- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
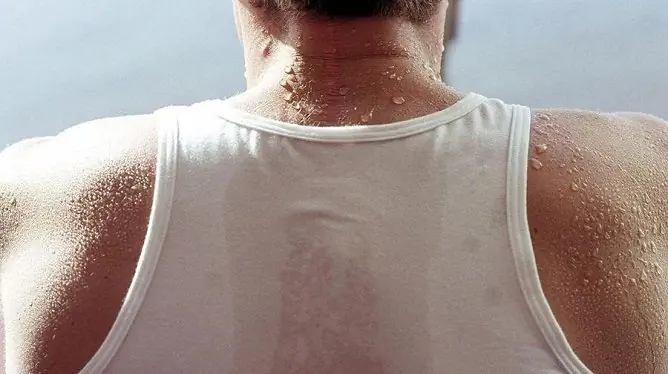
Heavy sweating in men: causes, diagnosis and treatment
The content of the article:
- Causes of profuse sweating in men
- Diagnosis of increased sweating in men
-
What to do with male hyperhidrosis
- Antiperspirants
- Powders and creams
- Iontophoresis
- Botox injections
- Sympathectomy
- Video
With strong sweating in men, an important role for the selection of effective treatment is played by the establishment of the true cause of this pathology. The diagnosis of hyperhidrosis is made when sweat production exceeds the norm.

In case of excessive sweating, it is important to see a doctor and establish the cause of this disorder.
Excessive sweating can be both a congenital feature of the patient and a complication of some diseases, for example, thyroiditis, obesity, tuberculosis. The disease can be localized and spread to specific areas of the body.
Depending on the place of manifestation, inguinal-perineal, facial, palmar, plantar and axillary forms are distinguished. Also, hyperhidrosis can be common - then there is severe sweating of the whole body.

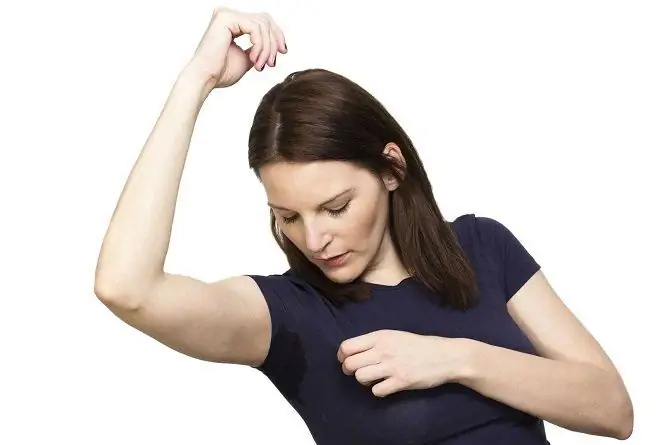
Sweating is increased by many factors, including stress
Only a small number of patients perspire constantly. For the selection of adequate therapy, you should seek the help of a dermatologist.
Causes of profuse sweating in men
To eliminate the excessive production of sweat, in many cases, it is sufficient to exclude the cause that provokes it. The list of possible factors of the origin of pathology is extensive and includes:
| Factor | Influence |
| Dysfunction of the nervous system | The ganglia located near the spine, the centers of the autonomic nervous system in the spinal cord and medulla oblongata, and also the hypothalamus are responsible for heat regulation and sweat excretion. Failure of any of these parts of the nervous system can increase fluid secretion. |
| Nervous tension and frequent stress | An increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine leads to the excitation of the entire nervous system, including the centers that regulate the work of the sweat glands. These centers are instructed to produce more sweat. Hyperhidrosis against a background of stress is called psychogenic |
| Acute and chronic infectious diseases |
In response to viruses and bacteria entering the bloodstream, the body produces pyrogens, which affect the thermal sensitivity neurons. Influenza, tuberculosis, septicemia, tonsillitis, brucellosis, malaria and syphilis lead to sweating. |
| Reception of spicy and hot food | The relationship between food and hyperhidrosis is due to reflex connections between the centers of salivation and sweating. Increased perspiration is caused by alcohol, coffee, tea, spices, as well as extractive substances contained in mushrooms, meat and fish |
| Exercise stress | The active work of the muscles helps to release a large amount of energy, which increases the body temperature. Sweating in this case provides protection against overheating |
| Elevated levels of catecholamines | Catecholamines are responsible for the transmission of impulses in the nerve trunks and ensure the interaction of cells in the body. Their appearance in the blood is recorded with pain of various origins, intense physical activity, heart pathologies, respiratory failure, alcohol or drug withdrawal |
| Hormonal disorders | Contribute to the development of endocrine hyperhidrosis disorders of hormones of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus and gonads |
| Hereditary predisposition | Studies have shown that the tendency to hyperhidrosis is inherited, but the cause of this phenomenon has not been established |
| Systemic pathologies | Due to the development of an autoimmune process against the background of rheumatoid arthritis or Raynaud's disease, the blood capillaries that feed the nerve trunks are damaged. The consequence of this is a violation of the functions of the organs for the work of which these nerves are responsible. |
| Taking medications | Taking some drugs that affect the autonomic nervous system stimulates the production of sweat. These medicines include antidepressants, antiemetics, Aspirin, Insulin, and others. |
|
High ambient temperature |
Recording an increase in air temperature, heat recipes transmit a signal to the parts of the spinal cord and brain responsible for thermoregulation. These divisions give impulses to the sweat glands to increase fluid production. |
Diagnosis of increased sweating in men
In case of high sweat production, the first step is to consult a physician or dermatologist. During a physical examination, a specialist will be able to determine why the disease has developed and its type, and also refer the patient to a specialized specialist. For example, with a psychogenic form, it is better to start therapy as directed and under the supervision of a neurologist.

