- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Low diastolic pressure: causes, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Signs of decreased diastolic pressure
- Treatment for low diastolic pressure
- Video
The causes of low diastolic pressure can be physiological or pathological; in the latter case, their identification plays an important role in choosing a treatment regimen. Slight fluctuations in blood pressure up or down are permissible and usually do not require correction, however, if this condition repeats regularly or is constantly present, and also if the fluctuations are significant, you should consult a doctor.

Low diastolic blood pressure with normal or high systolic blood pressure may indicate dehydration, kidney disease, and a variety of other conditions
Blood pressure (BP, blood pressure) is the pressure that blood puts on the walls of the vessels. Its value is influenced by the total blood volume, the work of the heart, the patency of the blood vessels and the state of their walls. Blood pressure is one of the most important diagnostic indicators of body functions. Blood pressure can change not only with diseases, but also when taking certain medications and natural stimulants (coffee, tea), its level can be influenced by the psychoemotional state of a person and environmental factors (for example, hot weather).
Blood pressure consists of two parameters - systolic (upper) and diastolic (lower). Systolic pressure characterizes the work of the heart, and diastolic pressure - of peripheral vessels. The difference between the upper and lower values should normally not exceed 40 mm Hg. Art. A persistently low blood pressure of more than 20% of normal values is called arterial hypotension (hypotension). Most often, both blood pressure indicators (systolic and diastolic) decrease, but it so happens that only one of them deviates from the norm.
Causes and risk factors
A pathological condition in which there is a low diastolic pressure with a normal systolic pressure is rare. What does low diastolic pressure mean? If it falls, this may be a sign of kidney disease, dehydration, an allergic reaction, disorders of the cardiovascular system, and infectious toxic shock.
One of the reasons for the decrease in diastolic blood pressure is neurocirculatory dystonia. The most vulnerable in relation to it are adolescents and young people (under 30). This condition requires consultation with a neurologist.
Other reasons why a person's diastolic pressure may decrease include hormonal disorders, in particular, thyroid pathology (hypothyroidism), massive blood loss, and anemia.
Low diastolic pressure in older people with arterial hypertension of 2 and 3 degrees is often a consequence of atherosclerotic lesions of the blood vessels, renal failure, stroke, myocardial infarction.
Malignant neoplasms, cervical osteochondrosis, a lack of vitamins B, C, and E, marijuana use, smoking and alcohol abuse, as well as insufficient exposure to fresh air and physical inactivity can lead to a decrease in lower pressure.
A decrease in blood pressure is often observed in women during pregnancy. In the first trimester in women, both systolic and diastolic pressure are often lowered, which is due to a change in hormonal levels (increased production of hormones that lower blood pressure). In the second trimester, the pressure is usually within normal limits, only occasionally its slight deviations are noted. In late pregnancy, systolic blood pressure may increase and diastolic pressure may decrease. If the difference between the upper and lower pressure exceeds 40 mm Hg. Art., this is an alarming sign that may indicate the onset of gestosis.
High systolic pressure with low diastolic pressure is called isolated systolic hypertension. This situation is often a consequence of the uncontrolled use of antihypertensive drugs.
Signs of decreased diastolic pressure
Low lower pressure is manifested by lethargy, rapid fatigability, drowsiness, apathy, nervousness, and increased irritability. Patients complain of an aching headache that is not eliminated by conventional analgesics, blurred vision, chest discomfort, increased sweating, dizziness and fainting. Symptoms of low blood pressure occur or are aggravated in the heat, when staying in a stuffy room, after physical exertion, while drinking alcohol.

Low blood pressure is manifested by lethargy, drowsiness, and rapid fatigue
With a decrease in diastolic pressure against a background of normal or low systolic, patients have pallor of the skin, blueness of the lips, and cooling of the upper and lower extremities.
Reduced lower and increased upper pressure are characterized by headache, facial flushing, shortness of breath, tremor of the upper limbs, high pulse. The intensity of clinical manifestations in this case depends on the difference between systolic and diastolic indicators - the greater the difference, the more discomfort the patient experiences.
Why is low lower pressure dangerous? With long-term existence, it can lead to depletion of the heart muscle, the risk of developing such a complication is especially high in elderly people. With a decrease in diastolic pressure below 60 mm Hg. Art. vascular collapse may develop, below 40 mm Hg. Art. - cardiac arrest.
Treatment for low diastolic pressure
What if the lower pressure drops suddenly and critically? This usually means that the patient has developed toxic shock or internal bleeding. In addition to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, such conditions are manifested by ringing in the ears, darkening in the eyes, pallor of the lips, light-headedness or fainting, that is, signs of heart failure. In this case, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, and before its arrival, provide first aid: lay the patient with a raised head end, provide him with an influx of fresh air, free him from tight clothes and calm him down. You cannot leave a person alone, especially if he is unconscious. When cardiac arrest occurs, resuscitation measures are started.
With evenly reduced upper and lower pressure, you can drink a cup of strong tea or black coffee, do a few simple exercises, take a contrast shower or take a walk in the fresh air. Medication correction is started only when the decrease in blood pressure is threatening or it cannot be normalized by non-drug means.
With increased systolic and decreased diastolic pressure, independent attempts to normalize the lower pressure can lead to an increase in the upper indicator. In elderly patients with arterial hypertension, this can cause a hypertensive crisis or other adverse consequences.
How to treat long-term and / or significantly reduced diastolic pressure? First of all, you need to find out the reason. The main treatment is to eliminate it, and stimulants (for example, caffeine sodium benzoate, etc.) can be prescribed as symptomatic therapy. Complex therapy may include physical therapy classes, breathing exercises.
A patient with chronically low diastolic pressure is recommended to lead a moderately active lifestyle, to observe an adequate regimen of work and rest. A full night's sleep is also important, before going to bed, walking in the fresh air is recommended. A contrast shower helps to increase the tone and strengthen the walls of blood vessels; it is recommended to take it daily in the morning.
Stressful situations, physical overstrain should be avoided. It is recommended to include dark chocolate, nuts, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, lean meat in the diet. The patient should limit the use of table salt.
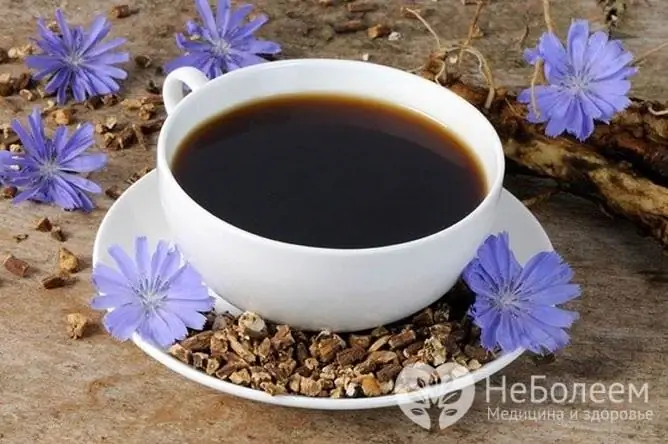

You can raise the reduced lower pressure using a decoction of chicory
In the absence of contraindications, folk remedies can be used to increase the slightly reduced lower pressure or as an addition to the main therapy. Black tea with the addition of currant leaves helps to raise blood pressure. For its preparation, take a teaspoon of black tea and crushed currant leaves, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 5 minutes. Drink like regular tea, 1-2 times a day.
A decoction of chicory root has a similar effect, for the preparation of which two tablespoons of chopped roots are poured with two glasses of warm water and left on low heat for 30 minutes. After that, filter the broth and take 1/3 cup three times a day.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.