- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
What are the differences between laryngitis and pharyngitis: the difference in symptoms and treatment
The content of the article:
- Causes of inflammation in the pharynx and larynx
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Laryngitis and pharyngitis treatment
- Video
Laryngitis and pharyngitis are common diseases that have similar clinical manifestations. What is the difference between laryngitis and pharyngitis? In order to understand this, it is necessary to define and study the main factors leading to the development of inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract.

To diagnose and prescribe adequate therapy, it is necessary to consult an ENT specialist and undergo appropriate examinations
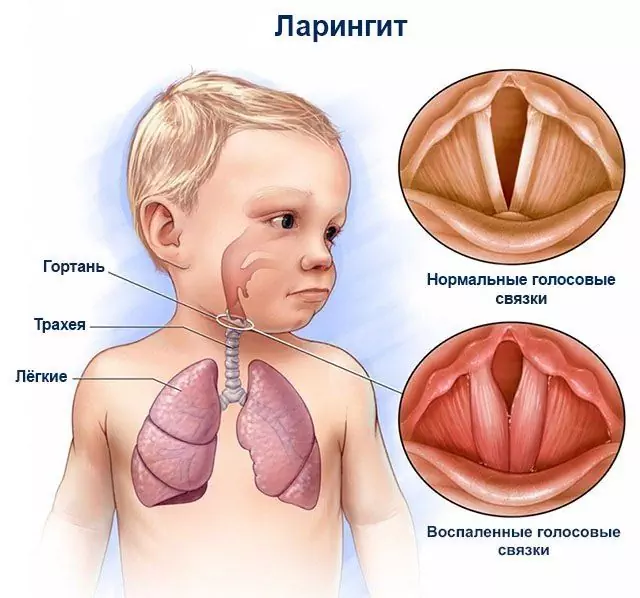
Inflammation with pharyngitis is localized in the mucous membrane of the pharynx, with laryngitis - in the larynx. And in fact, and in another case, the disease can occur in an acute and chronic form.
In addition to the different localization of the pathological process, diseases have differences in the mechanisms of pathogenesis, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of inflammation in the pharynx and larynx
Diseases are widespread and occur in both adults and children. Most often, acute laryngitis is a continuation of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat and occurs against the background of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection).

Hypothermia and prolonged inhalation of cold air can lead to the development of the inflammatory process.
The development of inflammation in the pharynx and larynx is facilitated by:
- general or local hypothermia of the body;
- mouth breathing;
- prolonged inhalation of cold air;
- overstrain of the vocal apparatus;
- eating irritating food: cold, hot, sour drinks and food;
- active and passive smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- harmful production factors: inhalation of dust, chemicals, polluted air;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- adverse environmental factors;
- allergy;
- metabolic disorders (for example, in diabetes mellitus);
- pathology of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses;
- the presence of chronic foci of infection (adenoids, carious teeth);
- concomitant viral, bacterial or somatic diseases;
- features of the immune response, for example, the immaturity of the immune system in children;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins and trace elements in the diet;
- frequent psycho-emotional stress.
Infection of the pharynx and larynx can be ascending or descending. In this case, infections can affect the mucous membranes primarily (when ingested with inhaled air) or secondarily, penetrating into the tissues with blood flow from the focus of chronic infection.
The microflora colonizing non-sterile parts of the respiratory tract, including the pharynx and larynx, is represented by saprophytic microorganisms and opportunistic bacteria, which, with a decrease in local immunity or conditions unfavorable for the microorganism, cause an inflammatory process.

Various pathogens can cause inflammation, including ureaplasma
The cause of inflammation can be:
- influenza and parainfluenza viruses;
- enteroviruses;
- respiratory syncytial virus;
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- diplococci;
- haemophilus influenzae;
- mycoplasma;
- ureaplasma;
- chlamydia;
- other bacteria and viruses.
Symptoms
With inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, the patient complains of dryness, rawness, pain or discomfort in the throat, especially when swallowing. Most often, the body temperature does not rise and the patient's general condition is satisfactory.

Symptoms of diseases are determined by the severity of the inflammatory process
The defeat of the larynx is accompanied by acute pain when talking or at rest, irradiation into the ear and an increase in body temperature are possible. There is a general malaise, cough, shortness of breath, the timbre of the voice changes.
The severity of symptoms directly depends on the severity of inflammatory changes in the tissues. Inflammation in the pharynx quickly passes to the lymphoid tissue, causing tonsillitis, in the larynx - in many cases accompanied by tracheitis.
Diagnostics
The variety and severity of existing respiratory diseases often cause difficulties in diagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze how the diseases differ in diagnostic terms.

Diagnosis can be difficult due to the variety of existing diseases of the pharynx and larynx
Screening includes laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- clinical blood test;
- microbiological examination with typing of microorganisms and determination of sensitivity to antibacterial drugs and diagnosis by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) of the discharge from the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx;
- pharyngoscopy (method of visual examination of the pharynx);
- laryngoscopy (a method of examining the larynx, including the vocal cords, using a special small speculum or flexible fibrolaryngoscope).
It is thanks to instrumental research methods that a specialist can assess the pathological process, determine its localization. Modern equipment allows you to take a photo or video if necessary.

X-rays of the nose are prescribed if necessary
According to the indications, an X-ray examination of the nose, sinuses or lungs, a biochemical blood test is additionally carried out.
Microorganisms in bacterial inoculation can be sown as monocultures or in various associations. The microflora of the laryngeal mucosa is also examined by microlaryngoscopy.
In some cases, it is necessary to consult doctors of related specialties: an allergist, a gastroenterologist, a neurologist.
Laryngitis and pharyngitis treatment
What is the difference between laryngitis and pharyngitis when choosing therapy? The tactics of managing patients with inflammation of the pharynx or larynx depends on the etiological agent and the severity of the pathological process.
Therapy of concomitant pathology, increased immunity is of great importance.
Treatment of uncomplicated forms is carried out on an outpatient basis and includes local and systemic therapy.

Inhalation therapy is effective in treating inflammation of the pharynx and larynx
Local anti-inflammatory inhalation therapy has proven highly effective. For this, mucolytics, herbal preparations with an antiseptic effect, antibiotics, corticosteroids are used. To eliminate dryness of the mucous membrane of the pharynx or larynx, alkaline inhalations are effective, which can be applied several times a day.
For pharyngitis, frequent rinses with antiseptics or sea salt solutions are prescribed, which also help moisturize the mucous membranes.
In case of suspicion or confirmation of bacterial lesion of mucous tissues, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed for 5-7 days. The most commonly used antibiotics are broad-spectrum.
In the case of severe inflammation in the larynx, endolaryngeal infusions of hydrocortisone and an antibiotic are indicated.
With a fungal infection, antimycotic drugs are prescribed.
It must be remembered that frequent relapses of diseases contribute to the transition of the process into chronic conditions. Therefore, it is important to consult a specialist on time and receive comprehensive treatment.
Preventive actions:
- timely diagnosis and therapy of inflammation of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- increasing the body's resistance;
- treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- sanitation of chronic foci of inflammation;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- compliance with the voice mode.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Alina Ervasova Obstetrician-gynecologist, consultant About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University. THEM. Sechenov.
Work experience: 4 years of work in private practice.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.