- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Genital warts
The content of the article:
- The reasons
-
Symptoms of anogenital warts in women and men
- Genital warts
- Condylomas Buschke - Levenshtein
- Possible complications
-
Diagnostics
Differential diagnosis
- What to do
- Prevention
- Video
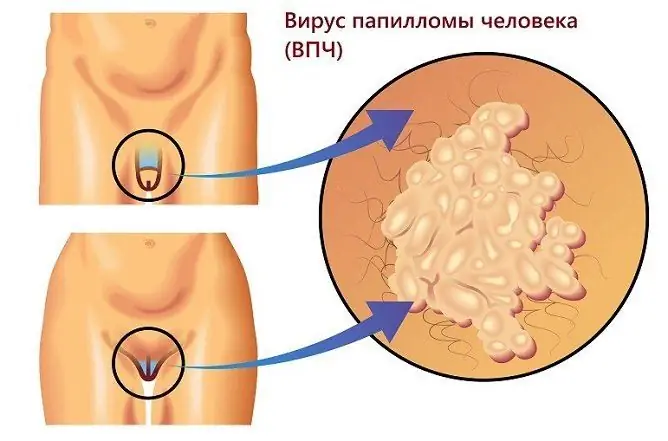
Genital warts are neoplasms that can occur when infected with human papillomavirus in males and females of different age groups.
Most often, the pathology is recorded in patients under 30 years of age, the development of genital papillomas in children is possible. According to research, about 85% of patients with warts in the genital and anus also have neoplasms on the cervix or vagina.
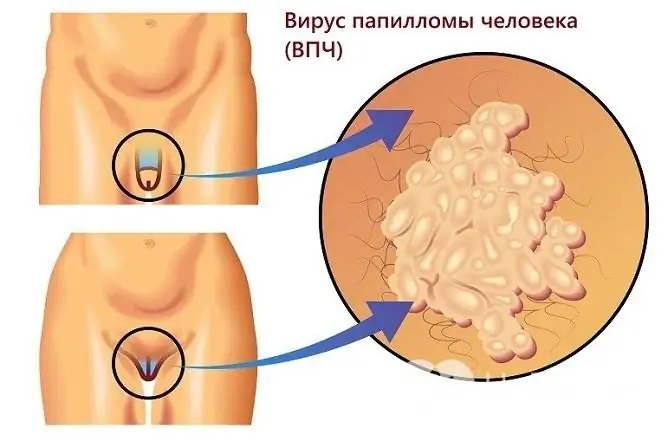
Anogenital warts, or condylomas, are caused by the human papillomavirus
In some cases, neoplasms can spontaneously regress, although their malignant transformation is also possible.
If neoplasms are found in the anogenital area, you need to consult a gynecologist or dermatovenerologist. The choice of the therapy scheme is carried out taking into account the localization of education, the presence of concomitant pathologies, the general state of health and the wishes of the patient.
The reasons
Human papillomavirus infection refers to diseases that can be sexually transmitted. To date, the role of the human papillomavirus (HPV) in the development of certain types of cancer (cancer of the cervix, penis, vagina, anus, etc.) has already been proven.
Papillomavirus has epitheliotropy and is detected on the skin, conjunctiva, on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, esophagus, bronchi, rectum, and organs of the reproductive system. Infection with a strain of papillomavirus that causes anogenital formations is facilitated by frequent changes in sexual partners, early onset of sexual activity, and refusal to use barrier methods of contraception.
Infection is possible through sexual and household contact, as well as during medical manipulations (cases of infection of medical personnel from infected patients are known), the passage of a child through the birth canal of an infected mother. In addition, transplacental infection of the fetus is possible in the presence of a viral infection in a pregnant woman.
Risk factors include:
- bad habits;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- hypothermia of the body;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- the use of immunosuppressive drugs;
- inflammatory processes in the body.
Genital papillomas can recur during pregnancy, during this period, against the background of changes in the woman's body, neoplasms can become loose and grow. Often there is an independent regression of formations after childbirth.
HPV infection is often combined with other sexually transmitted diseases.
Symptoms of anogenital warts in women and men
The papillomavirus infects epithelial cells, causing changes in their structure (benign or malignant neoplasia). The incubation period for virus infection is usually 3-6 months, but it can be up to several years. In the absence of treatment, neoplasms may disappear on their own, remain unchanged, or progress.
Warts in the anogenital area, as seen in the photo, are usually flesh-colored, brown or black. Flat neoplasms, as a rule, do not bother the patient; when they increase and reach large sizes, they cause discomfort. Pain and itching can occur during intercourse, when removing hair in intimate areas.
Anogenital warts are located mainly in places of tissue damage during prolonged contact with moisture:
- anal area;
- the mouth of the urethra;
- small labia;
- vagina;
- Cervix;
- foreskin;
- the head of the penis.