For hyperhidrosis, consult a dermatologist or therapist
Careful collection of anamnesis in combination with examination and recording of patient complaints are the most informative data for making a diagnosis. If the pathology is secondary and has developed as a result of the underlying disease, it is very important to determine it.
To determine the intensity, quantitative and qualitative characteristics of sweating, different tests are used, namely:
- Minor's test: localization sites are dried, moistened with an aqueous solution of iodine and sprinkled with starch. As a result, the areas on which the liquid protrudes acquire a dark blue tint, which makes it possible to mark their boundaries;
- gravimetric method: the filter paper is weighed and applied for 1 minute to the investigated area, then weighed again;
- chromatographic method: analysis, during which the spectrum of unsaturated fatty acids in the secretion of sweat glands is determined. The test allows you to reliably establish the type of pathology and optimize the tactics of therapy.
What to do with male hyperhidrosis
Treatment in men does not differ much from that in women. In the secondary form, symptoms will be observed until therapy of the underlying disease is carried out.
Antiperspirants
When applied to the skin, the active substances that make up medical antiperspirants (formaldehyde, zinc, aluminum salts) penetrate deeply into the sweat ducts and form plugs in them, without blocking the production of sweat. This allows you to hide the unpleasant odor, if any, and for some time to solve the problem of excessive sweating.

In many cases, the use of medical antiperspirants is effective
It is recommended to apply such funds at night before going to bed on dry skin 1-2 times a week.
Powders and creams
Such funds reduce the intensity of discharge by an average of 12 hours. The glutaraldehydes, chlorides and formalin contained in them constrict sweat ducts.

Powders are best used to treat shoe insoles.
Since dermatitis often develops when such products are applied directly to the skin, it is preferable to saturate shoe insoles or armpit pads with them.
Iontophoresis
This is a method of physiotherapy, which consists in acting on nerve fibers with an electric current. One procedure can reduce the activity and intensity of the sweat glands by an average of 14-21 days.
Botox injections
Botulinum toxins of type A or similar substances - xeomin or dysport - are injected under the skin using a thin needle. Their action consists in a temporary blockade of muscle activity and the activity of nerve fibers, as well as paralyzing the functioning of the sweat glands 4-6 days after injections.

An effective method of treating hyperhidrosis is the introduction of Botox
Most often, the result of the procedure lasts for 6 months, but there are cases when the effect lasted almost a year.
Sympathectomy
Sympathectomy is a surgical procedure in which a clip is used to block the sympathetic nerve that regulates the sweat glands. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, on average it takes half an hour.
Thanks to this procedure, you can get rid of the problem of increased sweating permanently, but it comes with some risks. For example, blockage of the sweat glands in the back area can serve to develop a compensatory reaction, as a result of which hyperhidrosis manifests itself on the palms or head.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.