- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Gemapaxan
Gemapaxan: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. In case of impaired renal function
- 12. For violations of liver function
- 13. Drug interactions
- 14. Analogs
- 15. Terms and conditions of storage
- 16. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 17. Reviews
- 18. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Hemapaxan
ATX code: B01AB05
Active ingredient: enoxaparin sodium (Enoxaparin Sodium)
Manufacturer: Italfarmako S.p. A. (Italfarmaco, SpA) (Italy)
Description and photo update: 2019-23-08

Gemapaxan is a direct-acting anticoagulant agent.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - solution for subcutaneous administration: colorless or light yellow, transparent [2000 IU (international units) / 0.2 ml, 4000 IU / 0.4 ml, 6000 IU / 0.6 ml in disposable glass syringes with attached a stainless steel needle, closed by pressing the plug-plunger blue (2000 IU / 0.2 ml), red (4000 IU / 0.4 ml), white transparent (6000 IU / 0.6 ml) or black (6000 IU / 0.6 ml in syringes equipped with a needle protection system) color; the syringe containing Gemapaxan at a dose of 6000 IU / 0.6 ml has a graduation with a division of 0.025 ml; 2 syringes in PVC contour packages, sealed with transparent film or paper foil, in a cardboard box 3 packages].
Active substance: enoxaparin sodium, its content in 0.1 ml of solution is 1000 IU, respectively, in a 0.2 ml syringe contains 2000 IU (20 mg), in a 0.4 ml syringe - 4000 IU (40 mg), in a syringe 0.6 ml - 6000 IU (60 mg).
Water for injection is used as an auxiliary substance.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The active substance of Gemapaxan, sodium enoxaparin, is a heparin with a low molecular weight. It has high activity against blood coagulation factor Xa (100 IU / mg) and low activity against factor IIa antithrombin (28 IU / mg).
When used in therapeutic doses, the bleeding time does not increase, the introduction of prophylactic doses does not lead to a noticeable change in APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time). Enoxaparin sodium does not affect the binding of fibrinogen to platelets and platelet aggregation.
Pharmacokinetics
After subcutaneous administration, the absolute bioavailability of sodium enoxaparin is close to 100%.
On average, after injection, the maximum anti-Xa activity of plasma is observed in the range of 3-5 hours, anti-IIa activity - 3-4 hours. The pharmacokinetic parameters of enoxaparin sodium in the recommended dose ranges are likely to be linear. With single and repeated use, the difference in pharmacokinetic parameters in the equilibrium state is within the therapeutic ranges.
Enoxaparin sodium undergoes primary metabolism in the liver. For anti-Xa activity, the half-life after a single administration is approximately 4 hours, after repeated administration - up to 7 hours.
Renal clearance of active metabolites is about 10% of the administered dose, total renal excretion is 40%. Against the background of a decrease in renal function in elderly patients, excretion may be reduced. In severe renal failure (creatinine clearance <30 ml / min), AUC (area under the concentration-time curve) after repeated subcutaneous administration of 4000 anti-Xa ME once a day increases significantly.
Indications for use
Solutions containing 2000 ME / 0.2 ml and 4000 ME / 0.4 ml are used to prevent the following diseases:
- thromboembolism and venous thrombosis (especially during surgical and orthopedic operations);
- thromboembolism and venous thrombosis in bed rest patients (New York Heart Association class III and IV chronic heart failure, acute respiratory failure, acute rheumatic diseases, or acute infections with any of the following risk factors for venous thrombosis: chronic respiratory or heart failure, thrombosis and thromboembolism in history, cancer, hormone therapy, obesity, age over 75 years).
A solution of 6000 ME / 0.6 ml is prescribed in the following cases:
- treatment of deep vein thrombosis, even if the disease is accompanied by pulmonary embolism;
- prevention of hypercoagulation in the extracorporeal circulation system during hemodialysis;
- treatment of unstable angina pectoris and myocardial infarction without Q wave on the electrocardiogram (in combination therapy).
Contraindications
Absolute:
- severe thrombocytopenia caused by enoxaparin or heparin (during the last months);
- high risk of uncontrolled bleeding;
- cerebral aneurysm, dissecting aortic aneurysm (excluding surgical interventions);
- diagnosed or suspected hemorrhagic stroke;
- severe, uncontrollable arterial hypertension;
- childhood;
- known hypersensitivity to the active component of Gemapaxan, heparin or other heparins of low molecular weight.
Relative:
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, including peptic ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer;
- renal and / or hepatic impairment;
- diseases of the respiratory system or urinary tract in the acute stage;
- active tuberculosis;
- pericardial effusion;
- arterial hypertension;
- pericarditis;
- diabetic or hemorrhagic retinopathy;
- severe vasculitis;
- acute and subacute bacterial endocarditis;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- conditions associated with the risk of bleeding (including hypocoagulation, thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, von Willebrand disease);
- open wounds on large surfaces;
- serious injury (especially the central nervous system);
- lumbar puncture in a recent history;
- performing manipulations under epidural / spinal anesthesia;
- intrauterine contraception;
- recent history of radiation therapy;
- recent neurological or ophthalmic surgery;
- recent childbirth.