With a significant size or number of neoplasms of this type in the mouth of the urethra, it is possible to overlap the lumen of the urethra, which leads to a delay and / or painful urination. If this growth occurs in the anal region, patients may experience discomfort during bowel movements.
Genital warts
Genital warts are neoplasms with a thin stem or broad base, which may look like a single nodule or multiple outgrowths resembling a cockscomb. Their appearance is possible both on the skin and on the mucous membranes.
Condylomas Buschke - Levenshtein
With the development of condyloma Buschke-Levenshtein, the patient develops several formations, which then merge with each other. The neoplasm has a wide base, the growths are separated by furrows, over time they become rough to the touch, covered with scales. In the furrows, transparent contents usually accumulate, which has an unpleasant odor. Education is prone to malignancy.
Possible complications
Complications of pathology can be:
- bleeding from a neoplasm (usually develops with mechanical damage to the growths, including when shaving, during intercourse);
- the addition of a bacterial infection with the development of a purulent process;
- papillomatosis (multiple papillomas);
- malignant transformation.
There are types of papillomavirus with high and low oncogenicity. Common strains cause the development of warts, papillomas. Highly oncogenic strains are detected in 50-80% of cases with moderate and severe dysplasia, which are precancerous conditions, as well as in 90% of cases of invasive cancer.
With malignancy, the neoplasm shows growth, ulcerates, bleeds.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic methods include an objective examination, cytological examination of smears and biopsies. A general blood and urine test may be required. With asymptomatic and low-symptom forms of pathology, they resort to the polymerase chain reaction method.
Diagnosis of neoplasms with endophytic growth is often a problem, since there are no pronounced epithelial lesions.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of genital warts is carried out with genital herpes, molluscum contagiosum, moles. With genital herpes, a group of small vesicles, filled with transparent contents, appears on the skin. Unlike warts, herpes usually has more pronounced clinical manifestations (pain, burning, itching in the groin, erosion at the site of the opened vesicles, an increase in body temperature to 38 ° C, an increase in the inguinal lymph nodes).
Molluscum contagiosum visually resembles an ordinary pimple, which can appear on any part of the body, including in the anogenital area. The surface of the neoplasm has a pearlescent hue, the education has an umbilical impression in the center. When pressed, a mushy content is released from it.
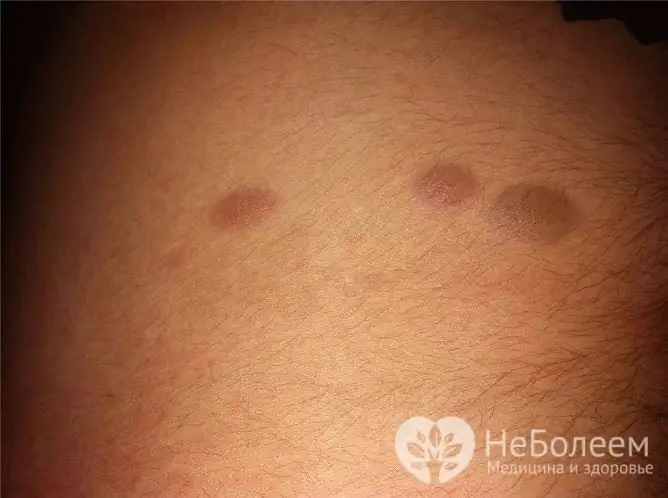
Dark condylomas sometimes look like moles
Moles can be localized in the perineum in females and males. They usually do not rise above the level of the skin, are small and dark in color. If a mole rises above the level of the skin, it can be confused with a wart.
What to do
The main method of treatment is the removal of neoplasms. General treatment is to strengthen the immune system to prevent recurrence. For this, antiviral, immunomodulating drugs, vitamin and mineral complexes can be prescribed.
Methods for removing genital warts
| Method | Description |
| Cryodestruction | With the help of liquid nitrogen, small neoplasms are usually removed in the vagina, on the head of the penis |
| Electrosurgical method | This method can be used to eliminate large formations. |
| Laser removal | It can be used in hard-to-reach places. |
| Surgical excision | It is rarely used, only in cases where other methods are not suitable for one reason or another. |
During pregnancy, treatment is recommended in the early stages, using only physical destructive methods (for example, cryodestruction, carbon dioxide laser. General antiviral drugs are not used in this case.
Prevention
For prevention purposes, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of sexually transmitted infections;
- the use of barrier methods of contraception (especially when changing a sexual partner);
- avoidance of promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- increased immunity;
- wearing underwear made from natural materials;
- refusal to use other people's hygiene products;
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Relapses occur in about 25% of patients within 3 months after treatment. Usually, recurrence is not associated with re-infection from a sexual partner, but with reactivation of the infection.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.