- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyvinyl alcohol

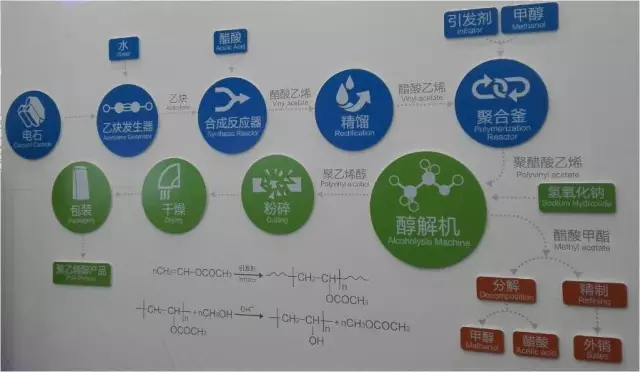
Polyvinyl alcohol is an artificial water-soluble synthetic thermoplastic polymer. The synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol is an exchange reaction of alkaline hydrolysis or alcoholysis.
The pioneers of polyvinyl alcohol were German chemists Willie Hermann and Wolfram Gonel in 1924.
Unlike many vinyl polymers, polyvinyl alcohol is not produced by polymerizing the corresponding monomers. Polyvinyl alcohol monomer exists exclusively as a tautomeric form of resistant acetaldehyde. The production of polyvinyl alcohol occurs by partial or complete hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate to remove ethyl acetate groups.
Industrial methods of producing polyvinyl alcohol are various options for saponification of polyvinyl alcohol in an aqueous or alcoholic medium in the presence of acids and bases.
In 2002, under the leadership of AA Kuznetsov, the laboratory of heat-resistant thermoplastics ISPM named after Enikolopov in Moscow, a gel-free method for producing polyvinyl alcohol was developed, which has a number of advantages over other methods, such as low cost, high productivity, and short-term synthesis.
Properties of polyvinyl alcohol
Film-forming, emulsifying and gluing properties of polyvinyl alcohol make it possible to use it in various industries and areas. Polyvinyl alcohol is resistant to oils, fats and solvents. It is odorless and non-toxic, has high tensile strength and flexibility, and has a high oxygen content.
However, these properties of polyvinyl alcohol are in direct proportion to the moisture content, with an increase in which it absorbs water. Water, which acts as a plasticizer, reduces the strength of the polyvinyl alcohol. It completely disintegrates and quickly dissolves in it.
The molecular formula of polyvinyl alcohol is C2H4Ox, density - from 1.19 to 1.31 g / cm³, melting point - 200 ° C, boiling point - 228 ° C.
The use of polyvinyl alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol is a raw material for the manufacture of other polymers, such as:
- Polyvinyl nitrate is an ester of nitric acid and polyvinyl alcohol;
- Polyvinyl acetal - it is obtained by reacting aldehydes with polyvinyl alcohol.
It is also known to use polyvinyl alcohol as a thickener and modifier in polyvinyl acetate adhesives.

In China, polyvinyl alcohol is widely used as an emulsion polymerization stabilizer and a protective colloid for the production of polyvinyl acetate dispersions.
In the textile industry in Japan and North Korea, the use of polyvinyl alcohol is widespread in fiber production.
Polyvinyl alcohol has found application in various industries and areas as:
- Paper coating for liners;
- Water-soluble film for packaging washing powder in dissolving tablets;
- Barrier layer for carbon dioxide in PET bottles;
- Lubricants for eye drops and hard contact lenses;
- Fibers for reinforcement in concrete;
- A surfactant to form a polymer of encapsulated nanoparticles;
- Clamp for collecting samples;
- Embolization agent in medical procedures;
- Thickener and adhesive for the production of shampoos and latex;
- Emulsifier in the food industry;
- An embolizing agent in the non-surgical treatment of cancer.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.