Instructions for the use of Gemapaxan: method and dosage
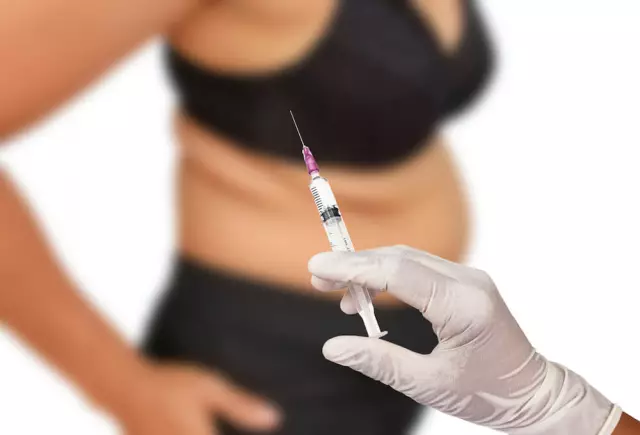
Hemapaxan is a solution intended for injection deep under the skin (for therapeutic and prophylactic use) or into the arterial circuit (during a hemodialysis session).
The subcutaneous injection must be done while the patient is in the supine position.
Gemapaksan injections are given alternately in the right and left anterior and posterior lateral parts of the anterior abdominal wall. During the injection, the needle is inserted perpendicularly (not at an angle!) Along its entire length into the thickness of the skin, clamped in a fold between the index and thumb. Keep the fold of skin until the end of the injection. You should not rub the place where Gemapaxan was injected.
Prevention of venous thrombosis and thromboembolism in surgical patients
With an average risk of thromboembolism (for example, during abdominal operations), 2,000 IU / 0.2 ml or 4,000 IU / 0.4 ml are prescribed once a day. The first injection in general surgery is done 2 hours before surgery.
With a high risk of thromboembolism and thrombosis (for example, in orthopedic surgery), 4000 IU / 0.4 ml is prescribed once a day (the first injection is 12 hours before surgery) or 3000 IU (30 mg) 2 times a day 12-24 hours after surgery.
The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. If there is a need to continue therapy, it is prolonged until there is a risk of thrombosis and thromboembolism (in orthopedics, Gemapaxan is used at a dose of 4000 IU / 0.4 ml once a day for 5 weeks).
Prevention of venous thrombosis and thromboembolism in patients on bed rest
Usually prescribed at 4000 IU / 0.4 ml 1 time per day for a course of 6-14 days.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
The recommended dose of Gemapaxan is 150 IU / kg (1.5 mg / kg) once a day or 100 IU / kg (1 mg / kg) 2 times a day.
In the presence of complicated thromboembolic disorders, it is usually prescribed at 100 IU / kg 2 times a day.
The duration of therapy is 10 days.
It is advisable to immediately start using oral anticoagulants, while Hemapaxan therapy should be continued until a sufficient anticoagulant effect is achieved (International Normalized Ratio - 2-3).
Prevention of hypercoagulation in the extracorporeal circulation system during hemodialysis
Gemapaxan is introduced into the arterial circuit at the beginning of the hemodialysis session.
Usually prescribed at 100 IU / kg.
With a high risk of bleeding, the dose should be reduced: with a single vascular access - up to 75 IU / kg, with a double vascular access - up to 50 IU / kg.
Typically, one dose is sufficient for a 4 hour session. With a longer hemodialysis, as well as in the case of detection of fibrin rings, it is necessary to introduce an additional dose of Gemapaxan - 50-100 IU / kg.
Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction
A single dose of Gemapaxan is 100 IU / kg, the frequency of use is 2 times a day (at intervals of 12 hours).
The drug is prescribed together with acetylsalicylic acid, which should be taken once a day. Its effective dose is determined individually in the range from 100 to 325 mg.
Duration of treatment - until the patient's clinical condition stabilizes. This usually takes 2 to 8 days.
Special categories of patients
Elderly patients with normal renal function do not need Gemapaxan dose adjustment.
With mild to moderate renal impairment, there is no need to adjust the dose.
In severe renal failure, the dose is set depending on creatinine clearance. If this figure is below 30 ml / minute, the therapeutic dose is 100 IU / kg of body weight once a day, the prophylactic dose is 2000 IU once a day.
Side effects
During the period of treatment with Gemapaxan, punctate hemorrhages (petechiae), ecchymosis, hyperemia and pain at the injection site are possible.
