- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
First aid for burns

A burn is damage to body tissues resulting from exposure to high temperatures. In addition to thermal burns, there are also electrical, chemical and radiation burns.
Thermal or thermal burns are among the most common, especially in the younger age group - in young children, the vast majority of burns occur as a result of scalding with boiling water.
Panthenolsprey can be successfully used to help with household burns.
Panthenolspray aerosol for external use 1:
- has anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects;
- helps to reduce irritation;
- sprayed as a thick foam, does not require an additional bandage;
- is the number 1 agent among aerosols for external use based on dexpanthenol 2.
Panthenolspray contains dexpanthenol in the form of an aerosol, which makes it easy to apply - just spray on the skin without rubbing 3. This helps to reduce additional trauma to the skin, in contrast to the use of creams and ointments.
Panthenolspray is a certified drug (that is, it has a healing effect), unlike many products that have a similar name and similar packaging, but are cosmetic. You can find out the same Panthenolspray - a medicine by the smiley on the package. Panthenolsprey is produced in the European Union, in compliance with high European quality standards.
There are several classifications of burns, in our country the classification of A. A. Vishnevsky, dividing damage into degrees depending on the depth of tissue damage. Knowledge of the classification allows you to quickly navigate the situation and not make mistakes when providing first aid. So, according to Vishnevsky, there are 4 degrees of burns:
- Stage of erythema, or redness;
- Bubble stage;
- Stage of skin necrosis;
- The stage of necrosis of the skin and underlying tissues (fatty tissue, muscles, tendons, and sometimes bones), also called the carbonization stage.
The first two stages are classified as mild, the third and fourth are severe burns, or deep burns. This division is arbitrary, since it does not take into account the area of the lesion and special anatomical zones (these include the face, eyes, groin, joints), however, it gives an idea of the severity of the lesion and what first aid measures should be taken.
First aid for mild burns
Mild burns do not require hospitalization, as a rule, home treatment is sufficient, but only if first aid was provided correctly.
So, with such lesions, after the cessation of exposure to the traumatic factor, it is necessary:
- Remove clothing from the burn site, if any. In this case, it is unacceptable to pull clothes together, because you can damage the skin even more (if necessary, the fabric should be cut);
- Place the burned area under running cold water for 10-20 minutes or apply a cold compress. It is unacceptable to use ice to cool the skin, because frostbite of tissues may be added to the burn;
- Treat the affected area with an antiseptic. You can use anti-burn agents, it is allowed to treat the burnt surface with alcohol. You can not use iodine, a solution of potassium permanganate, as well as oil, fatty ointments and creams - that interferes with air exchange;
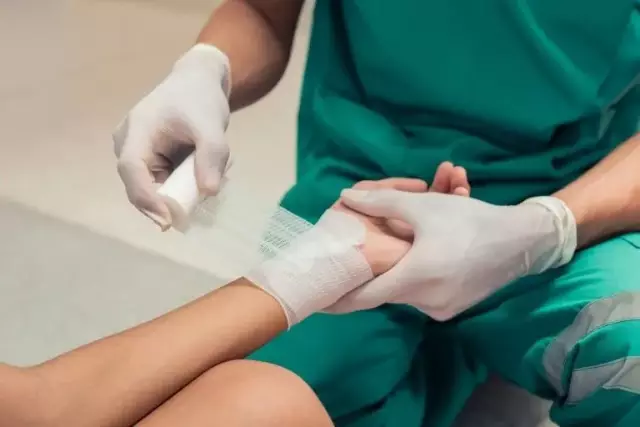
- Apply a loose sterile bandage to the damaged area of the skin, and do not use cotton wool, because its fibers are quite difficult to remove from the wound surface;
- If the pain is intense, give the victim a pain reliever. You can use Paracetamol, Aspirin (it is undesirable to give it to children), Nimesil, Nurofen, etc.
As a rule, these first aid measures for mild burns are sufficient. Such injuries heal within 10-14 days, the main task in their treatment is to prevent additional trauma to the affected area and infection.
First aid for severe burns
In the case of thermal injuries of the III and IV degrees, as well as burns of the II degree, affecting large areas of the skin or anatomically significant areas, assistance is provided in a hospital, therefore it is necessary to call an ambulance to the victim as soon as possible. Pending the arrival of the doctor and after eliminating the damaging factor, first aid measures for severe burns are as follows:
- Make sure that no smoldering clothing remains. No need to remove scraps of clothing from damaged skin;
- Cover the burned surface with a sterile, or at least a clean, loose bandage, if possible;
- With deep injuries, do not immerse the injured area of the body under water, and ice should also not be used. Instead, moisten the dressing with cold water;
- Give the victim warm tea or warm salted alkaline water (for its preparation, stir 1-2 g of baking soda and 3 g of salt in 1 liter of water);
- Place the victim in such a way that the burned part of the body is above the level of the heart.
Local medications, even such as Panthenol, should not be used in this case, the wound treatment will be done in the hospital
First aid for electrical burns
First aid for electrical burns consists in isolating the victim from exposure to a damaging agent, after which it is necessary to check for the presence of pulse and breathing. If they are absent, it is necessary to start resuscitation measures - closed heart massage, mouth-to-mouth breathing or mouth-to-nose. An ambulance should be called as soon as possible, continuing resuscitation measures until the pulse and respiration stabilize or until a doctor arrives.
Superficial skin lesions resulting from an electrical burn are treated in the same way as with a thermal burn.
First aid for chemical burns
A chemical burn is caused by exposure to the skin or mucous membrane of acids, alkalis and other corrosive substances. Despite the fact that the damaging agents can be different, first aid for this type of burn begins the same: the damaged area must be placed under running water for 10-20 minutes. This is true for all chemical burns, with the exception of quicklime and sulfuric acid burns.
After washing with water, the burn site is treated with a weak alkali solution, such as soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water) or soapy water (it is advisable to take household soap, without additives). Sulfuric acid burns should be treated with a slightly alkaline solution, without prior rinsing with water.
Alkaline burns after washing are treated with a weakly acidic solution - a solution of vinegar or citric acid is suitable.
Burns caused by quicklime are treated immediately with oil or fat - and this is the only case when fatty ointments are used in first aid for burns.
It should be borne in mind that alkali burns are more dangerous, since they do not form a clear boundary between the damaged area and healthy tissue. This is the so-called colliquation necrosis, which tends to spread even after the end of exposure to the damaging agent.
1 Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Panthenolspray
2 According to AlPharm databases, the drug "Panthenolsprey" aerosol for external use manufactured by Aeropharm GmbH is the leader in sales in physical and monetary terms among aerosols for external use based on dexpanthenol at the end of 2019 in the Russian Federation
3 When applied to the face, do not spray the aerosol directly onto the face. It is recommended to first apply the drug to the hand, then spread over the damaged skin area
Bausch Health LLC 115162, Russia, Moscow, st. Shabolovka, 31, building 5. Tel./fax: (495) 510-28-79
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. PLEASE READ THE INSTRUCTIONS OR CONSULT A SPECIALIST
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.