- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Rickets
Brief description of the disease

Rickets is a disease characterized by a deficiency in the body of vitamin D. It helps the body absorb calcium, which is necessary for the construction and development of bone tissue, as well as for the normal functioning of the nervous system and other organs. Rickets most often occurs in children, mainly up to three years old. Although the possibility of rickets appearing in older children, as well as in adults, is not excluded.
The causes of rickets
The main reason for the appearance of rickets is a lack of vitamin D in the human body, which leads to metabolic disorders in the body of substances such as calcium and phosphorus. As a result, bone mineralization and growth are disrupted, pathological changes are observed in the nervous system and internal organs. The lack of this vitamin may be due to a poor monotonous diet, we rarely stay in the sun, since vitamin D is produced under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Sometimes the cause of rickets can be unfavorable living conditions of the mother and child, complications during childbirth, taking certain medications, overweight at birth or prematurity.
Rickets symptoms
The symptoms of rickets depend on the degree of the disease. Changes in the nervous system are observed, which are manifested by frequent crying, anxiety and irritability. Fear of bright flashes of light and loud sounds is also possible.
One of the signs of rickets is excessive sweating, which most often manifests itself at night, when crying, and when feeding. The child sweats even when the room is cool and is lightly dressed. Sweat has an unpleasant sour odor and irritates the skin. The child turns his head on the pillow, which causes hair to fall out on the back of his head, and a bald spot forms, which is another sign of rickets. The patient's palms and feet are always wet.
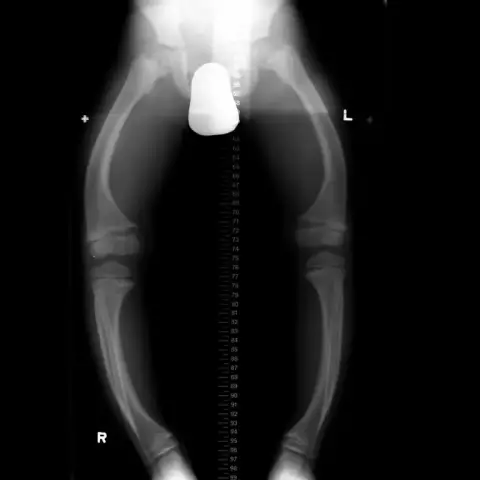
Rickets up to a year is manifested by damage to the chest and skull. At the initial stage, softening of the parietal and occipital bones, fontanelles and their edges occurs. If you do not carry out adequate treatment, then after a short time rickets progresses. In this case, there is an increase in the frontal and parietal tubercles, the head becomes square. The chest is deformed, the hips are bent. The baby's chest becomes like a chicken. There is a thickening of the tubular bones on the forearm and phalanges of the fingers ("rickety bracelets" and "strings of pearls"). The legs are bent, they take the letter O or X, the pelvic bones are deformed. If untreated, signs of rickets can also appear in the second and third years of life; skeletal deformity can remain for life.
Rickets in children is characterized by slow growth of teeth, disruption of the lungs and heart, vegetative-vascular changes, which are manifested in excessive sweating and marbling of the skin, disorders of the stomach and intestines are possible. If rickets is observed up to a year, then such a child begins to get up or sit later, and is often sick.
Rickets degrees
There are three degrees of rickets.
The first degree - the symptoms of rickets appear on the part of the nervous and muscular system, do not leave consequences. This is the mildest degree of rickets.
Second degree - there is a deformation of the skull, limbs and chest, moderate disturbances in organs and systems occur, anemia appears, an increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
The third degree is the most severe. The symptoms of rickets are quite pronounced and are characterized by severe changes in various organs and systems (bone, muscle, hematopoietic). The baby is not getting enough oxygen due to the deformity of the sternum.
Rickets treatment

The main treatment for rickets in children is the regular intake of vitamin D in the dose prescribed by the doctor. The dosage depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the child. Also, ultraviolet irradiation has a good effect, under the influence of which the production of its own vitamin D is observed in the body. They carry out therapeutic massage and special gymnastics. Treatment of rickets involves the appointment of baths with infusions of herbs (string, oak bark, plantain). It is important to remember: only a doctor should treat the disease, since an overdose of vitamin D can provoke serious consequences from the internal organs, especially the liver, heart and kidneys.
Prevention of rickets
Prevention of rickets consists in the correct organization of nutrition and the daily routine of the child. Prevention of rickets for up to a year involves breastfeeding, taking into account the balanced nutrition of the mother. In this case, the child will receive the necessary dose of vitamin D from breast milk. If the child is artificially fed, then a high-quality adapted mixture should be chosen. Such mixtures also contain the right amount of vitamin D. The child's menu after one year should be varied and include dairy products, yolk and fish. They are high in vitamin D.
Fresh air and sun rays are an excellent prevention of disease. Walk more with your child, especially during the warmer months. Ultraviolet rays help produce vitamin D.
Do gymnastics and massage with your child. Good muscle activity contributes to better blood saturation of the bones, which reduces the risk of rickets.
In the autumn-winter period, the doctor may prescribe a prophylactic intake of vitamin D. Do not exceed the recommended dose, as this can lead to negative consequences.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!