include angina, as well as inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis), which usually occurs in newborns. Severe forms of viral infection can be complicated by the development of heart failure, cerebral edema, encephalitis.
Forecast
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. With the development of complications, especially with myocarditis in a newborn or serous meningitis, the prognosis worsens, severe complications can lead to death.
Prevention of Coxsackie virus in children
The specific prophylaxis of the Coxsackie virus in children has not been developed.
Measures to reduce the risk of viral infection include:
- early isolation of the sick from the children's team;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during the epidemic (for the Coxsackie virus - summer-autumn) period;
- avoiding eating foods that have not been properly processed;
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoiding sun and heatstroke;
- sufficient ventilation of the room in which the child is located throughout the day;
- restorative measures.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






