- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
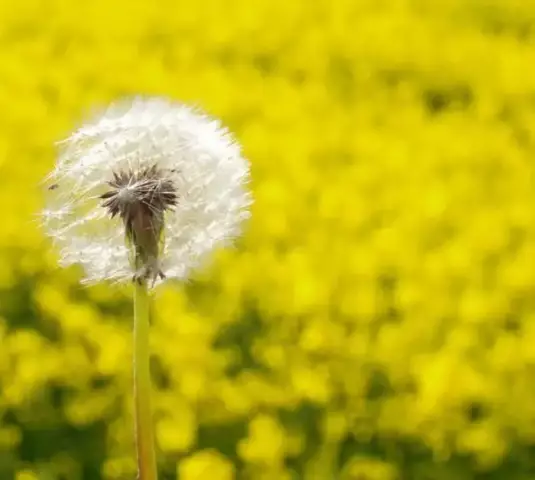
Hay fever

Hypersensitivity to pollen from trees, shrubs and plants provokes the development of a disease such as hay fever or seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. The popular name is "hay fever", although the disease has nothing to do with fever, and hay is not a trigger for the onset of the disease.
A distinctive feature of hay fever is seasonality. Symptoms of the disease from year to year appear only during the flowering period of certain plant species. With pollinosis, the mucous membranes of the eyes and upper respiratory tract are damaged as a result of the deposition of pollen in them. Also, this disease affects the nervous system and internal organs. Cross-allergy often occurs, when allergic reactions to pollen from related shrubs and trees occur, with intolerance to certain foods, or combined, in which hay fever develops in response to the introduction of several types of pollen.
The risk group is mainly women aged 25 to 45 years. In childhood, boys most often suffer from hay fever. The prevalence of the disease is quite significant. Despite the fact that hay fever is not included in the group of diseases that affect life expectancy, it can significantly reduce the quality of life. Especially in cases where dust sensitization is added to existing allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis or bronchial asthma.
Types of hay fever and their symptoms
Very often, hay fever is mistaken for acute respiratory infections, especially at the very beginning. After all, the signs in these diseases are almost identical to each other: lacrimation, headache, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing and coughing. But at the same time, a number of differences can still be distinguished, on the basis of which the development of pollen allergy, i.e., hay fever, can be suspected.

Most often, hay fever manifests itself in the form of rhinitis and conjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis and seasonal bronchial asthma are slightly less common:
- Seasonal rhinitis is characterized by profuse watery nasal discharge, accompanied by tickling and itching in the nose, nasal congestion, and paroxysmal cough. In children, hay fever of this type can occur in combination with noise and pain in the ears.
- With seasonal conjunctivitis, there is swelling and redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes, lacrimation, itching and "sand" feeling. As a rule, with true seasonal conjunctivitis, mucous discharge from the eyes, purulent discharge appears only in case of infection.
- atopic dermatitis with pollinosis is manifested by rashes on open areas of the body. The disease occurs in varying degrees of severity, from minor urticaria to severe angioedema Quincke.
- asthma attacks are characteristic of seasonal bronchial asthma.
With lesions of the nervous system and internal organs, hay fever may be accompanied by diseases such as vulvitis, epileptic seizures, and arachnoencephalitis.
All signs of hay fever disappear as plants, shrubs and trees fade. In total, the disease lasts for 4-6 weeks, in severe cases - the entire spring-summer period.
Pollinosis treatment
With pollinosis, treatment is aimed at reducing the sensitization of the body. For this purpose, antihistamines are used, in case of their ineffectiveness or in severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. At the same time, agents are used to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, both local and general. It is not recommended to use preparations containing leaves, buds, flowers, bark and roots of various plants, shrubs and trees for the treatment of hay fever in children.
In the acute period with hay fever, you should strictly follow the diet. It is imperative that honey and cross-reacting foods should be excluded from the diet. For example, if you are allergic to cereals, cereal porridges, bakery products, pasta are excluded as much as possible. Do not eat apples, kiwi, nuts, plums, potatoes and a number of other products with sensitization to the pollen of alder, birch, apple trees. Citrus fruits are not used for reactions to weed pollen.
In severe cases, moving to another climatic zone is indicated.
Prevention of pollinosis
Prevention of hay fever should be comprehensive, including elimination measures, specific immunotherapy and adherence to diet.
Elimination measures for a tendency to hay fever consist in fulfilling a number of requirements to minimize the harmful effects of pollen on the body. For this purpose, it is necessary to avoid visiting squares, parks and similar objects. The amount of pollen entering the room can be limited by hanging open vents and windows with gauze.
To prevent the development of atopic dermatitis, it is advisable to wear clothes with long sleeves and trousers. It is recommended to remove bouquets of flowers and indoor flowering plants from the room.
One of the most effective methods in achieving remission in hay fever is specific immunotherapy. It consists in introducing small doses of causally significant allergens into the patient's body outside the exacerbation phase. With each injection, the amount of injected allergen increases, as a result of manipulation, hypersensitivity decreases. Treatment procedures are carried out only in specialized rooms under the supervision of a specialist.
In the stage of remission, you can eat all foods, but do not abuse them.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!