In rare cases, the following side effects are noted:
- hematoma, dense inflammatory nodes (resolve after a few days, discontinuation of treatment is not required);
- asymptomatic thrombocytopenia (in the first days of treatment);
- necrosis of the skin at the injection site, preceded by erythematous plaques (painful and infiltrated) or purpura;
- hemorrhagic syndrome (including intracranial and retroperitoneal bleeding up to death);
- asymptomatic reversible increase in the activity of hepatic transaminases;
- immunoallergic thrombocytopenia (on days 5-21 of therapy) with the development of rebound thrombosis (heparin thrombotic thrombocytopenia), which may be complicated by limb ischemia or organ infarction;
- dermatological and systemic allergic reactions;
- intraspinal hematoma, which can lead to temporary or permanent paralysis - with traumatic spinal / epidural anesthesia (especially when using a permanent postoperative epidural catheter).
Overdose
The main symptom of an overdose of Gemapaxan is bleeding.
Therapy: the use of protamine sulfate (1 mg of the substance neutralizes the anti-IIa activity, which is caused by 1 mg of enoxaparin sodium); high doses neutralize the anti-Xa activity of Gemapaxan by 60%.
special instructions
It is forbidden to inject Gemapaxan intramuscularly!
There is insufficient data on the safety and efficacy of the drug for the prevention of thromboembolic complications in patients with artificial heart valve.
In high doses, enoxaparin sodium can increase the activated blood clotting time and the activated partial thromboplastin time.
For patients with a history of thrombocytopenia caused by heparin, Gemapaxan is prescribed in exceptional cases, since there is a risk of immunoallergic thrombotic thrombocytopenia (on days 5-21 of treatment). The risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia may persist for several years.
Hemapaxan should be discontinued if the platelet count falls below normal by 30-50%, as well as when signs of internal bleeding appear, such as hypochromic anemia, vomiting with blood, fresh blood in the stool or melena.
To reduce the risk of bleeding in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome, involving surgical invasive methods of therapy with a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall, Gemapaxan should be administered at least 6-8 hours before manipulation or 6-8 hours after it.
In the case of using Gemapaxan during epidural / spinal anesthesia, the patient's condition should be carefully monitored for the appearance of any neurological symptoms: impaired motor and sensory functions (including weakness in the lower extremities or numbness), median back pain, dysfunction of the bladder and / or the gastrointestinal tract. If symptoms are identified that may indicate brainstem hematomas, urgent diagnosis and treatment is required, if necessary, including spinal decompression.
Rare cases of spinal cord hematoma with the use of enoxaparin sodium during epidural / spinal anesthesia with the development of persistent paralysis are described. The risk of this complication is reduced when the drug is prescribed in a dose of up to 4000 IU. The risk increases with an increase in the dose of Hemapaxan, with the use of penetrating epidural catheters after surgery, with the concomitant use of additional drugs that affect hemostasis (including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Also, the risk increases with traumatic or repeated lumbar puncture.
During spinal / epidural anesthesia, the introduction and removal of the catheter is recommended when the anticoagulant effect of Gemapaxan is low: 10-12 hours after the administration of prophylactic doses of the drug or 24 hours after the administration of higher doses (100 IU / kg 2 times a day or 150 IU / kg once a day). Further administration of enoxaparin sodium is possible no earlier than 2 hours after removing the catheter.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, Gemapaxan should be used only under strict indications. In pregnant women with artificial heart valves, therapy is not recommended.
The drug should not be used during lactation.
Pediatric use
Injections of Gemapaxan are contraindicated in patients under 18 years of age.
With impaired renal function
According to the instructions, Gemapaxan for renal failure should be administered under medical supervision.
For violations of liver function
Gemapaxan for liver failure should be administered under medical supervision.
Drug interactions
Hemapaxan should not be mixed with any medicinal solutions in the same syringe.
Patients receiving medications affecting hemostasis are advised to cancel them before prescribing Gemapaxan, except in cases of urgent need.
Enoxaparin sodium, if possible, should not be combined with the following drugs: valproic acid, thrombolytics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including ketorolac), sulfinpyrazone, clopidogrel, high molecular weight dextrans, systemic glucocorticosteroids, vitamin K antagonists, anti-agonists including blockers of glycoprotein receptors IIb / IIIa, acetylsalicylic acid and its derivatives). If the use of such combinations is advisable, the hemostasis indicators and the patient's condition should be carefully monitored.
In order to avoid possible drug interactions, the attending physician should be informed about all the drugs that the patient is taking at the time of Gemapaxan prescription.
Analogs
The analogues of Gemapaksan are: Anfibra, Kleksan, Eniksum.
Terms and conditions of storage
Keep out of the reach of children. Do not freeze or exceed 25 ° C.
The shelf life is 3 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Gemapaksan
According to reviews, Gemapaxan is an effective drug. The use of Gemapaxan during pregnancy is often justified. The convenience of the release form is noted. The cost of the drug is estimated as high, while it is indicated that it is cheaper than some analogues.
Price for Gemapaxan in pharmacies
The approximate price for Gemapaxan for 6 disposable syringes in a package is: 0.2 ml - 822-885 rubles; 0.4 ml each - 1207-1345 rubles; 0.6 ml 1314-1352 rubles.

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!